Abstract
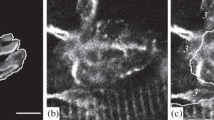
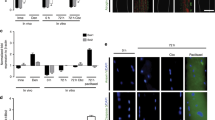
Segregation of voltage-dependent sodium channels to the hillock of motoneurones and nodes of Ranvier in myelinated axons is crucial for conduction of the nerve impulse1,2. Much less is known, however, about the distribution of voltage-dependent Na+ channels on muscle fibres. Recently, Beam et al.3 have shown that Na+ channels are concentrated near the neuromuscular junction. To determine the topography and mechanisms governing the distribution of voltage-dependent Na+ channels on muscle, microfluorimetry and fluorescence photobleach recovery (FPR) have now been used to measure the density and lateral mobility of fluorescently labelled Na+ channels on uninnervated and innervated muscle fibres. On uninnervated myotubes, Na+ channels are diffusely distributed and freely mobile, whereas after innervation the channels concentrate at neuronal contact sites. These channels are immobile and co-localize with acetylcholine receptors (AChRs). At extrajunctional regions the Na+ channel density is lower and the channels more mobile. The results suggest that the nerve induces Na+ channels to redistribute, immobilize and co-localize with AChRs at sites of neuronal contact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coombs, J. S., Eccles, J. C. & Fatt, P. J. Physiol., Lond. 130, 291–325 (1955).
Waxman, S. G. & Ritchie, J. M. Science 228, 1502–1507 (1985).
Beam, K. G., Caldwell, J. H. & Campbell, J. T. Nature 313, 588–590 (1985).
Angelides, K. J. & Nutter, T. J. J. biol. Chem. 258, 11948–11957 (1983).
Darbon, H. & Angelides, K. J. J. biol. Chem. 259, 6074–6084 (1984).
Angelides, K. J. Biochemistry 20, 4107–4118 (1981).
Axelrod, D. A., Koppel, D. E., Schlessinger, J., Elson, E. L. & Webb, W. W. Biophys. J. 16, 1055–1069 (1976).
Ravdin, P. & Axelrod, D. A. Analyt. Biochem. 58, 585–592 (1977).
Role, L. W., Matossian, V. R., O'Brien, R. J. & Fischbach, G.-D. J. Neurosci. 5, 2197–2204 (1985).
Roberts, W. M. & Almers, W. Biophys. J. 47, abstr. 189 (1985).
Brockes, J. P. & Hall, Z. W. Biochemistry 14, 2100–2106 (1975).
Cohen, S. & Barchi, R. L. Biochim. biophys. Acta 645, 253–261 (1981).
Elmer, L. W., O'Brien, B., Nutter, T. J. & Angelides, K. J. Biochemistry 24, 8128–8137 (1985).
Klausner, R. D., Kleinfeld, A. M., Hoover, R. L. & Karnovsky, M. J. biol. Chem. 255, 1286–1295 (1980).
Stuhmer, W. & Almers, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 946–950 (1983).
Stya, M. & Axelrod, D. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 449–453 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelides, K. Fluorescently labelled Na+ channels are localized and immobilized to synapses of innervated muscle fibres. Nature 321, 63–66 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/321063a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/321063a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Neurotoxin-Derived Optical Probes for Biological and Medical Imaging
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2023)
-
Functional localization of single active ion channels on the surface of a living cell
Nature Cell Biology (2000)
-
Na channel density in extrajunctional sarcolemma of fast and slow twitch mouse skeletal muscle fibres: functional implications and plasticity after fast motoneuron transplantation on to a slow muscle
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1995)
-
Nicotinic receptor-associated 43K protein and progressive stabilization of the postsynaptic membrane
Molecular Neurobiology (1992)
-
Localization of voltage-sensitive sodium channels on the extrasynaptic membrane surface of mouse skeletal muscle by autoradiography of scorpion toxin binding sites
Journal of Neurocytology (1990)