Abstract
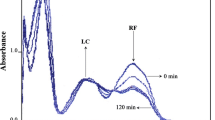
THE photoreduction of riboflavin in aqueous buffered solutions illuminated with visible light is considerably enhanced when colloidal substances such as micellar sodium decyl sulphate, the non-ionic surface-active agent polyoxyethylene 20 sorbitanmono-oleate, and the non-ionic polymer polyvinylpyrrolidone are present. Although a part of the catalysis produced by the non-ionic surfactant and the polyvinylpyrrolidone might be attributed to the presence of residual reducing groups, the effect of micellar sodium decyl sulphate appears to be wholly a result of its colloidal nature. Non-micellar sodium decyl sulphate has no effect on the photolysis of riboflavin as illustrated in Fig. 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halwer, M., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 73, 4870 (1951).
DeLuca, P. P., and Kostenbauder, H. B. (to be published).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KOSTENBAUDER, H., DELUCA, P. Enhanced Photoreactivity of Riboflavin in Aqueous Solution in the Presence of Macromolecules. Nature 199, 999–1000 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/199999a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/199999a0
- Springer Nature Limited