Abstract
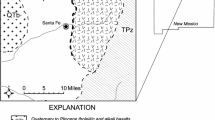
Wastewater and groundwater has been used for irrigation in the Valsequillo District, east central Mexico, for nearly 50 years. The environmental impact of wastewater on groundwater in the unconfined shallow aquifer is evaluated by means of hydrogeological, microbiological, hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidences. The shallow aquifer consists of upper Tertiary volcano-sedimentary rocks with a calcite-rich matrix. Groundwater from wells near the wastewater canal had similar total coliforms concentrations as the wastewater (∼100 MPN 100 mL-1). The hydraulic head in near-canal wells had a recovery of 10 m until 1983, indicating shallow recharge from wastewater. A bicarbonate vs. calcium plot shows a well-defined mixing process between wastewater and unaffected groundwater. Stable isotopic data (δD and δ18O) show characteristic signatures for wastewater and non-impacted groundwater, and define a mixing line between those end-members and groundwater affected by wastewater infiltration. Tritium data indicate that non-impacted groundwater is ‘pre-atomic hydrogen bomb’ (>50 yr), whereas the wastewater has a ‘younger’ signature. Tritium data from wells inside the district clearly indicate a mixing process between waste and groundwater. These results demonstrate the interaction and hydrochemical processes between wastewater and shallow groundwater at the site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boon, D. Y. and Soltanpour, P. N.: 1992, ‘Lead, cadmium and zinc contamination of aspen garden soils and vegetation’, J. Environ. Qual. 21, 82–86.
Clark, I. D. and Fritz, P.: 1997, Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp. 328.
Comisión Nacional del Agua (CNA): 1995, ‘Estudio de la Migración de Contaminantes hacia el Acuífero Regional Derivados del Riego con Aguas Residuales del Distrito de Riego de Valsequillo, Puebla’, Technical Report, Comisión Nacional del Agua, México, D.F., pp. 56.
Comisión Nacional del Agua (CNA): 1996, ‘Actualización Geohidrológica del Acuífero de Tecamachalo’, Puebla, México‘, Technical Report, Comisión Nacional del Agua, México, D.F., pp. 167.
Coleman, M. L., Sheperd, T. J., Durham, J. J., Rouse J. E. and Moore, G. R.: 1982, ’Reduction of water with zinc or hydrogen isotope analysis‘, Anal. Chem. 54, 993–995.
Contla, C. R.: 1976, ’La importancia económica de los Distritos de Riego en México, el caso del Distrito de Riego de Valsequillo, Puebla‘, B.S. Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Fac. de Economía, México, D.F., pp. 141.
Chilton, P. J., Morris, B. L. and Foster, S. S. D.: 1996, ’Impacto del reuso de las aguas residuales sobre el agua subterránea en el Valle del Mezquital, Edo de Hidalgo, México‘, in VIII Curso Internacional Los Recursos Hídricos Subterráneos y la Disposición de Aguas Residuales Urbanas. Interacciones Positivas y Negativas, 36–43, Querétaro, México, 6 March 1996, Organización Mundial de la Salud, el Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente, Organización Panamericana de la Salud, Centro Panamericano de Ingeniería Sanitaria, Overseas Development Administration, British Geological Survey (OMS-PNUMA-GEM/OPSCEPIS/ ODA-BGS), Querétaro, México.
Environment and Resources National Research Council, Academia de la Investigacion Científica and Academia Nacional de Ingeniería (ERNR, AIC and ANI): 1995, El Suministro de Agua de la Ciudad de México, National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pp. 114.
Epstein, S. and Mayeda, T. K.: 1953, ’Variation 18O/16O ratio in natural sources‘, Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 4, 213–224.
Fazeli, M. S., Sathyanarayan, S., Satish, P. N. and Muthana, L.: 1991, ’Effects of paper mill effluents on the accumulation of heavy metals in coconut trees near Nanjangud, Mysore District, Karnatake, India‘, Environ. Geol. Water S. 17, 47–50.
Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática (INEGI): 2000, Indicadores de Desarrollo Sustentable en México, www.inegi.gob.mx/, May, 2002.
Norma Oficial Mexicana (NOM): 1997, ’Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-001-ECOL-1996. Que Establece los Límites Máximos Permisibles de Contaminantes en las Descargas de Aguas Residuales en Aguas y Bienes Nacionales‘, Diario Oficial de la Federación (DOF), México, 6 January 1997, pp. 68–85.
Orta-Ledezma, M. T.: 1985, ’Criterios para el Aprovechamiento de Aguas Residuales en Riego Agrícola en México‘, M.Sc. Thesis, Fac. de Ingeniería, División de Estudios de Posgrado, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, México, D.F., pp. 112.
Programa de Desarrollo Regional Angelópolis (PRDA): 1995, ’Estudio de Factibilidad del Proyecto de Restauración de la Presa Valsequillo, Puebla‘, Technical Report, Gobierno del Estado de Puebla, Programa de Desarrollo Regional Angelópolis, Puebla, México, pp. varia.
Rao, A. V., Jain, B. L. and Gupta, I. C.: 1993, ’Impact of textile industrial effluents on agricultural land — Case study, Indian J. Environ. Health 35, 132–138.
Rodríguez-Velasco, F. M.: 1996, ‘Caracterización Fisico-Química de la PresaManuel Ávila Camacho Valsequillo y Planteamiento de una Planta para Tratamiento del Agua’, B.S. Thesis, Fac. de Ciencias Químicas, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla (BUAP), México.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1973, ‘Estudio geohidrológico de la región de Palmar de Bravo y Esperanza’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1974a, ‘Estudio Geohidrológico Preliminar de las Zonas de Tepeaca y del Distrito de Riego de Valsequillo en el Estado de Puebla, I and II’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1974b, ‘Estudio Geohidrológico de la Región de Palmar de Bravo y Esperanza, Edo. de Puebla. Segunda Etapa’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1976, ‘Estudio Geohidrológico Detallado de Zonas Secas, Valsequillo, Puebla’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1979, ‘Algunos Aspectos de la Geohidrología Isotópica de la Región de Valsequillo, Puebla’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1982a, ‘Actualización de los Valles de Palmar de Bravo y Esperanza’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F.
Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos (SARH): 1982b, ‘La Hidrología Isotópica de las Aguas Subterráneas de la Porción Central de México’, Technical Report, Secretaría de Agricultura y Recursos Hidráulicos, México, D.F., pp. 25.
Taylor, C. B.: 1977, ‘Tritium Enrichment of Environmental Waters by Electrolysis: Development of Cathodes Exhibiting High Isotopic Separation and Precise Measurement of Tritium Enrichment Factors’, Proceedings of the International Conference of Low-Radioactivity Measurements and Applications, Bratislava, Slovenski Pedagogicke Nakladatelstvo, pp. 131–125.
Tchobanoglous, G. and Burton, F. L.: 1991, Metcalf & Eddy Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal and Reuse, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, pp. 1334.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domínguez-Mariani, E., Carrillo-Chávez, A., Ortega, A. et al. Wastewater Reuse in Valsequillo Agricultural Area, Mexico: Environmental Impact on Groundwater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 155, 251–267 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000026531.37877.f8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000026531.37877.f8