Abstract
Organic wastes such as sewage sludge and compost increase the input of carbon and nutrients to the soil. However, sewage sludge-applied heavy metals, and organic pollutants adversely affect soil biochemical properties. Therefore, an incubation experiment lasting 90 days was carried out to evaluate the effect of the addition of two sources of organic C: sewage sludge or composted turf and plant residues to a calcareous soil at three rates (15, 45, and 90 t of dry matter ha−1) on pH, EC, dissolved organic C, humic substances C, organic matter mineralization, microbial biomass C, and metabolic quotient. The mobile fraction of heavy metals (Zn, Cd, Cu, Ni, and Pb) extracted by NH4NO3 was also investigated.
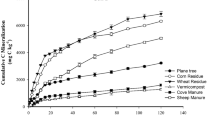
The addition of sewage sludge decreased soil pH and increased soil salinity to a greater extent than the addition of compost. Both sewage sludge and compost increased significantly the values of the cumulative C mineralized, dissolved organic C, humic and fulvic acid C, microbial biomass C, and metabolic quotient (qCO2), especially with increasing application rate. Compared to compost, the addition of sewage sludge caused higher increases in the values of these parameters. The values of dissolved organic C, fulvic acid C, microbial biomass C, metabolic quotient, and C/N ratio tended to decrease with time. The soil treated with sewage sludge showed a significant increase in the mobile fractions of Zn, Cd, Cu, and Ni and a significant decrease in the mobile fraction of Pb compared to control. The high application rate of compost resulted in the lowest mobility of Cu, Ni, and Pb. The results suggest that biochemical properties of calcareous soil can be enhanced by both organic wastes. But, the high salinity and extractability of heavy metals, due to the addition of sewage sludge, may limit the application of sewage sludge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almas, A.R., McBride, M.B. and Singh, B.R.: 2000, 'Solubility and lability of cadmium and zinc in two soils treated with organic matter', Soil Sci. 5, 250–259.
Amrhein, C., Strong, J.E. and Mosher, P.A.: 1992, 'Effect of deicing salts on metal and organic matter mobility in roadside soils', Environ. Sci. Technol. 6, 703–709.
Anderson T. and Domsch, K.H.: 1993, 'The metabolic quotient for CO2 (qCO2)as aspecific activity parameter to asses the effects of environmental conditions, such as pH, on the microbial biomass of the soil', Soil Biol. Biochem. 5, 393–395.
Anderson, J.P.E. and Domsch, K.H.: 1978, 'A physiological method for the quantitative measurement of microbial biomass in soil', Soil Biol. Biochem. 0, 215–221.
Berrow, M.L. and Webber, J.: 1972, 'Trace elements in sewage sludges', J. Sci. Food Agric. 3, 93–100
Black, C.A. 1965.: Methods of Soil Analysis, American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Brallier, S., Harrison, R.B., Henry, C.L. and Dongsen, X.: 1996, 'Liming effects on availability of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn in a soil amended with sewage sludge 16 years previously', Water Air Soil Pollut. 6, 195–206.
Brown, S., Chaney, R.L., Hallfrisch, J.G. and Xue, Q.: 2003, 'Effect of biosolids processing on lead bioavailability in an urban soil', J. Environ. Qual. 2, 100–108.
Chander, K. and Brookes, P.C.: 1991, 'Effects of heavy metals from past applications of sewage sludge on microbial biomass and organic matter accumulation in a sandy loam and silty loam U.K. soil', Soil Biol. Biochem. 3, 927–932.
Chander, K., Brookes, P.C. and Harding, S.A.: 1995, 'Microbial biomass dynamic following ad-dition of metal-enriched sewage sludge to a sandy loam', Soil Biol. Biochem. 1409–1421.
Chander, K., Dyckmans, J., Joergensen, R.G., Meyer, B.and Raubuch, M.: 2001, 'Different sources of heavy metals and their long-term effects on soil microbial properties', Biol. Fertil. Soils 4, 241–247.
Chuan, M.C., Shu, G.Y. and Liu, J.C.: 1996, 'Solubility of heavy metals in a contaminated soil: Effects of redox potential and pH', Water Air Soil Pollut. 543–556.
