Abstract
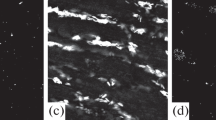
Basal lamina-rich extracts of Torpedo californica electric organ contain a factor that causes acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on cultured myotubes to aggregate into patches1–3. Our previous studies have indicated that the active component of these extracts is similar to the molecules in the basal lamina which direct the aggregation of AChRs in the muscle fibre plasma membrane at regenerating neuromuscular junctions in vivo2,4,5. Because it can be obtained in large amounts and assayed in controlled conditions in cell culture, the AChR-aggregating factor from electric organ may be especially useful for examining in detail how the postsynaptic apparatus of regenerating muscle is assembled. Here we demonstrate that the electric organ factor causes not only the formation of AChR aggregates on cultured myotubes, but also the formation of patches of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). This finding, together with the observation that basal lamina directs the formation of both AChR and AChE aggregates at regenerating neuromuscular junctions in vivo6, leads us to hypothesize that a single component of the synaptic basal lamina causes the formation of both these synaptic specializations on regenerating myofibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubin, L. L. & McMahan, U. J. in Disorders of the Motor Unit (ed. Schotland, D. L.) 187–196 (Wiley, New York, 1982).
Nitkin, R. M., Wallace, B. G., Spira, M. E., Godfrey, E. W. & McMahan, U. J. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 48, 653–665 (1983).
Godfrey, E. W., Nitkin, R. M., Wallace, B. G., Rubin, L. L. & McMahan, U. J. J. Cell Biol. 99, 615–627 (1984).
Burden, S. J., Sargent, P. B. & McMahan, U. J. J. Cell Biol. 82, 412–425 (1979).
McMahan, U. J. & Slater, C. R. J. Cell Biol. 98, 1453–1473 (1984).
Anglister, L. & McMahan, U. J. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 10, 281 (1984).
Karnovsky, M. J. J. Cell Biol. 23, 217–232 (1964).
Kordas, M., Brzin, M. & Majcen, Z. Neuropharmacology 14, 791–800 (1975).
Rotundo, R. L. J. biol. Chem. 21, 13186–13194 (1984).
Fallon, J. R., Nitkin, R. M., Reist, N. E., Wallace, B. G. & McMahan, U. J. Nature 315, this issue.
Anderson, M. J. & Cohen, M. W. J. Physiol., Lond. 268, 751–773 (1977).
Rubin, L. L., Schuetze, S. M. & Fischbach, G. D. Devl Biol. 69, 46–58 (1979).
Ziskind-Conhaim, L., Geffen, I. & Hall, Z. W. J. Neurosci. 4, 2346–2349 (1984).
Rubin, L. L., Schuetze, S. M., Weill, C. L. & Fischbach, G. D. Nature 283, 264–267 (1980).
Lømo, T. & Slater, C. R. J. Physiol., Lond. 303, 173–189 (1980).
Weinberg, C. B. & Hall, Z. W. Devl Biol. 68, 631–635 (1979).
Christian, C. M. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4011–4105 (1978).
Bauer, H. C. et al. Brain Res. 209, 395–404 (1981).
Kalcheim, C., Vogel, Z. & Duksin, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 3077–3081 (1982).
Podleski, T. R. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 2035–2039 (1978).
Jessell, T. M., Siegel, R. E. & Fischbach, G. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 5397–5401 (1979).
Markelonis, G. J., Oh, T. H., Eldefrawi, M. E. & Guth, L. Devl Biol. 89, 353–361 (1982).
Salpeter, M. M., Spanton, S., Holley, K. & Podleski, T. R. J. Cell Biol. 93, 417–425 (1982).
Connolly, J. A., St John, P. A. & Fischbach, G. D. J. Neurosci. 2, 1207–1213 (1982).
Sanes, J. R., Feldman, D. H., Cheney, J. M. & Lawrence, J. C. Jr J. Neurosci. 4, 464–473 (1984).
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. D., Andres, V. & Featherstone, R. M. Biochem. Pharmac. 7, 88–95 (1961).
Ravdin, P. & Axelrod, D. Analyt. Biochem. 80, 585–592 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallace, B., Nitkin, R., Reist, N. et al. Aggregates of acetylcholinesterase induced by acetylcholine receptor-aggregating factor. Nature 315, 574–577 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/315574a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/315574a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Chicken retinospheroids as developmental and pharmacological in vitro models: acetylcholinesterase is regulated by its own and by butyrylcholinesterase activity
Cell & Tissue Research (1992)
-
Interactions between intrinsic regulation and neural modulation of acetylcholinesterase in fast and slow skeletal muscles
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1991)
-
Tissue-specific processing and polarized compartmentalization of clone-produced cholinesterase in microinjectedXenopus oocytes
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1989)
-
Molecular forms and localization of acetylcholinesterase and nonspecific cholinesterase in regenerating skeletal muscles
Neurochemical Research (1987)
-
Acetylcholine receptor-aggregating factor is similar to molecules concentrated at neuromuscular junctions
Nature (1985)