Abstract
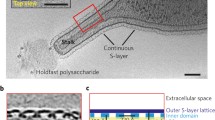
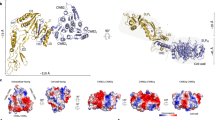
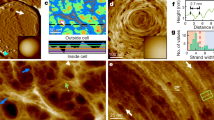
The outermost component of many bacterial cell envelopes is a two-dimensional crystalline array of protein molecules, termed the S-layer1. Despite considerable effort to investigate its structure and composition, its precise function remains uncertain. We report here the first determination of the three-dimensional structure of an S-layer, that from the thermophilic bacterium, Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Our map shows a complex and strongly interconnected structure, penetrated by numerous channels which appear to provide little barrier to anything but rather large molecules. The external surface is fairly smooth, but the cellular side is sculpted with large cavities and protruding ‘pedestals’. The protein substructure consists of three types of globular domain, connected by narrow bridges. We suggest that these may be flexible ‘hinges’, allowing the S-layer to form a curved surface, and that the multidomain structure allows the S-layer to maintain strong connectivity as it grows with the bacterium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sleytr, U. B. Int. Rev. Cytol. 53, 1–64 (1978).
Brock, T. D. Thermophilic Microorganisms and Life at High Temperatures, 117–179 (Springer, New York, 1978).
Weiss, R. L. J. gen. Microbiol. 77, 501–507 (1973).
Weiss, R. L. J. Bact. 118, 275–284 (1974).
Michel, H., Neugebauer, D.-Ch. & Oesterhelt, D. in Electron Microscopy at Molecular Dimensions (eds Baumeister, W. & Vogell, W.) 27–35 (Springer, New York, 1980).
Brock, T. D., Brock, K. M., Belly, R. T. & Weiss, R. L. Arch. Mikrobiol. 84, 54–68 (1972).
Harrison, S. C., Olson, A. J., Schutt, C. E., Winkler, F. K. & Bricogne, G. Nature 276, 368–373 (1978).
Harris, W. F. & Scriven, L. E. Nature 228, 827–829 (1970).
Watson, S. W. & Remsen, C. C. Science 163, 685 (1969).
Sleytr, U. B. & Glauert, A. M. J. ultrastruct. Res. 50, 103–116 (1975).
Caspar, D. L. D. & Klug, A. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 27, 1–24 (1962).
Heuser, J. J. Cell Biol. 84, 560–583 (1980).
Glaeser, R. M., Chiu, W. & Grano, D. J. ultrastruct. Res. 66, 235–242 (1979).
Thorne, K. J. I. Biol. Rev. 52, 219–234 (1977).
Cohen-Bazire, G., Kunisawa, R. & Pfennig, N. J. Bact. 100, 1049–1061 (1969).
Wilkinson, J. F. Symp. Soc. gen. Microbiol. 21, 15–46 (1971).
Stewart, M. & Beveridge, T. J. J. Bact. 142, 302–309 (1980).
Stewart, M., Beveridge, T. J. & Murray, R. G. E. J. molec. Biol. 137, 1–8 (1980).
Henderson, R. & Unwin, P. N. T. Nature 257, 28–32 (1975).
Deatherage, J. F., Taylor, K. A. & Amos, L. A. J. molec. Biol. (submitted).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, K., Deatherage, J. & Amos, L. Structure of the S-layer of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Nature 299, 840–842 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299840a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/299840a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Preservation of Archaeal Surface Layer Structure During Mineralization
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Inhibition of a conjugation-like gene transfer process in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis by the anti-s-layer protein antibody
Current Microbiology (1995)
-
Structural features of archaebacterial cell envelopes
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (1992)
-
Face to face with proteins
Nature (1990)