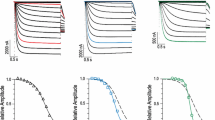
Abstract
Adenosine and its 5′-phosphorylated congeners evoke specific membrane-mediated responses in excitable tissues1,2. Available data suggest that inhibition of the target cell occurs due to hyperpolarization3,4, and in some preparations a compound effect of ATP (excitation and inhibition) has been found5,6. However, the ionic mechanism of the purinergic-mediated response has not been studied by standard intracellular voltage-clamping techniques. Recently, we have discovered purinergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte, a well defined giant cell amenable to rigorous electrophysiological7 and biochemical8 studies. We report here that in these cells, adenosine-induced slow membrane responses consisted of an early depolarizing (D) transient current carried by Cl− ions, followed by a steady hyperpolarizing (H) current involving K+ ions. The relative potency sequence for the D current was ATP≃ ADP > AMP ≃ adenosine; this order was reversed for the H current.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnstock, G. Circulation Res. 46, 1175–1182 (1980).
Urthaler, F., Woods, W. T., James, T. N. & Walker, A. A. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 216, 254–260 (1981).
Hartzell, H. C. J. Physiol., Lond. 293, 23–50 (1979).
Tomita, T. & Watanabe, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 231, 167–178 (1973).
Flitney, F. W. & Singh, I. J. Physiol., Lond. 304, 21–42 (1980).
Yatani, A., Goto, M. & Tsuda, Y. Jap. J. Physiol. 28, 47–61 (1978).
Kusano, K., Miledi, R. & Stinnakre, J. Nature 270, 739–741 (1977).
Maller, J. L., Butcher, F. R. & Krebs, E. G. J. biol. Chem. 254, 579–582 (1979).
Dumont, J. N. J. Morph. 136, 153–180 (1972).
Morrill, G. A. & Ziegler, D. Devl Biol. 14, 216–223 (1980).
Burnstock, G. J. Physiol., Lond. 313, 1–34 (1981).
Van Calker, D., Muller, M. & Hamprecht, B. Nature 276, 839–841 (1978).
Londos, C. & Wolff, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5482–5486 (1977).
Londos, C., Cooper, D. M. F. & Wolff, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 2551–2554 (1980).
Brown, C. M. & Burnstock, G. Br. J. Pharmac. 73, 617–624 (1981).
Dascal, N. & Landau, E. M. Life Sci. 27, 1423–1428 (1980).
Rodbell, M. Nature 284, 17–22 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lotan, I., Dascal, N., Cohen, S. et al. Adenosine-induced slow ionic currents in the Xenopus oocyte. Nature 298, 572–574 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/298572a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/298572a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Functional characterization of an endogenous Xenopus oocyte adenosine receptor
British Journal of Pharmacology (2002)
-
Influence of extracellur Ca2+ on endogenous Cl? channels in Xenopus oocytes
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1995)
-
Single-channel properties and regulation of pinacidil/glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in follicular cells from Xenopus oocyte
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1993)
-
Regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function by adenine nucleotides
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1990)
-
Dual regulation by protein kinase C of the muscarinic response in Xenopus oocytes
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1989)