Abstract
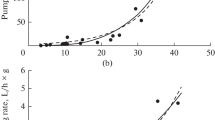
IN an account of experiments with the copepod Calanus finmarchicus (Gunn.), Hardy and Paton1 suggested that the behaviour in vertical migration of this and perhaps other plankton animals might be influenced by the differences in pressure at various depths. The following experiments have been made to test this hypothesis. Two vertical ‘Perspex’ tubes, each 20 in. tall and having an internal rectangular cross-section of 2 in. × 1 ½ in., were placed side by side. After filling with sea water, experimental animals were introduced and each tube was closed by a flanged, water-tight, ‘Perspex’ lid (tightly screwed down), and the pressure in one, called the experimental tube, was varied while that in the other, the control tube, was kept at zero. The pressure in the former was changed by raising or lowering a column of mercury which communicated with the tube through a freshwater buffer and a rubber diaphragm, designed to prevent contamination of the sea water by poisons from the mercury. The pressure was measured either by the height of the mercury column or by the level of the meniscus in a manometer and was recorded in terms of ‘metres depth of water’ equivalent to the number of atmospheres of pressure found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy, A. C., and Paton, W. N., J. Mar. Biol. Assoc., 26, 467 (1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HARDY, A., BAINBRIDGE, R. Effect of Pressure on the Behaviour of Decapod Larvæ (Crustacea). Nature 167, 354–355 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1038/167354a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/167354a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Crab hydrostatic pressure sensors
Nature (1994)
-
Behavioral responses of a larval crustacean to hydrostatic pressure: Rhithropanopeus harrisii (Brachyura: Xanthidae)
Marine Biology (1989)
-
Locomotion, feeding, grooming and the behavioural responses to gravity, light and hydrostatic pressure in the stage I zoea larvae of Ebalia tuberosa (Crustacea: Decapoda: Leucosiidae)
Marine Biology (1982)
-
The pressure responses of lobster larvae following selective cautery and treatment with surface active substances
Experientia (1979)
-
Ontogeny of light and gravity responses in rock crab larvae (Cancer irroratus)
Marine Biology (1979)