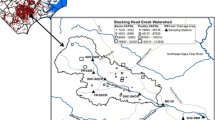
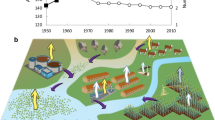
Abstract
Livestock production has undergone massive industrialization in recent decades. Nationwide, millions of swine, poultry, and cattle are raised and fed in concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) owned by large, vertically integrated producer corporations. The amount of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) in animal manure produced by CAFOs is enormous. For example, on the North Carolina Coastal Plain alone an estimated 124,000 metric tons of nitrogen and 29,000 metric tons of phosphorus are generated annually by livestock. CAFO wastes are largely either spread on fields as dry litter or pumped into waste lagoons and sprayed as liquid onto fields. Large amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus enter the environment through runoff, percolation into groundwater, and volatilization of ammonia. Many CAFOs are located in nutrient-sensitive watersheds where the wastes contribute to the eutrophication of streams, rivers, and estuaries. There is as yet no comprehensive Federal policy in place to protect the environment and human health from CAFO generated pollutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aneja, V.P., Chauhan, J.P., & Walker, J.P. (2000). Characterization of atmospheric ammonia emissions from swine waste storage and treatment lagoons. Journal of Geophysical Research 105, 11, 535-11545.
Barker, J.C., & Zublena, J. P. (1995). Livestock manure nutrient assessment in North Carolina. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Agricultural and Food Processing Wastes (ISAFPW95) (pp. 98-106). Chicago: American Society of Agricultural Engineering.
Burkholder, J. M., & Glasgow, H. B. Jr. (1997). Pfiesteria piscicida and other Pfiesteria-like dinoflagellates: Behavior, impacts, and environmental controls. Limnology and Oceanography 42, 1052-1075.
Burkholder, J. M., & Glasgow, H. B. Jr. (2001). History of toxic Pfiesteria in North Carolina estuaries from 1991 to the present. BioScience 51: 827-841.
Burkholder, J. M., Glasgow, H. B. Jr., & Cooke, J. E. (1994). Comparative effects of watercolumn nitrate enrichment on eelgrass Zostera marina, shoalgrass Halodule wrightii, and widgeongrass Ruppia marina. Marine Ecology Progress Series 105, 121-138.
Burkholder, J. M., Glasgow, H. B. Jr., & Hobbs, C. W. (1995). Distribution and environmental conditions for fish kills linked to a toxic ambush predator dinoflagellate. Marine Ecology Progress Series 124, 43-61.
Burkholder, J. M., Mallin, M. A., Glasgow, H. B. Jr., Larsen, L. M., McIver, M. R., Shank, G. C., Deamer-Melia, N., Briley, D. S., Springer, J., Touchette, B. W., & Hannon, E. K. (1997). Impacts to a coastal river and estuary from rupture of a swine waste holding lagoon. Journal of Environmental Quality 26, 1451-1466.
Burkholder, J. M., Mason, K. M., & Glasgow, H. B. Jr. (1992). Water-column nitrate enrichment promotes decline of eelgrass Zostera marina L.: Evidence from seasonal mesocosm experiments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 81, 163-178.
Cahoon, L. B., Mickucki, J. A., & Mallin, M. A. (1999). Nutrient imports to the Cape Fear and Neuse River basins to support animal production. Environmental Science and Technology 33, 410-415.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications 8, 559-568.
Correll, D. L. (1998). The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. Journal of Environmental Quality 27, 261-266.
Crane, S. R., Moore, J. A., Grismer, M. E., & Miner, J. R. (1983). Bacterial pollution from agricultural sources: A review. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 26, 858-872.
Dame, R., Alber, M., Allen, D., Chalmers, A., Gardner, R., Gilman, C., Kjerfve, B., Lewitus, A., Mallin, M., Montague, C., Pinckney, J., & Smith, N. (2000). Estuaries of the south Atlantic coast of North America: Their geographical signatures. Estuaries 23, 793-819.
Davies, C. M., Long, J. A. H., Donald, M. & Ashbolt, N. J. (1995). Survival of fecal microorganisms in marine and freshwater sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61, 1888-1896.
