Abstract
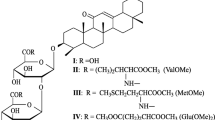
RECENTLY the use of metabolic inhibitors, particularly analogues of nucleic acid components, has been proving an effective tool for investigating the processes involved in antibody formation1–8. The direct determination of the metabolic changes attendant on these processes is practically impossible at the present stage. After the first immunizing dose, only a very small proportion (about 1 per cent) of the lymphoid cells isolated from the spleen or the lymph nodes is active in antibody formation. The detection of any biochemical changes in these cells is made exceedingly difficult not only by the large ‘background’ of inactive cells (99 per cent) but also by the absence of serologically demonstrable antibody from the active cells in the initial (inductive) phase. Earlier I showed that the nucleic acid antimetabolite 6-mercaptopurine acts only during this inductive phase, but does not affect antibody production if administered during the productive phase9. If, then, antibody formation is inhibited by means of suitable agents without affecting protein synthesis in general, we may with some degree of plausibility draw conclusions about the processes taking place in the inductive phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malmgren, R. A., Bennison, B. E., and McKinley, T. W., J. Nat. Cancer, 12, 807 (1952).
Šterzl, J., and Holub, M., Cs. biol., 6, 75 (1957); Folia boil., 4, 59 (1958).
Schwartz, R., Stack, J., and Dameshek, W., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 99, 164 (1958); J. Clin. Invest., 38, 1394 (1959).
Uphoff, D. E., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 99, 651 (1959).
Dutton, R. W., Dutton, A. H., et al., Nature, 182, 1377 (1958); Biochem. J., 75, 230 (1960).
Mecker, W., and Condie, R., et al., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 102, 459 (1959).
Hoyer, L. W., Condie, R. M., and Good, R. A., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 103, 205 (1960).
Berenbaum, M. C., Nature, 185, 167 (1960).
Šterzl, J., Nature, 185, 256 (1960).
Šterzl, J., Folia biol., 3, 1 (1957).
Bieber, S., Bieber, R., and Hitschings, G. H., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 60, 207 (1955). Thiersch, J. B., ibid., 60, 220 (1955).
Heidelberger, Ch., Chaudhuri, N. K., and Danneberg, P., Nature, 179, 663 (1957).
Škoda, J., Hess, V. F., and Šorm, F., Experientia, 13, 150 (1957).
Gut, J., Morávek, C., et al., Coll. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun., 24, 3154 (1959).
Šterzl, J., The Inductive Phase of Antibody Formation (Prague, 1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ŠTERZL, J. Effect of some Metabolic Inhibitors on Antibody Formation. Nature 189, 1022–1023 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1038/1891022a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1891022a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Effect of colchicine derivatives on the antibody response inducedin vitro
Folia Microbiologica (1982)
-
Antibody response in psoriatic patients treated with 6-azauridine-triacetate
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (1973)
-
New indications for 6-azauridine treatment in man. A review
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (1972)
-
Induction of 19S Antibody Synthesis without Stimulation of Cellular Proliferation
Nature (1967)