Abstract
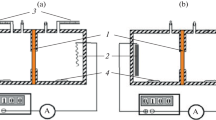
PERMEABILITY to electrolytes. Under normal conditions the membranes of plant cells are impermeable to electrolytes. But under abnormal conditions (transfer to solutions of pure electrolytes) the electrolytes can pass through (deplasmolysis). In this connexion, if one compares solutions of different electrolytes, one can observe that they follow the Hofmeister series. The series in which the hypotonic solution of electrolytes can cause haemolysis of the red corpuscles is the same as the Hofmeister series. We have examined these conditions, using hen‘s egg membranes. According to the experiments of A. Orru1, the permeability of the vitelline membrane to water was influenced by hydrogen and hydroxyl ions and by the presence of different electrolytes, and that complex ions can pass through as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orru, A., Biol. Abstr., 14, 2, 211 (1940); Chem. Zentralbl., 1, 534 (1941); 2, 1462 (1940).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KLISSIUNIS, N. Permeability of the Membranes of the Hen‘s Egg. Nature 162, 77–78 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1038/162077a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/162077a0
- Springer Nature Limited