Abstract
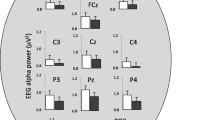
DESPITE a rich literature of anecdotal and clinical material on the relationship of hypnosis to physiological functions, especially to events in the central nervous system, the research findings are highly equivocal. Most relevant studies have been concerned with shifts in brain wave patterns, as measured by the electroencephalogram (EEG). The studies have attempted to identify the underlying processes which accompany the observed or reported events characteristic of passage between waking and hypnotic states of consciousness. With some exceptions, however, most studies have failed to demonstrate EEG correlations of the hypnotic state1,2. Similarly, most studies of physiological functioning have failed to find clear-cut changes in the autonomic nervous system resulting from “hypnosis per se, that is, without further verbal instructions”3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weitzenhoffer, A. M., Hypnotism: an Objective Study in Suggestibility (Wiley, New York, 1953).
True, R. M., and Stephenson, C. W., in Clinical Correlations of Experimental Hypnosis (edit. by Kline, M. V.) (Thomas, Springfield, Illinois, 1963).
Edmonston, W. E., in Handbook of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis (edit. by Jordon, J. E.) (Macmillan, New York, 1967).
Hilgard, E. R., Hypnotic Susceptibility (Harcourt, New York, 1965).
London, P., and McDevitt, R. A., AMRL-TR-67-142 (W-P AF Base, Ohio: Aerospace Medical Research Laboratories, 1967).
Hart, J. T., paper presented at the seventh Annual Meeting of the Society for Psychophysiological Research, San Diego, October 20–22 (1967).
Shor, R. E., and Orne, Emily C., Harvard Group Scale of Hypnotic Susceptibility, Form A (Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, California, 1962).
Fenton, G. W., and Scotton, L., Brit. J. Psychiat., 113, 1283 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LONDON, P., HART, J. & LEIBOVITZ, M. EEG Alpha Rhythms and Susceptibility to Hypnosis. Nature 219, 71–72 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/219071a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/219071a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Hypnosis modelling in neural networks
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (1995)
-
EEG correlates of hypnotic susceptibility based upon fast Fourier power spectral analysis
Biofeedback and Self-Regulation (1991)
-
On the Recently Reported Physiological and Pharmacological Reality of the Hypnotic State
The Psychological Record (1973)