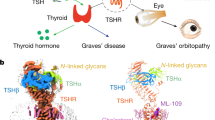
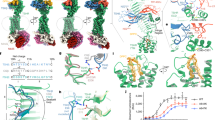
Abstract
WE report the unexpected finding that the adrenocortico-tropic hormone (ACTH)-secreting cells of the human anterior pituitary gland show an affinity for human immunoglobulins resembling that of normal mast cells for IgE. This phenomenon could have physiological significance if considered in relation to the messages leading to synthesis or release of the hormone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottazzo, G. F., Pouplard, A., Florin-Christensen, A., and Doniach, D., Lancet ii, 97–101 (1975).
Porter, R. R., Biochem J., 73, 119–126 (1959).
Greaves, M. F., Owen, J., and Raff, M., T and B Lymphocytes (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1973).
Stanworth, D. R., Haematologia, 8, 299–319 (1974).
Stanworth, D. R., Folia allerg. Immun. Clin., 22, 279–283 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
POUPLARD, A., BOTTAZZO, GF., DONIACH, D. et al. Binding of human immunoglobulins to pituitary ACTH cells. Nature 261, 142–144 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/261142a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/261142a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Anti-pituitary antibodies against corticotrophs in IgG4-related hypophysitis
Pituitary (2017)
-
The immunofluorescence techniques in the diagnosis of endocrine autoimmune diseases
Autoimmunity Highlights (2012)
-
Growth hormone and proopiomelanocortin are targeted by autoantibodies in a patient with biopsy-proven IgG4-related hypophysitis
Pituitary (2012)
-
Lymphocytic hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary tumor in a 63-year-old man
Endocrine Pathology (1995)
-
Mast cell immunohistochemistry: non-immunological immunostaining mediated by non-specific F(ab?)2-mast cell secretory granule interaction
The Histochemical Journal (1993)