Abstract
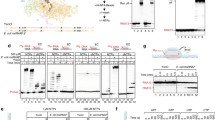
Bacillus subtilis phage SP01 directs the synthesis of at least six temporally defined classes of phage-specified transcripts1. Synthesis of the two earliest classes of phage RNA (e and em) does not require phage protein synthesis, while the synthesis of middle (m and m1l) and late (m2l and l) transcripts requires the protein product of regulatory gene 28 and the products of regulatory genes 33 and 34, respectively2,3. The discovery of SP0l-induced polypeptides associated with B. subtilis RNA polymerase suggested that the products of SP01 regulatory genes could control transcription by interacting directly with the host RNA polymerase4,5. In support of this idea, we reported6 that a form of RNA polymerase from SP01-infected cells copies middle RNA almost exclusively from the heavy (H) strand of native SP01 DNA, the DNA strand from which middle and late genes are transcribed in vivo. This enzyme contains an SP01-induced polypeptide termed IV (molecular weight 26,000) that is now known to be the product of regulatory gene 28 (T. Fox, R. L. and J. P., manuscript in preparation). Accurate middle gene transcription by this phage-modified RNA polymerase does not require σ factor but is apparently dependent on a newly described host subunit of RNA polymerase called δ (molecular weight 21,500)6. Other workers have also reported the preferential synthesis of middle RNA by RNA polymerase from phage-infected B. subtilis7,8. Here we report that in the presence of host δ protein a form of RNA polymerase containing phage-induced polypeptides termed V (molecular weight 24,000) and VI (molecular weight 13,500) asymmetrically transcribes a class of SP01 late genes in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gage, L. P., and Geiduschek, E. P., J. molec. Biol., 57 279–300 (1971).
Fujita, D. J., Ohlsson-Wilhelm, B. M., and Geiduschek, E. P., J. molec. Biol., 57, 301–317 (1971).
Okubo, S., Yanagida, T., Fujita, D. J., and Ohlsson-Wilhelm, B. M., Biken J., 15, 81–87 (1972).
Fox, T. D., and Pero, J., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 71, 2761–2765 (1974).
Duffy, J. J., and Geiduschek, E. P., J. biol. Chem., 250, 4530–4541 (1975).
Pero, J., Nelson, J., and Fox, T. D., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 72, 1589–1593 (1975).
Duffy, J. J., and Geiduschek, E. P., FEBS Lett., 34, 172–174 (1973).
Spiegelman, G. B., and Whiteley, H. R., J. biol. Chem., 249, 1483–1489 (1974).
Shorenstein, R. G., and Losick, R., J. biol. Chem., 248, 6163–6169 (1973).
Carmichael, G. G., J. biol. Chem. (in the press).
Studier, F. W., J. molec. Biol., 79, 237–248 (1973).
Segall, J., and Losick, R., in Spores, VI (edit. by Gerhardt, P., Sadoff, H. L., and Costilow, R. N.), 221–225 (American Society for Microbiology, 1975).
Stevens, A., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 69, 603–607 (1972).
Horvitz, H. R., Nature new Biol., 244, 137–140 (1973).
Ratner, D., J. molec. Biol., 89, 803–807 (1974).
Stevens, A., Biochem. J., 13, 493–503 (1974).
Lembach, K., Kuninaka, A., and Buchanan, J. M., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 62, 446–453 (1969).
Riva, S., Cascino, A., and Geiduschek, E. P., J. molec. Biol., 54, 85–102 (1970).
Travers, A. A., Nature, 223, 1107–1110 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PERO, J., TJIAN, R., NELSON, J. et al. In vitro transcription of a late class of phage SP01 genes. Nature 257, 248–251 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/257248a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/257248a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The nature of transcription selectivity of bacteriophage SPO1-modified RNA polymerase
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1979)
-
Purification of a positive regulatory subunit from phage SP01-modified RNA polymerase
Nature (1977)
-
Bacteriophage SP01 regulatory proteins directing late gene transcription in vitro
Nature (1976)
-
Identification of phage SP01 proteins coded by regulatory genes 33 and 34
Nature (1976)