Abstract
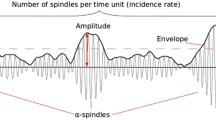
MORE than a decade of research on hypnotic susceptibility and its correlates has demonstrated repeatedly the stability of the phenomenon, its independence from standard tests of suggestibility and of personality, and its relative imperviousness to most efforts to manipulate it, in particular to increase it1,2. Several recent studies have shown, however, that hypnotic susceptibility is significantly correlated with brain wave activity, including the duration of electroencephalogram (EEG) alpha rhythms3–5. Other studies have shown that the production of alpha rhythms can be systematically increased by teaching subjects to accommodate their subjective mental states to sustained auditory feedback signals which indicate the continuous manifestation of this rhythm6,7.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, L., Banford, S., Schubot, E., and Tart, C., Inter. J. Clin. Expt. Hypnosis, 15, 118 (1967).
Sachs, L., and Anderson, W., Inter. J. Clin. Exp. Hypnosis, 15, 172 (1967).
London, P., Hart, J., and Leibovitz, M., Nature, 219, 71 (1968).
London, P., Hart, J., Leibovitz, M., and McDevitt, R., In Proc. Inter. Sympos. Psychophysiol. Mechanisms of Hypnosis (edit. by Cherlock, L., 151 (Springer, Heidelberg, 1969).
Galbraith, G., London, P., Leibovitz, M., Cooper, L., and Hart, J., J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 72, 125 (1970).
Hart, J., Psychophysiology, 4, 506 (1967).
Kamiya, J., Altered States of Consciousness (edit. by Tart, C.), 507 (Wiley, New York, 1969).
Shor, R. E., and Orne, E., Harvard Group Scale of Hypnotic Susceptibility, Form A (Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, 1962); Weitzenhoffer, A. M., and Hilgard, E. R., Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale, Forms A and B (Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, California, 1959).
Kasamatsu, A., and Hirai, T., Folia Psychiat. Neurol. Japan, 20, 315 (1966).
Engstrom, D., The enhancement of EEG-alpha production and its effects on hypnotic susceptibility. PhD dissertation, USC (1970).
Nowlis, D., and McDonald, H., Hawthorne House Research Memorandum, No. 96 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ENGSTROM, D., LONDON, P. & HART, J. Hypnotic Susceptibility increased by EEG Alpha Training. Nature 227, 1261–1262 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/2271261a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2271261a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Hypnosis modelling in neural networks
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (1995)
-
Conflicting results in EEG alpha feedback studies
Biofeedback and Self-Regulation (1976)