Abstract
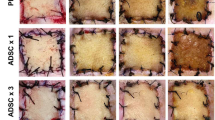
ɛ-AMINOCAPROIC acid has recently attracted a great deal of interest, mainly for its marked antifibrinolytic activity: it seems that it acts as an inhibitor of the transformation of profibrinolysin into fibrinolysin, or as an antagonist of the latter1–3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkjaersig, N., Pletscher, A. P., and Sherry, S. J. Biol. Chem., 234, 832 (1959).
Fukutake, K., Shida, K., Arakawa, T., and Kato, K., Blood, 15, 690 (1960).
Otto-Servais, M., and Lecomte, J., C.R. Soc. Biol., 155, 2050 (1961).
Amati, A., Libro, V., and Mariani, L., Atti Congresso Nazionale Societa' Italiana di Biologia Sperimentale, Padova, 1962 (in the press).
Bertelli, A., Proto, M., and Rossano, A., Atti Accad. Med. Lomb., 17, 214 (1962).
Bertelli, A., Proto, M., and Rossano, A., Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. (in the press).
Frontino, G., and Francesconi, E. Perelli Ercolini, Atti Accad. Med. Lomb., 17 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BERTELLI, A., FRONTINO, G. Protection of the Skin Homografts by ɛ-Acetamide Caproic Acid. Nature 197, 510–511 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/197510a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/197510a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Action of ?-aminocaproic acid on some serological and enzyme reactions
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1972)
-
Effekt des 6-hydroxydopamin auf Hauthomotransplantation der Mäuse
Experientia (1971)
-
Fibrin-clot Formation by Extracts of Rabbit-skin Homografts
Nature (1964)
-
Prolonged Survival of Kidney Homotransplants in Dog treated by Epsilon-acetamide Caproic Acid
Nature (1964)
-
Beitrag zur Homotransplantation der Menschenhaut
Experientia (1964)