Abstract
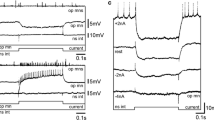
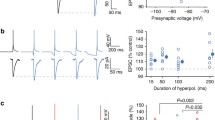
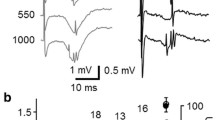
IN the molluscan nervous system, action potentials and synaptic potentials invade the soma so that its potential reflects intrinsically and extrinsically initiated electrical activity1. However, its functions related to the electrical activity of the neurone are unknown. Recently, it was shown that the soma potentials of arthropod interneurones controlled transmitter release on to motoneurones2,3. In Aplysia, soma potentials of some interneurones have been observed to have an effect on the size of post synaptic potentials (p.s.ps) in the cell with which they synapse; the possibility that p.s.ps were affected by changes in temporal properties of the spike induced by the soma potential4 or electronic coupling between cells9 was not excluded. We investigated this observation and report here that soma potentials of one interneurone regulate the release of transmitter, possibly by a direct effect on its terminals. Release can be sustained beyond the normal time course of the p.s.p. by prolonged depolarisation of the soma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tauc, L. J. gen. Physiol. 45, 1077–1097 (1962).
Maynard, D. & Walton, K. J. comp. Physiol. 97, 215–243 (1975).
Burrows, M. & Siegler, M. Nature 262, 222–224 (1976).
Shimahara, T. & Tauc, L. J. Physiol., Lond. 247, 299–319 (1975).
Geduldig, D. & Junge, D. J. Physiol., Lond. 199, 347–365 (1968).
Takeuchi, A. & Takeuchi, N. J. gen. Physiol. 45, 1181–1193 (1962).
Katz, B. & Miledi, R. J. Physiol., Lond. 203, 459–487 (1969).
Llinas, R., Steinberg, I. Z. & Walton, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 2918–2922 (1976).
Shimahara, T. & Peretz, B., in preparation.
Kado, R. T. Science 182, 845–848 (1973).
Miledi, R. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B 183, 421–425 (1973).
Graubard, K. Brain Res. 88, 325–332 (1975).
Baker, P. F., Meves, H. & Ridgway, E. B. J. Physiol., Lond. 231, 527–548 (1973).
Mullins, L. J. Fedn Proc. 35, 2583–2588 (1976).
Tauc, L. & Gerschenfeld, H. Nature 192, 366–367 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SHIMAHARA, T., PERETZ, B. Soma potential of an interneurone controls transmitter release in a monosynaptic pathway in Aplysia. Nature 273, 158–160 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/273158a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/273158a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
What are the mechanisms for analogue and digital signalling in the brain?
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2013)
-
Calcium and the control of synaptic strength by learning
Nature (1981)
-
Organization of synaptic inputs of two identified Helix pomatia neurons
Neurophysiology (1980)