Dennison, W. C., Orth, R. J., Moore, K. A., Stevenson, J. C., Carter, V., Kollar, S., Bergstrom, P. W., & Batiuk, R. A. (1993). Assessing water quality with submersed aquatic vegetation. BioScience 43, 86-94.
Diamond, J. (1997). Guns, Germs, and Steel. W. W. New York, Norton and Company.
Edwards, D. R., & Daniel, T. C. (1992). Environmental impacts of on-farm poultry waste disposal-a review. Bioresource Technology 41, 9-33.
Evans, R.O., Westerman, P. W., & Overcash, M. R. (1984). Subsurface drainage water quality from land application of swine lagoon effluent. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 27, 473-480.
Gilliam, J. W., Huffman, R. L., Daniels, R. B., Buffington, D. E., Morey, A. E., & Leclerc, S. A. (1996). Contamination of surficial aquifers with nitrogen applied to agricultural land. Report No. 306. Water Resources Research Institute of the University of North Carolina, Raleigh, N.C.
Glasgow H. B., & Burkholder, J. M. (2000). Water quality trends and management implications from a five-year study of a eutrophic estuary. Ecological Applications 10, 1024-1046.
Glasgow, H. B., Burkholder, J. M., Mallin, M. A., Deamer-Melia, N. J., & Reed, R. R. (2001). Field ecology of toxic Pfiesteria complex species and a conservative analysis of their role in estuarine fish kills. Environmental Health Perspectives 109, 715-730.
Harkin, T. (1997). Animal waste pollution in America: an emerging national problem. Environmental risks of livestock and poultry production. Report compiled by the minority staff of the United States Senate Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition and Forestry for Senator Tom Harkin (D-IA).
Huffman, R. L., & Westerman, P. W. (1995). Estimated seepage losses from established swine waste lagoons in the lower coastal plain of North Carolina. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 38, 449-453.
Kellogg, R. L. (2000). Potential priority watersheds for protection of water quality from contamination by manure nutrients. Paper presented at the Animal Residuals Management Conference 2000, November 12-14, Kansas City, MO.
Jackson, L. L., Keeney, D. R. & Gilbert, E. M. 2000. Swine manure management plans in north-central Iowa: nutrient loading and policy implications. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 55, 205-212.
Karr, J. D., Showers, W. J., Gilliam, J. W., & Andres, A. S. (2001). Tracing nitrate transport and environmental impact from intensive swine farming using Delta nitrogen-15. Journal of Environmental Quality 30, 1163-1175.
Liebhardt, W. C., Golt, C., & Tupin, J. (1979). Nitrate and ammonium concentrations of ground water resulting from poultry manure applications. Journal of Environmental Quality 8, 211-215.
Mallin, M. A. (2000). Impacts of industrial-scale swine and poultry production on rivers and estuaries. American Scientist 88, 26-37.
Mallin, M. A., Burkholder, J. M., Cahoon, L. B., & Posey, M. H. (2000). The North and South Carolina coasts. Marine Pollution Bulletin 41, 56-75.
Mallin, M. A., Burkholder, J. M., McIver, M. R., Shank, G. C., Glasgow, H. B. Jr., Touchette, B. W., & Springer, J. (1997). Comparative effects of poultry and swine waste lagoon spills on the quality of receiving stream waters. Journal of Environmental Quality 26, 1622-1631.
Mallin, M. A., Cahoon, L. B., Parsons, D. C. & Ensign, S. H. (2001). Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus loading on plankton in Coastal Plain blackwater streams. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 16, 455-466.
Mallin, M. A., Paerl, H. W., Rudek, J., & Bates, P. W. (1993). Regulation of estuarine primary production by rainfall and river flow. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 93, 199-203.
Mallin, M. A., Posey, M. H., Shank, G. C., McIver, M. R., Ensign, S. H., & Alphin, T. D. (1999). Hurricane effects on water quality and benthos in the Cape Fear Watershed: Natural and anthropogenic impacts. Ecological Applications 9, 350-362.
Mawdsley, J. L., Bardgett, R. D., Merry, R. J., Pain, B. F., & Theodorou, M. K. (1995). Pathogens in livestock waste, their potential for movement through soil and environmental pollution. Applied Soil Ecology 2, 1-15.
