Abstract
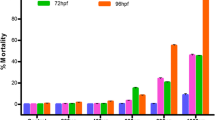
CAPTAN (N-trichloromethylthio-4-cyclohexene-1,2-dicarboxyimide) is an agricultural fungicide of low mammalian toxicity, and its residues*; in agricultural products are considered to offer less risk than most pesticides. A recent report1 draws attention to the mutagenic and teratogenic properties of captan, which has been observed to increase the mutation rate in bacteria (Escherichia coli), to inhibit mitotic division in the cell cultures and to induce physical abnormalities in chicks treated in the embryonic stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Legator, M., and Verrett, J., New York Academy of Sciences, Conference on Biological Effects of Pesticides in Mammalian Systems”, abstract of paper 6, 17 (1967).
Richmond, D. V., and Somers, E., Ann. Appl. Biol., 50, 33 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ABEDI, Z., MCKINLEY, W. Bioassay of Captan by Zebrafish Larvae. Nature 216, 1321–1322 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/2161321a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2161321a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Toxicity testing of pesticides in zebrafish—a systematic review on chemicals and associated toxicological endpoints
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2020)
-
Toxicity of the fungicide captan to the Dungeness crab Cancer magister
Marine Biology (1978)
-
Toxicity of zinc and cygon, applied singly and jointly, to zebrafish embryos
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (1974)