Abstract
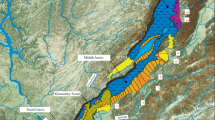
THE floor of the lower part of the estuary of Southampton Water (Fig. 1) has been examined with a Kelvin Hughes MS 43 transit sonar and an MS 36 echo sounder1. Upstream of Fawley the almost central deep channel is maintained by dredging to a least depth at low tide of about 11 m. On the western side the slope is a steady 1°–2°, but on the eastern side there is a wide shelf at about 2 m below port datum. To the seaward of Fawley there is a natural depth of 14 m below port datum. The sea bed consists of a soft mud made up of flocculated clay and fine silt particles. The flocculants have an equivalent mean grain size of about 5.5 Φ (22 µm). The mud is comparable with other marine muds having a moisture content of 120–220 per cent dry weight and a surface cohesion between 4–2 g cm−2. Occasional shell banks and gravel patches exist, especially near Calshot and on the eastern side.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haslett, R. W. G., and Honnor, D., Proc. IERE Conf. Electronic Engineering in Oceanography (1966).
Kuenen, P. H., J. Geol., 65, 231 (1957).
Karcz, I., J. Geol., 75, 113 (1967).
Pritchard, D. W., Proc. Amer. Soc. Civ. Eng., 81, No. 717 (1955).
Dyer, K. R., Rept. Challenger Soc., 3, No. 19 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DYER, K. Linear Erosional Furrows in Southampton Water. Nature 225, 56–58 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/225056a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/225056a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
A Saxon Fish Weir and Undated Fish Trap Frames Near Ashlett Creek, Hampshire, UK: Static Structures on a Dynamic Foreshore
Journal of Maritime Archaeology (2017)
-
Origin of rippled scour depressions associated with cohesive sediments in a shoreface setting (eastern Bay of Seine, France)
Geo-Marine Letters (2005)
-
The impact of mobile disarticulated shells ofCerastoderma edulis on the abrasion of a cohesive substrate
Estuaries (2002)
-
Giant comet marks
Geo-Marine Letters (1984)
-
Erosional furrows on continental shelf edge, Mississippi delta region
Geo-Marine Letters (1981)