Abstract
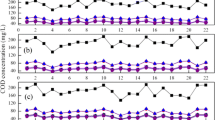
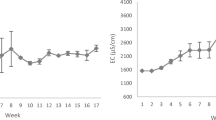
The aim of this work is optimising operating conditions for a possibleimplementation of a Biological Nutrient Removal (BNR) process in the Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) of Ciudad Real (Spain). Several factors (hydraulic retention times, anaerobic nitrate concentration, sludge age and wastewater biodegradability) were tested using a pilot scale VIP (Virginia Initiative Plant) activated sludge process and domestic wastewater from the full scale plant. Hydraulic retention times used did not cause changes in N and P removal. P removal was adversely affected by anaerobic NO3 - and improved with higher BOD5/COD ratios in wastewater. Influence of sludge age was very low in P removal, but N removal was mainly affected by this factor. Final operating conditions were selected taking into account their effects over one of both nutrients. COD and SS removal were always successful. N removal was also easily reached and the main difficulty was P removal. P sludge content was very low (2.5–4%) approximately and was also affected by the same factors tested. The main factor to improve P removal was supposed to be the organic wastewater composition. Wastewater characteristics were modified by using different sources from the WWTP. Volatile fatty acids (VFA) addition to the wastewater by using supernatant of the anaerobic sludge digesters seemed to be the best practical solution for a future BNR implementation in the WWTP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-gararah, Z. H. and Randall, C. W.: 1991, 'The effect of organics compounds on biological phosphorus removal', Water Sci. Technol. 23, 585–594.
APHA/AWWA/WEF: 1995, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed., American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environmental Federation, Washington, DC.
Austermann, U., Lange, R., Seyfried, C. F. and Rosenwinkel, K. H.: 1998, 'Upgrading anaerobic/ aerobic wastewater treatment plant', Water Sci. Technol. 37, 243–350.
Barker, P. S. and Dold, P. L.: 1997, 'General model for biological nutrient removal activated-sludge systems: Model presentation', Water Environ. Res. 69, 969–984.
Barnard, J. L.: 1974, 'Cut P and N without chemicals', Water Wastes Eng. 11, 33–36.
Barnard, J. L.: 1975, 'Nutrient removal in biological systems', J. Water Pollut. Contr. 74, 143–154.
Barnard, J. L.: 1976, 'A review of biological phosphorus removal in the activated sludge process', Water SA 2, 126–144.
Barnard, J. L.: 1983, 'Background to biological phosphorus removal', Water Sci. Technol. 15, 1–13.
Brdjanovic, D., Logemann, S., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., Hooijmans, C. M., Alaerts, G. J. and Heijnen, J. J.: 1998, 'Influence of temperature on biological phosphorus removal: Process and molecular ecological studies', Water Res. 32, 1035–1048.
Cañizares, P., Rodriguez, L., Villaseñor, J. and Rodríguez, J.: 1998, 'Effect of wastewater composition on the development of an activated sludge biological phosphorus removal system', Environ. Technol. 20, 159–169.
Cañizares, P., De Lucas, A., Rodriguez, L. and Villaseñor, J.: 2000, 'Anaerobic uptake of different organic substrates by enhanced biological phosphorus removal sludge', Environ. Technol. 21, 397–405.
Cech, J. and Hartman, P.: 1993, 'Competition between polyphosphate and polysaccharide accumulating bacteria in enhanced biological phosphate removal systems', Water Res. 27, 1219–1225.
Coen, F., Vanderhaegen, B., Boonen, I., Vanrolleghem, P. A. and van Meenen, P.: 1997, 'Improved design and control of industrial and municipal nutrient removal plants using dynamic models', Water Sci. Technol. 35, 53–61.
De Lucas Martínez, A., Cañizares, P., Rodríguez, L. and Villaseñor, J.: 2001, 'Short-term effects of wastewater biodegradability on Biological Phosphorus Removal', J. Environ. Eng. ASCE 127, 259–265.
Ekama, G. A. and Wentzel, M. C.: 1999, 'Difficulties and developments in biological nutrient removal technology and modelling', Water Sci. Technol. 39, 1–11.
Gujer, W., Henze, M., Mino, T. and van Loosdrecht, M. C. M.: 1999, 'Activated Sludge Model No. 3', Water Sci. Technol. 39, 183–193.
Henze, M., Harremoës, P., LaCour Jansen, J. and Arvin, E.: 1995, Wastewater Treatment, Biological and Chemical Processes, Springer, Heidelberg, pp. 197–198.
