Abstract
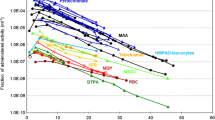
Wilson and Spiers1 reported that fallout 137Cs in powdered milk accumulated in the body of infants whose body burden could be fitted by an exponential model of a single compartment. Our calculations based on the model of Wilson and Spiers have shown that the concentration of 137Cs in the infant, expressed as pCi/kg of body weight, increases from birth to a maximum at about 50 days and then decreases slowly until the infant is 180 days old, when the observations ceased. The maximum concentration in infants is more than twice that in the mother.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson, A. R., and Spiers, F. W., Nature, 215, 470 (1967).
Iinuma, T. A., Uchiyama, M., Nagai, T., Ishihara, T., Saiki, M., and Yamagata, N., Nature, 241, 133 (1966).
Radioactivity Survey Data in Japan, No. 4, 29 (1964).
UN Scientific Committee on Effects of Atomic Radiation, Suppl. No. 14 (A/63/4) 79 (1966).
Bengtsson, L. G., Naversten, Y., and Svensson, K. G., in Assessment of Radioactivity in Man, 2, 21 (IAEA, Vienna, 1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
IINUMA, T., ISHIHARA, T., YASHIRO, S. et al. Accumulation of Fallout Caesium-137 in Newborn Infants. Nature 222, 478–480 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/222478a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/222478a0
- Springer Nature Limited