Friedel, J.K., Langer, T., Siebe, C. and Stahr. K.: 2000, 'Effects of long-term waste water irrigation on soil organic matter, soil microbial biomass and its activities in central Mexico', Biol. Fertil. Soils414–421.
Goyal, S., Mishra, M.M., Dhankar, S.S., Kapoor, K.K. and Batra, R.: 1993, 'Microbial biomass turnover and enzyme activities following the application of farmyard manure to field soils with and without previous long-term applications', Biol. Fertil. Soils 5, 60–64.
Holm, P.E., Anderson, B.B.H. and Christensen, T.H.: 1996, 'Cadmium solubility in aerobic soils', Soil Sci. Soc. Am.J. 0, 775–780.
Jin, Q., Zi-jian, W., Xiao-quann, S., Qiang, T., Bei, W. and Bin, C.: 1996, 'Evaluation of plant avail-ability of soil trace metals by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis', Environ. Pollut. 1, 309–315.
Johansson, M., Stenberg, B. and Torstensson, L.: 1999, 'Microbiological and chemical changes in two arable soils after long-term sludge amendments', Biol. Fertil. Soils 0, 160–167.
Jörgensen, R.G.: 1996, 'The fumigation-extraction method to estimate soil microbial biomass: Cali-bration of the kEC value', Soil Biol. Biochem. 8,25–31.
Kiikilä, O., Pennanen, T., Perkiömäki, J. and Derome, J.: 2002. 'Organic material as a copper immo-bilizing agent: A microcosm study on remediation', Basic Appl. Ecol. 3, 245–253.
Leifeld, J., Siebert, S. and Kögel-Knabner, I.: 2002, 'Biological activity and organic matter min-eralization of soil amended with biowaste composts', J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 5, 151–159.
Leita, L., De Nobili, M., Muhlbachova, G., Mondini, C., Marchiol, L. and Zerbi, G.: 1995, 'Bioavail-ability and effects of heavy metals on soil microbial biomass survival during laboratory incuba-tion', Biol. Fertil. Soils 9, 103–108.
Leita, L., Nobili, M.D. and Mondini, C.: 1999, 'Influence of inorganic and organic fertilization on soil microbial biomass, metabolic quotient and heavy metal bioavailability', Biol. Fertil. Soils 8, 371–376.
McBride, M.B.: 1978, 'Transition metal bonding in humic acid: An ESR study', Soil Sci. 6, 200–209.
McBride, M.B.: 1995, 'Toxic metal accumulation from agriculture use of sludge: Are USEPA regu-lations protective?', J. Environ. Qual. 4, 5–18.
McBride, M., Sauve, S. and Hendershot, W.: 1997, Solubility control of Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in contaminated soil', Eur. J. Soil Sci. 8, 337–346
Moolenaar, S.W. and Beltrami, P.: 1998, 'Heavy metal balances of an Italian soil as affected by sewage sludge and Bordeaux mixture applications', J. Environ. Qual. 7, 828–835.
Moreno, J.L., Hernandez, T. and Garcia, C.: 1999, 'Effects of a cadmium-contaminated sewage sludge compost on dynamics of organic matter and microbial activity in an arid soil', Biol. Fertil. Soils 8, 230–237.
Morera, M.T., Echeverria, J. and Garrido, J.: 2002, 'Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils amended with sewage sludge', Can. J. Soil Sci. 2, 433–438.
Neal, R.H. and Sposito, G.: 1986, 'Effects of soluble organic matter and sewage sludge amendments on Cd sorption by soils at low Cadmium concentrations', Soil Sci. 2, 164–172.
Osman, A.Z., Wassif, M.M., El-Kadi, M.A. and Abdel Salam, M.A.: 1980, 'Effect of carbonate in clay fraction on fixation of zinc', Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenkdl. 3, 524–529.
Pascual, J.A., Garcia, C. and Hernandez, T.: 1999, 'Lasting microbiological and biochemical effects of the addition of municipal solid waste to an arid soil', Biol. Fertil. Soils 0, 1–6.
Pascual, J.A., Garcia, C., Hernandez, T. and Ayuso, M.: 1997, 'Changes in the microbial activity of an arid soil amended with urban organic wastes', Biol. Fertil. Soils 4, 429–434.
