Abstract
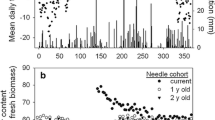
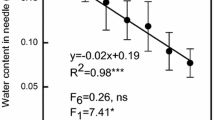
Japanese fir (Abies firma) forests on the urban-facing side ofMt. Oyama, eastern Japan are frequently exposed to acidic depositions. These forests have been declining more severely than those on the mountain-facing side. Chlorophyll, N, Mg, K, Ca, P and Al contents were determined for current, one- and two-year-old needles collected from the crown surfaces of Japanese fir tree forming the forest canopy (ca. 30 m height) on both sides of Mt. Oyama. Needle dry mass per needle area on the urban-facing side was significantly smaller than that on the mountain-facing sides for each needle age class. This result suggests that the development of internal tissues of fir needles on the urban-facing side is defective. N and Chl contents per needle area on the urban-facing side were smaller than those on the mountain-facing sides, indicating that photosynthetic activity per needle area is suppressed in the needles from the urban-facing side. For each needle age class, both area- and mass-based Mg contents were smaller on the urban-facing side than on the mountain-facing side, but mass-based Al contents were greater on the urban-facing side. These results suggest that acidic depositions cause nutritional disorders, which, in turn, leads to decreased needle productivity in the fir trees on the urban-facing side.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boudot, J. P., Becquer, T., Merlet, D. and Rouiller, J.: 1994, 'Aluminium toxicity in declining forests: A general overview with a seasonal assessment in a silver fir forest in the Vosges Mountains (France)', Ann. Sci. For. 51, 27–51.
Bussotti, F., Borghini, F., Celesti, C., Leonzio, C. and Bruschi, P.: 2000, 'Leaf morphology and macronutrients in broadleaved trees in Central Italy', Trees 14, 361–368.
Cronan, C. S. and Grigal, D. F.: 1995, 'Use of calcium/aluminium ratios as indicators of stress in forest ecosystems', J. Environ. Qual. 24, 209—226.
De Wit, H. A., Mulder, J., Nygaard, P. H. and Aamlid, D.: 2001, 'Testing the aluminium toxicity hypothesis: A field manipulation experiment in mature spruce forest in Norway', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 130, 995–1000.
Ende, H.-P. and Evers, F. H.: 1997, 'Visual Magnesium Deficiency Symptoms (Coniferous, Deciduous Trees) and Threshold Values (Foliar, Soil)', in R. F. Hüttl and W. Schaaf (eds), Magnesium Deficiency in Forest Ecosystems, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 3–21.
Evans, J. R.: 1989, 'Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants', Oecologia 78, 9–19.
Evans, J. R.: 1998, 'Photosynthetic Characteristics of Fast-and Slow-Growing Species', in H. Lambers, H. Poorter and M. M. I. V. Vuuren (eds), Inherent Variation in Plant Growth, Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands, pp. 101–119.
Hoshi, N., Yamamoto, E., Yoshikawa, K., Kawamura, M., Mochida, K. and Tohyama, M.: 1997, 'Present Situation of Natural Forest and its Conservation', in Environment Abteilung of Kanagawa Prefecture (ed.), Comprehensive Research Report of Natural Environment in Tanzawa-Oyama Mountains, Environment Abteilung of Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, pp. 175– 257 (in Japanese).
Hosono, T., Okochi, H. and Igawa, M.: 1994, 'Fogwater chemistry at a mountainside in Japan', Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 67, 368–374.
Igawa, M., Kameda, H., Maruyama, F., Okochi, H. and Otsuka, I.: 1997, 'Effect of simulated acid fog on needles of fir seedlings', Environ. Exp. Bot. 38, 155–163.
Igawa, M., Kase, T., Satake, K. and Okochi, H.: 2002a, 'Severe leaching of calcium ions from fir needles caused by acid fog', Environ. Pollut. 119, 357–382.
Igawa, M., Matsumura, K. and Okochi, H.: 2002b, 'High frequency and large deposition of acid fog on high elevation forest', Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 1–6.
Igawa, M., Tsutsumi, Y., Mori, T. and Okochi, H.: 1998, 'Fogwater chemistry at a mountainside forest and the estimation of the air pollutant deposition via fog droplets based on the atmospheric quality at the mountain base', Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 1566–1572.
Izuta, T., Ohtani, T., Yokoyama, M., Horie, K. and Totsuka, T.: 1993, 'Effects of simulated acid rain on the growth of fir seedlings', J. Japan Soc. Air Pollut. 28, 29–37 (in Japanese with English summary).
Kanagawa Prefecture: 1994, Report of Research and Investigation on Acid Rain, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, pp. 286 (in Japanese).
Laing, W., Greer, D., Sun, O., Beets, P., Lowe, A. and Payn, T.: 2000, 'Physiological impacts of Mg deficiency in Pinus radiata: Growth and photosynthesis', New Phytol. 146, 47–57.
Landmann, G.: 1995, 'Forest Decline and Air Pollution Effects in the French Mountains: A Synthesis', in G. Landmann and M. Bonneau (eds), Forest Decline and Atmospheric Deposition Effects in the French Mountains, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp. 407–452.
