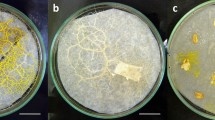
Abstract
CAIRNS1 observed in the United States that a species of Aphelenchus fed on and destroyed mushroom mycelium. During the past eight years, nearly 300 samples of mushroom compost have been examined at Rothamsted. Harmful nematodes usually present were Aphelenchoides composticola2, Ditylenchus myceliophagus3, and occasionally Paraphelenchus myceliophthorus4. The effect of these three species on the growth of mycelium and the yield of mushrooms has been described by Goodey5. Of the 300 samples examined, four contained Aphelenchus avenae6; two of these contained a few A. avenae together with many Diplogaster sp. and Panagrolaimus sp. The other two samples came from different houses on the same mushroom farm and had 6,000 and 18,000 A. avenae/100 gm. compost respectively; Rhabditis sp. and Panagrolaimus sp. were even more numerous.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cairns, E. J., Phytopath., 42, 4 (1952).
Franklin, M. T., Nematologica, 2, 306 (1957).
Goodey, J. B., Nematologica, 3, 1 (1958a).
Goodey, J. B., Nematologica, 3, 91 (1958b).
Goodey, J. B., Ann. App. Biol., 48, 655 (1960).
Bastian, H. C., Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond., 25, 73 (1865).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOOPER, D. Effects of a Nematode on the Growth of Mushroom Mycelium. Nature 193, 496–497 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/193496a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/193496a0
- Springer Nature Limited