Abstract
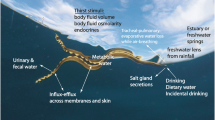
SMITH1 has shown that seawater teleosts maintain their water balance by drinking water and eliminating the divalent ions really and the monovalent ions extra-renally. Keys2 demonstrated that the extra-renal route of excretion is most probably the gills. On the other hand, Smith3 and Krogh4 say that “the freshwater teleost apparently does not drink water but absorbs it through the oral membranes or perhaps through the gills”. This statement has been challenged by several authors5,6, but no quantitative evaluation of the drinking rate was attempted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, H. W., Amer. J. Physiol., 93, 480 (1930).
Keys, A. B., Z. Vergl. Physiol., 15, 364 (1931).
Smith, H. W., Quart. Rev. Biol., 7, 1 (1932).
Krogh, A., Osmotic Regulation in Aquatic Animals (Cambridge University Press).
Allee, W. C., and Frank, P., Physiol. Zool., 21, 381 (1948).
Bergeron, J. A., Doc. Diss. Series, No. 19, 154 (Cornell University, 1956).
Mullins, L. J., Acta Physiol. Scand., 21, 303 (1950).
Motais, R., CR Acad. Sci., 253, 724 (1961).
House, C. R., J. Exp. Biol., 40, 87 (1963).
Gordon, M. S., Biol. Bull., 124, 45 (1963).
Motais, R., and Maetz, J., Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 4, 210 (1964).
Motais, R., and Maetz, J., CR Acad. Sci., 261, 532 (1965).
Potts, W. T. W., and Evans, D. H., Biol Bull., 131, 363 (1966).
Potts, W. T. W., and Evans, D. H., Biol. Bull., 133, 411 (1967).
Evans, D. H., J. Exp. Biol., 47, 525 (1967).
Skadhauge, E., and Maetz, J., CR Acad. Sci., 265, 247 (1967); ibid., 265, 923 (1967).
Garcia Romeu, F., and Motais, R., Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 17, 1201 (1966).
Motais, R., Garcia Romeu, F., and Maetz, J., J. Gen. Physiol., 50, 391 (1966).
Motais, R., Ann. Inst. Oceanog. Monaco, 45, 1 (1967).
Utida, S., Isono, N., and Hirano, T., Zool. Mag., 76, 203 (1967).
Butler, D. G., Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 18, 773 (1966).
Sharratt, B. M., Chester Jones, I., and Bellamy, D., Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 11, 9 (1964).
Maetz, J., and Morel, F., Arch. Anat. Microsc. Morphol. Exp., 54, 515 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MAETZ, J., SKADHAUGE, E. Drinking Rates and Gill Ionic Turnover in relation to External Salinities in the Eel. Nature 217, 371–373 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/217371a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/217371a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The digestive tract as an essential organ for water acquisition in marine teleosts: lessons from euryhaline eels
Zoological Letters (2021)
-
Impact of Tide Gates on the Migration of Adult European Eels, Anguilla anguilla
Estuaries and Coasts (2015)
-
Effect of seasonal variation in seawater dissolved mercury concentrations on mercury accumulation in the muscle of red sea bream (Pagrus major) held in Minamata Bay, Japan
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2013)
-
Hyposmoregulatory ability and ion- and water-regulatory mechanisms during the leptocephalus stages of Japanese eel Anguilla japonica
Fisheries Science (2013)
-
Osmoregulation and epithelial water transport: lessons from the intestine of marine teleost fish
Journal of Comparative Physiology B (2012)