Abstract
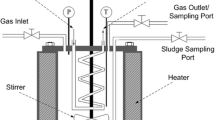
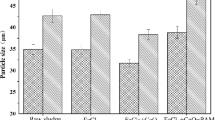
An active component of Moringa oleifera (MO) has been used in comparison with synthetic polymers and alum for the conditioning of chemical sludge from a drinking water treatment plant. The comparison was based on dewatering characteristics of the conditioned sludge determined by capillary suction time (CST), specific resistance to filtration (SRF), sand column drainage and shear strength tests. The results indicated that MO showed comparable conditioning effect as alum. Polyelectrolytes were more effective than MO and alum. Sludge conditioned with MO and alum, as in dual chemical conditioning, showed better results than MO alone. According to CST, SRF and sand drainage results, optimum doses for MO, alum and polyelectrolytes were 125, 63, and 1.8 kg/t, respectively. Comparison of the two polyelectrolytes showed that the cationic polyelectrolyte was more effective. For sand drainage tests both polyelectrolytes improved the drainage rate by 2 orders of magnitude. MO and alum improved the drainage rate by about 4.2 times. On the other hand, the improvements in cake solids concentration were similar for all the chemical conditioners. Flocs from MO and alum were relatively stronger compared to those of the polyelectrolytes. From the results of the study it could be concluded that MO alone or in combination could be effectively used and replace alum for dewatering of chemical sludge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ademiluyi, J.O.: 1988, 'Sludge conditioning with moringa seed', Environ. Int. 14(1), 59–63.
APHA, AWWA and WEF: 1995, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th edn., pp. 2–54.
AWWA Committee Report: 1978a, 'Water treatment plant sludges-an update of the state of the art: Part 1', J. AWWA 70(9), 498–503.
AWWA Committee Report: 1978b, 'Water treatment plant sludges-an update of the state of the art: Part 2', J. AWWA 70(10), 548–554.
Chang, M.C., Lin, H.L., Huang, C.L., Wang, Y.Y. and Wan, C.C.: 1998, 'Conditioning characteristics of kaolin sludge with different cationic polyelectrolytes', Colloids Surf. A: Physiochem. Eng. Aspects, 139, 75–80.
Christensen, G.L. and Stulc, D.A.: 1979, 'Chemical reactions affecting filterability in iron-lime sludge conditioning', J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 51, 2499–2512.
Dharmappa, H.B., Hasia, A. and Hagare, P.: 1997, 'Water treatment plants residuals management', Wat. Sci. Tech. 35(8), 45–66.
Eriksson, L.: 1987, 'Conditioning of biological sludges with cationic polyelectrolytes', Wat. Sci. Tech. 19, 859–868.
HDR Engineering Inc.: 2001, Handbook of Public Water Systems, 2nd edn., Wiley, New York.
Hwa, T.J. and Jeyaseelan, S.: 1997, 'Comparison of lime and alum as oily sludge conditioners', Wat. Sci. Tech. 36(12), 117–124.
Jahn, S.A.A.: 1988, 'Using Moringa oleifera seeds as coagulants in developing countries', J. AWWA 80(6), 43–50.
Kaggwa, R.C., Mulalelo, C.I., Denny, P. and Okurut, T.O.: 2001, 'The impact of alum discharges on a natural tropical wetland in Uganda', Wat. Res. 35(3), 795–807.
Knocke, W.R. and Wakeland, D.L.: 1983, 'Fundamental characteristics of water treatment sludges' J. AWWA 75(10), 516–523.
Lee, C.H. and Liu, J.C.: 2000, 'Enhanced sludge dewatering by dual polyelectrolytes conditioning', Wat. Res. 34(18), 4430–4436.
Metcalf and Eddy Inc.: (Revised by Tchobanoglous, G., Burton, F.L. and Stensel, H.D.) 2003, Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th edn., McGraw-Hill, New York, p. 850.
Ndabigengesere, A., Narasiah, K.S. and Talbot, B.G.: 1995, 'Active agents and mechanisms of coag-ulation of turbid water using Moringa oleifera', Wat. Res. 29, 703–710.
Novak, J.T. and Langford, M.: 1977, 'The use of polymers for improving chemical sludge dewatering on sand beds', J.AWWA 69(2), 106–110.
Okuda, T., Baes, A.U., Nishijima, W. and Okada, M.: 1999, 'Improvements of extraction meth-ods of coagulation active components from Moringa oleifera seed', Wat. Res. 33(15), 3373–3378.
Okuda, T., Baes, A.U., Nishijima, W. and Okada, M.: 2001, 'Coagulation mechanism of salt solution extracted active component in Moringa oleifera seed', Wat. Res. 35(3), 830–834
Olsen, A.: 1987, 'Low technology water purification by bentonite clay and Moringa oleifera seed flocculation as performed in sudanese village: Effects on Schistosoma mansoni cercariae', Wat. Res. 21(5), 517–522.
Ozacar, M. and Sengil, I.A.: 2000, 'Effectiveness of tannins obtained from valonia as a coagulant aid for dewatering of sludge', Wat. Res. 34(4), 1407–1412.
Pan, J.R., Huang, C., Chuang, Y.A. and Wu, C.C.: 1999, 'Dewatering characteristics of algae-containing alum sludge', Colloids Surf. A. 150, 185–190.
Senthilnathan, P.R. and Sigler, R.G.: 1993, 'Improved sludge dewatering by dual polymer condition-ing', Wat. Sci. Tech. 28(1), 53–57.
Suarez, M., Entenza, J.M., Doerries, C., Meyer, E., Bourquin, L., Sutherland, J., Marison, I., Moreillon, P. and Mermod, N.: 2003, 'Expression of a plant-derived peptide harboring water-cleaning and antimicrobial activities', Biotechnol. Bioeng. 81(1), 13–20.
Sutherland, J.P., Folkard, G.K. and Grant, W.D.: 1990, 'Natural coagulants for appropriate water treatment: a novel approach', Waterlines 8(4), 30–32.
The Institute of Water Pollution Control: 1981, 'Unit Processes Sewage Sludge. II: Conditioning, Dewatering and Thermal Drying', Manuals of British Practice in Water Pollution Control.
Wu, C.C., Huang, C. and Lee, D.J.: 1997, 'Effects of polymer dosage on alum sludge dewatering characteristics and physical properties', Colloidal Surf. A: Physiochem. Eng. Aspects 122, 89–96.
Wu, C.C., Lee, D.J. and Huang, C.: 2000, 'Determination of the optimal dose of polyelectrolyte sludge conditioner considering particle sedimentation effects', Adv. Environ. Res. 4, 245–249.
Zhao, Y.Q. and Bache, D.H.: 2002, 'Integrated effect of applied pressure time and polymer dose on alum sludge dewatering behaviour', Waste Manag. 22, 813–819.
Zhao, Y.Q.: 2003, 'Correlation between floc physical properties and optimum polymer dosage in alum sludge conditioning and dewatering', Chem. Eng. J. 92, 227–235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghebremichael, K.A., Hultman, B. Alum Sludge Dewatering Using Moringa oleifera as a Conditioner. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 158, 153–167 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000044852.23764.9c
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000044852.23764.9c