Abstract
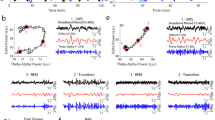
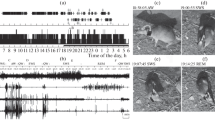
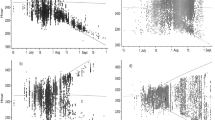
PREVIOUS work has shown that the bullfrog, Rana catesbiana, fulfils neither the electrographic nor the threshold criteria for sleep in the laboratory and that the animal is also vigilant when at diurnal rest in the field1. We describe here the field behaviour of tree frogs (genus Hyla) observed in Florida during March and contrast it with that seen in the laboratory where its electrographic correlates were studied. The findings are compared with previous observations of ranid frogs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hobson, J. A., EEG, Clin. Neurophysiol., 22, 113 (1967).
Hobson, J. A., Nature, 213, 988 (1967).
Kleitman, N., in Sleep and Wakefulness (University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOBSON, J., GOIN, O. & GOIN, C. Electrographic Correlates of Behaviour in Tree Frogs. Nature 220, 386–387 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/220386a0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/220386a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Electroencephalogram bands modulated by vigilance states in an anuran species: a factor analytic approach
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2012)
-
Sleep viewed as a state of adaptive inactivity
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2009)
-
Comparative electrophysiology of sleep in some vertebrates
Experientia (1980)