Henze, M., Gujer, W., Mino, T., Matsuo, T., Wentzel, M. C., Marais, G. V. R. and Van Loosdrecht, M. C. M.: 1999, 'Activated Sludge Model No. 2D', Water Sci. Technol. 39, 165–182.
Jones, M. and Stephenson, T.: 1996, 'The effects of temperature on enhanced biological phosphate removal', Environ. Technol. 17, 965–976.
Kiuru, H. J. and Rautiainen, J. A.: 1998, 'Biological nutrient removal at a very low-loaded activated sludge plant with biomass concentrations', Water Sci. Technol. 38, 63–70.
Ladiges, G., Bertram, N. P. and Otterpohl, R.: 2000, 'Concept development for the optimisation of the Hamburg Wastewater Treatment Plants', Water Sci. Technol. 41, 89–96.
Matsuo Y.: 1994, 'Effect of the anaerobic solids retention time on enhanced biological phosphorus removal', Water Sci. Technol. 30, 193–202.
McClintock, S. A., Randall, C. W. and Pattakine, V. M.: 1993, 'Effects of temperature and mean cell residence time on biological nutrient removal processes', Water Environ. Res. 65, 110–118.
Mino, T., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. and Heijnen, J. J.: 1998, 'Microbiology and biochemistry of the enhanced biological phosphate removal process', Water Res. 32, 3193–3207.
Mulkerrins, D., Jordan, C., McMahon, S. and Colleran, E.: 2000, 'Evaluation of the parameters affecting nitrogen and phosphorus removal in anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A/A/O) biological nutrient removal systems', J Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 75, 261–268.
Nicholls, H. A., Pitman, A. R. and Osborn, D. W.: 1985, 'The readily biodegradable fraction of sewage: its influence on phosphorus removal and measurement', Water Sci. Technol. 17, 73–87.
Randall, A. A., Benefield, L. D., Hill, W. E., Nicol, J. P., Boman, G. K. and Jing, S. R.: 1997, 'The effect of volatile fatty acids on enhanced biological phosphorus removal and population structure in anaerobic/aerobic sequencing batch reactors', Water Sci. Technol. 35, 153–160.
Rodrigo, M. A., Seco, A., Ferrer, J. and Penya-Roja, J. M.: 1999, 'The effect of sludge age on the deterioration of enhanced biological phosphorus removal process', Environ. Technol. 20, 1055–1063.
Satoh, H., Mino, T. and Matsuo, T.: 1994, 'Deterioration of enhanced biological phosphorus removal by the domination of microorganisms without polyphosphate accumulation', Water Sci. Technol. 30, 203–211.
Sedlak, R. I.: 1991, Phosphorous and Nitrogen Removal from Municipal Wastewater, The Soap and Detergent Association, New York, 1991.
Siegrist, H., Brack, T., Koch, A., Nussbaumer, A. and Gujer, W.: 2000, 'Optimization of nutrient removal in the WWTP Zürich-Werhölzli', Water Sci. Technol. 41, 63–71.
Smolders, G. J. F., Van der Meij, J., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. and Heijnen, J. J.: 1995, 'A structured metabolic model for the anaerobic and aerobic stoichiometry and kinetics of the biological phosphorus removal process', Biotech. Bioeng. 47, 227–287.
Solley, D. and Barr, K.: 1999, 'Optimise what you have first! Low cost upgrading of plants for improved nutrient removal', Water Sci. Technol. 39, 127–134.
STOWA: 1996, 'Methoden voor influentkarakterisering, inventarisatie en richtlijnen', Rapport Nr. 96-08 (in Dutch).
van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. and Jetten, M. S. M.: 1998, 'Microbiological conversions in nitrogen removal', Water Sci. Technol. 38, 1–7.
van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., Smolders, G. J., Kuba, Y. and Heijnen, J. J.: 1997, 'Metabolism of microorganisms responsible for enhanced biological phosphorus removal from wastewater. Use of dynamic enrichments cultures', Ant. Van Leeuwenhoek 71, 109–116.
Wentzel, M. C., Dold, P., Ekama, G. A. and Marais, G. v. R.: 1985, 'Kinetics of biological phosphorus release', Water Sci. Technol. 17, 51–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez Mayor, L., Villaseñor Camacho, J. & Fernández Morales, F.J. Operational Optimisation of Pilot Scale Biological Nutrient Removal at the Ciudad Real (Spain) Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 152, 279–296 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015366.39480.b1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015366.39480.b1