Lee, C. H., Izuta, T., Aoki, M. and Totsuka, T.: 1997, 'Growth and element content of red pine seedlings grown in brown forest soil acidified by adding H2SO4 solution', J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 32, 46–57 (in Japanese with English summary).
Likens, G. E., Driscoll, C. T. and Buso, D. C.: 1996, 'Long-term effects of acid rain: Response and recovery of a forest ecosystem', Science 272, 244—246.
Marschner, H.: 1995, Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, Academic Press, London, pp. 674.
Mehne-Jakobs, B.: 1996, 'Magnesium deficiency treatment causes reductions in photosynthesis of well-nourished Norway spruce', Trees 10, 293–300.
Mori, T., Okochi, H. and Igawa, M.: 1997, 'An episode of pH 1.95 acid fog containing high concentration of HCl in Mt. Oyama, Tanzawa Mountains', J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 32, 157–161 (in Japanese with English summary).
Okochi, H. and Igawa, M.: 2000, 'Chemical Characteristics of Surface Soil and Soil Water in Mt. Oyama during Observational Summer Campaign 1998', in Reports of Japanese Fir Decline and Air Pollution in Tanzawa-Oyama Mountains, Japan Science and Technology Corporation, Japan, pp. 66–76 (in Japanese).
Okochi, H., Hosono, T., Maruyama, F. and Igawa, M.: 1995, 'Interaction between acid deposition and the canopy of the Japanese cedar and fir in Mt. Oyama', Environ. Sci. 8, 305–315 (in Japanese with English summary).
Oleksyn, J., Zytkowiak, R., Reich, P. B., Tjoelker, M. G. and Karolewski, P.: 2000, 'Ontogenetic patterns of leaf CO2 exchange, morphology and chemistry in Betula pendura trees', Trees 14, 271–281.
Oren, R., Werk, K. S., Schulze, E.-D., Meyer, J., Schneider, B. U. and Schramel, P.: 1988, 'Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. VI. Nutrient concentration', Oecologia 77, 151–162.
Parker, G. G.: 1990, 'Evaluation of Dry Deposition, Pollutant Damage, and Forest Health with Throughfall Studies', in A. A. Lucier and S. G. Haines (eds), Mechanisms of Forest Response to Acidic Deposition, Springer-Verlag, New York, U.S.A., pp. 10–63.
Porra, R. J., Thompson, W. A. and Kriedemann, P. E.: 1989, 'Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: Verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy', Biochim. Biophys. Acta 975, 384–394.
Reich, P. B., Olekysn, J. and Tjoelker, M. G.: 1994, 'Relationship of aluminium and calcium to net CO2 exchange among diverse Scots pine provenances under pollution stress in Poland', Oecologia 97, 82–92.
Richter, D. D. and Markewitz, D.: 1996, 'Atmospheric Deposition and Soil Resources of the Southern Pine Forest', in S. Fox and R. A. Mickler (eds), Impact of Air Pollutants on Southern Pine Forests, Springer-Verlag, New York, U.S.A., pp. 315–336.
Sakata, M. and Suzuki, K.: 2000, 'Evaluating possible causes for the decline of Japanese fir (Abies firma) forests based on ? 13C records of annual growth rings', Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 373–376.
Schaberg, P. G., Dehayes, D. H., Hawley, G. J., Strimbeck, G. R., Cumming, J. R., Murakami, P. F. and Borer, C. H.: 2000, 'Acid mist and soil Ca and Al alter the mineral nutrition and physiology of red spruce', Tree physiol. 20, 73–85.
Tadaki, Y.: 1971, Mori no Seitai, Kyoritsu Shuppan, Tokyo, pp. 190 (in Japanese).
Takeuchi, M., Okouchi, H. and Igawa, M.: 2000, 'A study on chemical components and acidification mechanism of dew-water', J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 35, 158–169.
Thomas, P.: 2000, Trees: Their Natural History, Cambridge University, U.K., pp. 286.
Turner, D. P. and Tingey, D. T.: 1990, 'Foliar leaching and root uptake of Ca, Mg and K in relation to acid fog effects on Douglas-fir', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 49, 205–214.
Witkowski, E. T. F. and Lamont, B. B.: 1991, 'Leaf specific mass confounds leaf density and thickness', Oecologia 88, 486–493.
Wolt, J. D.: 1990, 'Bioavailability of Aluminium and Manganese', in A. A. Lucier and S. G. Haines (eds), Mechanisms of Forest Response to Acidic Deposition, Springer-Verlag, New York, U.S.A., pp. 62–107.
Wyttenbach, A., Schleppi, P., Tobler, L., Bajo, S. and Bucher, J.: 1995, 'Concentrations of nutritional and trace elements in needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst.) as functions of the needle age class', Plant Soil 168–169, 305–312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakatani, N., Kume, A., Kobayashi, T. et al. Needle Morphology Related to Chemical Contents in the Needles of Japanese Fir (Abies Firma) Trees Subjected to Acidic Depositions at Mt. Oyama, Eastern Japan. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 152, 97–110 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015343.24509.19
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015343.24509.19