McCulloch, R. B., Few, G. S., Murray, G. C., Jr., & Aneja, V. P. (1998). Analysis of ammonia, ammonium aerosols and acid gases in the atmosphere at a commercial hog farm in eastern North Carolina, USA. Environmental Pollution 102, 263-268.
MMWR. (1999). Public health dispatch: Outbreak of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 and Campylobacter among attendees of the Washington County fair, New York, 1999. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
N.C.D.A. (1999). North Carolina Agricultural Statistics. North Carolina Department of Agriculture, North Carolina Agricultural Statistics, Raleigh, N.C.
N.C. D.A.Q. (1997). Assessment plan for atmospheric nitrogen compounds: Emissions, transport, transformation, and deposition. N.C. Department of Environment, Health and Natural Resources, Division of Air Quality, Raleigh, N.C.
NRCS. (1996). Agricultural waste characteristics, Agricultural Waste Management Field Handbook. (pp. 4.1-4.24). Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Paerl, H. W., Mallin, M. A., Donahue, C. A., Go, M & Peierls, B. J. (1995). Nitrogen loading sources and eutrophication of the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina: Direct and indirect roles of atmospheric deposition. UNC WRRI-95-291. Water Resources Research Institute of the University of North Carolina, Raleigh, N.C.
Paerl, H. W., Rudek, J., & Mallin, M. A. (1990). Stimulation of phytoplankton productivity in coastal waters by natural rainfall inputs; nutritional and trophic implications. Marine Biology 107. 247-254.
Powers, W., & Van Horn, H. H. (1998). Whole-farm nutrient budgeting: A nutritional approach to manure management. In Soil and Water Conservation Society, Manure Management in Harmony with the Environment and Society (pp. 276-280). Ames, Iowa: Soil and Water Conservation Society West North Central Region.
Rudek, J., Paerl, H. W., Mallin, M. A., & Bates, P. W. (1991). Seasonal and hydrological control of phytoplankton nutrient limitation in the Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 75, 133-142.
Sharpley, A. N., Daniel, T., Sims, T., Lemunyon, J., Stevens, R., & Parry, R. (1999). Agricultural phosphorus and eutrophication. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, ARS-149.
Sharpley, A. N., Tunney, D. 2000. Phosphorus research strategies to meet agricultural and environmental challenges of the 21st century. Journal of Environmental Quality 29:176-181.
Sobsey, M. D. (1996). Pathogens and their indicators in North Carolina surface waters. In Solutions: Proceedings of a Technical Conference on Water Quality (pp 6-10). North Carolina State University, Raleigh, N.C.
Stone, K. C., Hunt, P. G., Coffey, S. W. & Matheny, T. A. (1995). Water quality status of a USDA water quality demonstration project in the Eastern Coastal Plain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 50, 567-571.
Thu, K. M., & Durrenberger, E. P. (1998). Pigs, Profits, and Rural Communities. Albany, State University of New York Press.
USNASS (1997) US National Agricultural Statistics Service census data for 1997. website: www.nass.usda.gov/census97/rankings.
Walker, J. T., V. P. Aneja, & Dickey, D. A. (2000). Atmospheric transport and wet deposition of ammonium in North Carolina. Atmospheric Environment 34, 3407-3418.
Westerman, P. W., Huffman, R. L., & Feng, J. S. (1995). Swine-lagoon seepage in sandy soil. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 38, 1749-1760.
Westerman, P. W., King, L. D., Burns, J. C., Cummings, G. A. & Overcash, M. R. (1987). Swine manure and lagoon effluent applied to a temperate forage mixture: II. Rainfall runoff and soil chemical properties. Journal of Environmental Quality 16, 106-112.
Williams, C. M., Barker, J. C., & Sims, T. (1999). Management and utilization of poultry wastes. Reviews in Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 162, 105-157.
Wing, S., Freedman, S., & Band, L. (2002). The potential impact of flooding on confined animal feeding operations in eastern North Carolina. Environmental Health Perspectives 110, 387-391.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallin, M.A., Cahoon, L.B. Industrialized Animal Production—A Major Source of Nutrient and Microbial Pollution to Aquatic Ecosystems. Population and Environment 24, 369–385 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023690824045
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023690824045