Powlson, D.S., Brookes, P.C. and Christensen, B.T.: 1987, Measurements of soil microbial biomass provides an early indication of changes in total soil organic matter due to straw incorporation', Soil Biol. Biochem. 9, 159–164.
Richards, L.A.: 1960, Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkaline Soils, U.S. Salinity Labo-ratory, Agricultural handbook No. 60.
Scheffer, F. and Schachtschabel, P.: 2002, Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, 15. Auflage. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg. Berlin.
Schlichting, E., Blume, H.P. and Stahr, K.: 1995, Bodenkundliches Praktikum, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Berlin.
Silveira, M.L.A., Alleoni, L.R.F. and Guilherme, L.R.G.: 2003, 'Review: Biosolids and heavy metals in soils', Scientia Agricola 0, 793–806.
Sloan, J.J. and Basta, N.T.: 1995, 'Remediation of acid soils by using alkaline biosolids', J. Environ. Qual. 4, 1097–1103.
Sloan, J.J., Dowdy, R.H., Dolan, M.S. and Linden, D.R.: 1997, 'Long-term effects of biosolids applications on heavy metal bioavailability in agriculture soils', J. Environ. Qual. 6, 966–974.
Speir, T.W., van Schaik, A.P., Lloyd-Jones, A.R. and Kettles, H.A.: 2003, 'Temporal response of soil after cultivation following high application rates of undigested sewage sludge', Biol. Fertil. Soils 8, 377–385.
Strawn, D.G. and Sparks, D.L.: 2000, 'Effects of soil organic matter on the kinetics and mechanisms of Pb (II) sorption and desorption in soil', Soil Sci. Soc. Am.J. 4, 144–156.
Temminghoff, E.J.M., van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M. and De Haan, F.A.M.: 1998, 'Effects of dissolved organic matter on the mobility of copper in a contaminated sandy soil', Eur. J. Soil Sci. 9, 617–628.
Tyler, L.D. and McBride, M.B.: 1982, 'Mobility and extractability of cadmium, copper, nickle, and zinc in organic and mineral soil columns', Soil Sci. 4, 198–205.
Van Dijk, J.: 1971, 'Cation binding of humic acids', Geoderma 5, 53–67.
Vance, E.D., Brookes, P.C. and Jenkinson, D.S.: 1987, 'An extraction method for measuring microbial biomass C', Soil Biol. Biochem. 9, 703–707.
Wang, P., Qu, E., Li, Z. and Shuman, L.M.: 1997, 'Fractions and availability of nickel in loessial soil amended with sewage or sewage sludge', J. Environ. Qual. 6, 795–801.
Welp, G.: 1989, 'Löslichkeit und Bioverfügbarkeit von Umwelt-Chemikalien in Böden unter-schiedlichen Stoffbestandes', Mitteilgn. Dtsch. Bodenkdl. Ges. 9, 43–52.
Welp, G.: 1999, 'Inhibitory effects of the total and water-soluble concentrations of nine different metals on the dehydrogenase activity of a loess soil', Biol. Fertil. Soils 0, 132–139.
Wong, J.W.C., Lai, K.M., Su, D.S. and Fang, M.: 2001, 'Availability of heavy metals for Brassica Chinensis growth in an acidic loamy soil amended with a domestic and an industrial sewage sludge', Water, Air Soil Pollut. 8, 339–353.
Wu, J., Jörgensen, R.G., Pommerening, B., Chaussod, R. and Brookes, P.C.: 1990, 'Measurement of soil microbial biomass Cby fumigation-extraction-an automated procedure', Soil Biol. Biochem. 2, 1167–1169.
Zeien, H. and Brümmer, G.W.: 1989, 'Chemische Extraktionen zur Bestimmung von Schwermetall-bindungsformen in Böden', Mitteilgn. Dtsch. Bodenkdl. Ges. 9, 505–510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usman, A.R.A., Kuzyakov, Y. & Stahr, K. Dynamics of Organic C Mineralization and the Mobile Fraction of Heavy Metals in a Calcareous Soil Incubated with Organic Wastes. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 158, 401–418 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000044864.07418.8f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000044864.07418.8f