Abstract
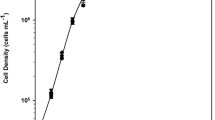
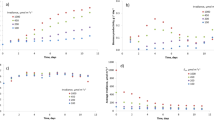
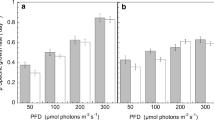
Nannochloropsis sp. was grown semicontinuously with a rate of daily renewal of the culture media of 40% of the volume of the culture under different irradiances (40, 60, 80, 220 and 480 μmol quanta m−2 s−1). Under the conditions tested, light saturation was achieved at 220 μmol quanta m−2 s−1 with no significant increase in steady-state cell density or of dry weight productivity with higher irradiance, reaching values of 115 × 106 cells ml−1 and 375 mg l−1 day−1 respectively. C/N ratios clearly indicated the point of light saturation, decreasing with increasing irradiance for light-limited conditions and increasing for light-saturated conditions. Under light-limited conditions, an increase in the irradiance produced an increase in the protein percentage of the organic fraction to the detriment of lipids and carbohydrates, while small changes were recorded under light-saturated conditions. The degree of unsaturation of fatty acids was lower with increasing irradiance, with a three-fold decrease of the percentage of total n−3 fatty acids, from 29 to 8% of total fatty acids, caused mainly by a decrease of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (20:5n−3). The microalga reached its maximal value of dry weight productivity (375 mg l−1 day−1), EPA productivity (3.2 mg l−1 day−1) and maximal protein content (36% of the organic content) at the point at which light saturation was achieved. Results demonstrate the efficiency of the use of the irradiance for the modification of the biochemical composition of Nannochloropsis sp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bligh, E.G. & Dyer, W.J. 1959 A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology 37, 911–917.
Claustre, H. & Gostan, J. 1987 Adaptation of biochemical composition and cell size to irradiance in two microalgae: possible ecological implications. Marine Ecology Progress Series 40, 167–174.
Cohen, Z., Vonshak, A. & Richmond, A. 1988 Effect of environmental conditions on fatty acid composition of the red alga Porphyridium cruentum: correlation to growth rate. Journal of Phycology 24, 328–332.
Eppley, R.W. & Coatsworth, J.L. 1966 Culture of the marine phytoplankter, Dunaliella tertiolecta, with light–dark cycles. Archives of Microbiology 55, 66–80.
Fábregas, J., Abalde, J., Herrero, C., Cabezas, B. & Veiga, M. 1984 Growth of the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica in batch cultures with different salinities and nutrients concentration. Aquaculture 42, 207–215.
Fábregas, J., Maseda, A., Domínguez, A., Ferreira, M. & Otero, A. 2002 Changes in the cell composition of the marine microalga, Nannochloropsis gaditana, during a light:dark cycle. Biotechnology Letters 24, 1699–1703.
Fábregas, J., Patiño, M., Morales, E.D., Cordero, B. & Otero, A. 1996 Optimal renewal rate and nutrient concentration for the production of the marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum in semicontinuous cultures. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 62, 266–268.
Fernández-Sevilla, J.M., Molina-Grima, E., García-Camacho, F., Acien-Fernández, F.G. & Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. 1998 Photolimitation and photoinhibition as factors determining optimal dilution rate to produce eicosapentaenoic acid from cultures of the microalga Isochrysis galbana. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 50, 199–205.
Garcia-Sanchez, J.L., Sanchez-Perez, J.A., Garcia-Camacho, F., Fernandez-Sevilla, J.M. & Molina-Grima, E. 1996 Optimization of light and temperature for growing Chlorella sp. using response surface methodology. Biotechnology Techniques 10, 329–334.
Gilstad, M., Johnsen, G. & Sakshaug, E. 1993 Photosynthetic parameters, pigment composition and respiration rates of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum in continuous light and a 12:12 h light–dark cycle. Journal of Plankton Research 15, 939–951.
James, C.M. & Al-Khars, A.M. 1990 An intensive continuous culture system using tubular photobioreactors for producing microalgae. Aquaculture 87, 381–393.
Kochert, G. 1978 Carbohydrate determination by the phenol–sulphuric acid method. In: Handbook of Phycological Methods. Physiological and Biochemical Methods, eds. Hellebust, J.A. & Craigie, J.S. pp. 95–97. London: Cambridge University press. ISBN 0-521-20049-0.
Marsh, J.B. & Weinstein, D.B. 1966 Simple charring method for determination of lipids. Journal of Lipid Research 7, 574–576.
Merchuk, J.C., Ronen, M., Giris, S. & Arad, S.M. 1998 Light/dark cycles in the growth of the red microalga Porphyridium sp. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 59, 705–713.
Molina-Grima, E., Fernández-Sevilla, J.M., Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. & García-Camacho, F. 1996 A study on simultaneous photolimitation and photoinhibition in dense microalgal cultures taking into account incident and averaged irradiances. Journal of Biotechnology 45, 59–69.
Orcutt, D.M. & Patterson, G.W. 1974 Effect of light intensity upon lipid composition of Nitzschia closterium (Cylindrotheca fusiformis). Lipids 9, 1000–1003.
Qiang, H. & Richmond, A. 1994 Optimizing the population density in Isochrysis galbana grown outdoors in a glass column photobioreactor. Journal of Applied Phycology 6, 391–396.
Renaud, S.M., Parry, D.L., Thinh, Luoung-Van, Kuo, C., Padovan, A. & Sammy, N. 1991 Effect of light intensity on the proximate biochemical and fatty acid composition of Isochrysis sp. and Nannochloropsis oculata for use in tropical aquaculture. Journal of Applied Phycology 3, 43–53.
Sato, N. & Murata, N. 1988 Membrane lipids. Methods in Enzymology 167, 251–259.
Schneider, J.C., Livne, A., Sukenik, A. & Roessler, P.G. 1995 A mutant of Nannochloropsis deficient in eicosapentaenoic acid production. Phytochemistry 40, 807–814.
Sukenik, A. & Carmeli, Y. 1990 Lipid synthesis and fatty acid composition in Nannochloropsis sp. (Eustigmatophyceae) grown in a light-dark cycle. Journal of Phycology 26, 463–469.
Sukenik, A., Carmeli, Y. & Berner, T. 1989 Regulation of fatty acid composition by irradiance level in the Eustigmatophyte Nannochloropsis sp. Journal of Phycology 25, 686–692.
Sukenik, A., Schneider, J.C., Roessler, P.G., Livne, A., Berner, T., Kolber, Z., Wyman, K., Prasil, O. & Falkowski, P.G. 1998 Photosynthetic characterization of a mutant of Nannochloropsis deficient in the synthesis of eicosapentaenoic acid. Israel Journal of Plant Sciences 46, 101–108.
Sukenik, A., Zmora, O. & Carmeli, Y. 1993 Biochemical quality of marine unicellular algae with special emphasis on lipid composition. 2. Nannochloropsis sp. Aquaculture 117, 313–326.
Thompson, P.A., Guo, M. & Harrison, P.J. 1993 The influence of irradiance on the biochemical composition of three phytoplankton species and their nutritional value for larvae of the Pacific Oyster (Cassostrea gigas). Marine Biology 117, 259–268.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fábregas, J., Maseda, A., Domínguez, A. et al. The cell composition of Nannochloropsis sp. changes under different irradiances in semicontinuous culture. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 20, 31–35 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000013288.67536.ed
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WIBI.0000013288.67536.ed