Abstract
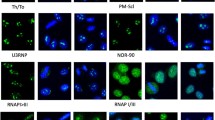
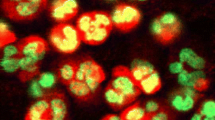
IT is commonly accepted that antibodies do not penetrate living cells. In only one study anti-purine and anti-nucleoside antibodies were found to penetrate fertilised sea urchin eggs and modify their development1. Such penetration has been considered unusual and the addition of anti-DNA antibodies does not affect mammalian tissue cells in culture2. Direct immunofluorescence of skin biopsies of patients with mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) using fluorescent anti-IgG has occasionally shown speckled intranuclear fluorescence3–5 but it is doubted that IgG entered the cells while still viable. Patients with MCTD have high titres of antibody to nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RNP)6,7 which also gives a nuclear speckled pattern on cell substrates in direct immunofluorescence8. Should the antibodies to cellular components and nucleic acids which occur in autoimmune diseases be able to penetrate living cells, a novel mechanism of immunologically mediated damage and/or dysfunction could operate. We show here that anti-RNP IgG can penetrate viable human mononuclear cells (MNC), by their surface Fc receptor, and react with their nuclear RNP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenkranz, H. S., Erlanger, B. F., Tanenbaum, S. W. & Beiser, S. M. Science 145, 282–284 (1964).
Stollar, B. D. in The Antigens (ed. Sela, M.) 70 (Academic, New York, 1973).
Shu, S., Provost, T., Croxdale, M. B., Reichlin, M. & Beutner, E. H. Clin. exp. Immun. 27, 238–244 (1977).
Gilliam, J. N., Smiley, J. D. & Ziff, M. Clin. Res. 23, 229A (1975).
Prystowsky, S. D. & Tuffanelli, D. L. Proc. XIV int. Congress Rheumatol. San Francisco, 40 (1977).
Holman, H. R. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 124, 800–806 (1965).
Sharp, G. C., Irwin, W. S., Tan, E. M., Gould, R. G. & Holman, H. R. Am. J. Med. 52, 148–159 (1972).
Northway, J. D. & Tan, E. M. Clin. Immun. Immunopath. 1, 140–149 (1972).
Alarcón-Segovia, D. J. Rheumatol. 3, 191–195 (1976).
Diaz-Jouanen, E., Llorente, L., Ramos-Niembro, F. & Alarcón-Segovia, D. J. Rheumatol. 4, 4–10 (1977).
Böyum, A. Scand. J. Lab. clin. Invest. 21, Suppl. 97, 77–89 (1968).
Reif, A. E. & Allen, J. M. V. J. exp. Med. 120, 413–424 (1964).
Kaplow, L. S. Blood 26, 215–219 (1965).
Mikulski, S. & Billing, R. Cell. Immun. 28, 69–74 (1977).
Diaz-Jouanen, E., Rivero, S. J., Llorente, L. & Alarcon-Segovia, D. Proc. XIV Int. Congress Rheumatol. San Francisco, 132 (1977).
Samarut Brochier, J. & Revillar, J. P. Scand. J. Immun. 5, 221–231 (1976).
WHO/I ARC Workshop on human B and T cells, London, 15–17 July 1974 Scand. J. Immun. 3, 521–536 (1974).
Stanworth, D. R. & Turner, M. W. in Handbook of Experimental Immunology (ed. Weir, D. M.) 2nd edn, 10. 11 -10. 20 (Blackwell, Oxford, 1973).
Roitt, I. Essential Immunology 2nd edn, 155–57 (Blackwell, London, 1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ALARCON-SEGOVIA, D., RUIZ-ARGUELLES, A. & FISHBEIN, E. Antibody to nuclear ribonucleoprotein penetrates live human mononuclear cells through Fc receptors. Nature 271, 67–69 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/271067a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/271067a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
DNA-damaging autoantibodies and cancer: the lupus butterfly theory
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2016)
-
Common Pathways of Autoimmune Inflammatory Myopathies and Genetic Neuromuscular Disorders
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2012)
-
The predestination of autoantibodies
Current Rheumatology Reports (2001)