Abstract
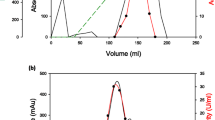
The present investigation was aimed at producing a thermostable and neutral glucoamylase (amyloglucosidase, EC 3.2.1.3) by a thermophilic mould, Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae in submerged cultivation and testing its applicability in starch saccharification. Parametric optimization resulted in the secretion of 30,000 U/l of glucoamylase in a synthetic medium (5% soluble starch, 0.1% yeast extract, 0.05% K2HPO4 and 0.01% MgSO4· 7H2O) using 5 × 106 spores/50 ml of a 3-day-old inoculum at 40 °C and 250 rev/min in shake flasks in 48 h. The enzyme secretion was not affected to any significant extent by the tested additives and detergents. A 1.7-fold increase in glucoamylase secretion was attained when T. indicae-seudaticae was grown in a laboratory fermenter. The enzyme alone catalysed the hydrolysis of soluble starch to an extent of 65%. A prior treatment of starch with thermostable α-amylase and amylopullulanase, followed by glucoamylase, resulted in a greater extent of hydrolysis, 79 and 91%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antranikian, G. 1992 Microbial degradation of starch. In Microbial Degradation of Natural Products, ed. Winkel, G. pp. 27–51. Weinheim, Germany: VCH Publishers. ISBN 3-527-28354-4.
Babu, K.R. & Satyanarayana, T. 1993 Extracellular calcium-inhibited ?-amylase of Bacillus coagulans B49. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 15, 1066–1069.
Bentley, I.S. & Williams, E.C. 1996 Starch conversion. In Industrial Enzymology, eds. Godfrey, T. & West, S. pp. 339–357. London, UK: Macmillan Press. ISBN 0-333-59464-9.
Bernfeld, P. 1955 Amylases, ? and ?. Methods in Enzymology 1, 149–158.
Emerson, R. 1941 An experimental study of the life cycles and taxonomy of Allomyces. Lloydia 4, 77–144.
Fogarty, W.M. 1983 Microbial amylases. In Microbial Enzymes and Biotechnology, ed. Fogarty, W.M. pp. 1–92. London: Applied Science Publishers. ISBN 0-8533-4185-0.
Fogarty, W.M. & Kelly, C.T. 1990 Recent advances in microbial amylases. In Microbial Enzymes and Biotechnology, 2nd edn, eds. Fogarty, W.M. & Kelly, C.T. pp. 71–132. London: Elsevier, Applied Science Publishers, ISBN 1-85166486-6.
Horvathova, V., Janecek, S.A. & Sturdik, E. 2001 Amylolytic enzymes: molecular aspects of their properties. General Physiology and Biophysics 20, 7–32.
James, J.A. & Lee, B.H. 1997 Glucoamylases: microbial sources, industrial applications and molecular biology, A review. Journal of Food Biochemistry 21, 1–52.
Kanlayakrit, W., Ishimatsu, K., Nakao, M. & Hayashida, S. 1987 Characteristics of raw starch-digesting glucoamylase from thermophilic Rhizomucor pusillus. Journal of Fermentation Technology 65, 379–385.
Kaur, P. & Satyanarayana, T. 2001 Partial purification and characterization of glucoamylase of thermophilic mould Thermomucor indicae-seudaticea. Indian Journal of Microbiology 41, 195–199.
Kelly, C.T., Giblin, M. & Fogarty,W.M. 1986 Resolution, purification and characterization of two extracellular glucohydrolases, ?-glucosidase and maltase of Bacillus licheniformis. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 32, 342–347.
Kumar, S. & Satyanarayana, T. 2001 Medium optimization for glucoamylase production by a yeast, Pichia subpelliculosa ABWF-64 in submerged cultivation. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 19, 598–601.
Kumar, S. & Satyanarayana, T. 2003 Purification and kinetics of a raw starch-hydrolyzing, thermostable, and neutral glucoamylase of the thermophilic mold Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae. Biotechnology Progress 19, 936–944.
Malhotra, R., Noorwez, S.M. & Satyanarayana, T. 2000 Production and partial characterization of thermostable and calcium independent ?-amylase of an extreme thermophile Bacillus thermooleovorans NP54. Letters in Applied Microbiology 31, 378–384.
Mishra, R. & Maheshwari, R. 1996 Amylases of the thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus; their purification, properties, action on starch and response to heat. Journal of Biosciences 21, 653–672.
Narang, S. & Satyanarayana, T. 2001 Thermostable ?-amylase production by an extreme thermophile Bacillus thermooleovorans. Letters in Applied Microbiology 32, 31–35.
Pandey, A. 1995. Glucoamylase research. An overview. Starch/Starke 47, 439–445.
Pandey, A., Nigam, P., Soccol, C.R., Soccol, V.T., Singh, D. & Mohan, R. 2000 Advances in microbial amylases. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry 31, 135–152.
Ramesh, M.V. & Lonsane, B.K. 1990 Production of bacterial thermostable ?-amylases by solid-state fermentation: a potential tool for achieving economy in enzyme production and starch hydrolysis. Advances in Applied Microbiology 35, 1–6.
Rao, V.B., Maheshwari, R., Sastry, N.V.S. & Rao, P.V.S. 1979 A thermostable glucoamylase from the thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus. Biochemical Journal 48, 113–115.
Reilly, P.J. 1999 Protein engineering of glucoamylase to improve industrial properties: a review. Starch/Starke 51, 269–274.
Rukhair, R. & Srivastava, S.K. 1995 Effect of various carbon substrates on ?-amylase production from Bacillus sp. Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology 10, 76–82.
Shaku, M., Koike, S. & Udaka, S. 1980 Cultural conditions for protein production by Bacillus brevis No. 47. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 44, 99–103.
Shu, P. & Blackwood, A.C. 1951 Studies of carbon and nitrogen sources for the production of amylolytic enzymes by submerged culture of Aspergillus niger. Canadian Journal of Botany 29, 113–124.
Soni, S.K., Rao, M.V. & Das, D. 1995 Studies on glucoamylase produced from Aspergillus awamori (NRRL-3112) and their effect on saccharification of potato starch. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology 33, 957–961.
Subrahmanyam, A., Mehrotra, B.S. & Thirumalachar 1977 Thermomucor, a new genus of Mucorales. Georgia Journal of Science 35, 106.
Tamura, M.K., Shimizu, M.H. & Tago, M. 1981 Highly thermostable glucoamylase and process for its production. United States Patent No. 4,247,637.
Taylor, P.M., Napier, E.J. & Fleming, I.D. 1978 Some properties of a glucoamylase produced by the thermophilic fungus Humicola lanuginosa. Carbohydrate Research 61, 301–308.
Tosi, L.R.O., Terenzi, H.F. & Jorge, J.A. 1993 Purification and characterization of an extracellular glucoamylase from the thermophilic fungus Humicola grisea var thermoidea. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 39, 846–852.
Vieille, C. & Zaikus, G.J. 2001 Hyperthermophilic enzymes: sources, uses and molecular mechanism for thermostability. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 65, 1–43.
Vihinen, M. & Mantsala, P. 1989 Microbial amylolytic enzymes. CRC Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 24, 329–419.
Yoon, M.Y., Yoo, Y.J. & Cadman, T.W. 1989 Phosphate effects in the fermentation of α-amylase by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Biotechnology Letters 11, 59–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, P., Satyanarayana, T. Production and Starch Saccharification by a Thermostable and Neutral Glucoamylase of a Thermophilic Mould Thermomucor Indicae-Seudaticae . World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 20, 419–425 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000033065.22647.5b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000033065.22647.5b