Abstract
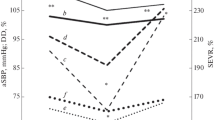
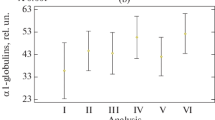
SEVERAL recent clinical studies1 have pointed out important relationships between alimentary lipæmia and the function of the circulatory system after a single large fat meal. The occurrence of typical attacks of angina pectoris especially was observed at the peak of the serum opalescence, accompanied by changes in the electrocardiogram and balistocardiogram. According to various authors many factors participate in these disturbances : increased blood sedimentation-rate and viscosity, decreased fibrinolysis, agglutination of erythrocytes in the blood vessels, and other factors. The possible effect of a relative lack of oxygen in the tissues when the organism is suddenly overloaded with fat was not taken into account. Therefore an experimental study of the effect of alimentary lipæmia upon the resistance of the animal organism to lack of oxygen was undertaken, as the first step towards solving this problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuo, P. T., and Joiner, C. R., J. Amer. Med. Assoc., 158, 1008 (1955). Harders, H., Schw. Med. Wchr., 81, 11 (1957).
Poupa, O., and Pražák, M., Proc. Cong. F.I.M.S., 1948, S.Z.N. Praha (1951).
Lichtfield, J. T., and Wilcoxon, F. W., J. Pharm. Exp. Therap., 95, 99 (1948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MOSINGER, B., KUHN, E. Alimentary Lipæmia and Resistance to Altitude Anoxia. Nature 180, 1140–1141 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1038/1801140a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1801140a0
- Springer Nature Limited