Abstract
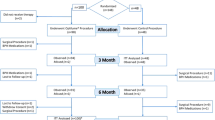
Introduction and objectives: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a progressive condition that is characterized by an increased risk of acute urinary retention and BPH — related surgery. This study evaluates the safety and efficacy of doxazosin over 10 years in men with BPH. Material and methods: The trial enrolled men (aged 49–83 years — mean 64.0) with symptomatic BPH (clinical stage II according to Alken) and no evidence of prostate cancer. The trial involved a 1.5 year controlled efficacy study with doxazosin (4 mg/day) 64 ambulatory patients with BPH, followed by a 5-year extension. During the study after 1 year 11 pts discontinued it (expense given as reason) and 6 pts underwent surgery. Then 47 pts (100%) receiving doxazosin continued therapy. After 5 years 32 pts (60%) aged 54–92 years — mean 69.4 years continued to be followed for further 5 years, giving a total follow-up of 10 years (next 8 pts underwent surgery; total 14 (26%) pts; and 14 (26%) pts died. Results: Twenty (38%) of the 47 pts (100%) enrolled into doxazosin were judged as being successfully treated during the 10-year follow-up. In further 5 years only 2 pts underwent surgery and 7 pts (13%) died for reasons unrelated to doxazosin treatment. Three pts after 6 years therapy left study. Excluding 14 pts who died plus 14 pts who left the trial it means that after 10 years 20 pts remained successfully treated and 16 pts who had to be surgically treated. Assuming that all group make 36 pts (100%) than long term follow-up showed effective results in doxazosin treated 20 pts (56%) and thus can obviate surgery. Adverse events associated with doxazosin therapy were insignificant. 10 years therapy proved effective in increasing urina flow rates and decreasing residual urine volume— respectively 14.6 ml/s and 57.0 ml (mean value). Conclusions: 1. Long-term 10 years doxazosin (4 mg/daily) therapy has demonstrated that appropriately selected BPH patients are likely to have an excellent response. 2. The a/m trial indicates that surgery can be obviated in up to half of BPH treated patients. 3. The results of the trial demonstrate that doxazosin is safe, efficacious and well-tolerated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobsen SJ, Jacobsen DJ, Girman CJ, Roberts R, Rhoodes T, Lieber MN. Natural history of prostatism: risk factors acute urinary retention. J Urol 1997; 158: 481–487.
Dutkiewicz S. Health of Man. Urinary and Sexual Tract. Warsaw: Amedic, 2002.
Macfarlane GJ, Sagnier PP, Richard F, Teillac P, Botto H, Boyle P. Determinants of treatment — seeking behaviour for urinary symptoms in older men. Br J Urol 1995; 76: 714–718.
Donovan JL, Kay HE, Peters TJ, Abrams P, Coust J, Matos-Ferriera A, Retzhog L, Bosch JLHR, Nordling J, Gajewski JB, Barbalias G, Schick E, Mendes Silva M, Nisselcorn I, de la Rosette JJMCH. ICS-BPH Study Group: Using the ICSQoL to measure the impact of lower urinary tract symptoms on quality of life: Evidence from the ICS-BPH study. Br J Urol 1997; 80: 712–721.
Seagroatt V. Mortality after prostatectomy: Selection and surgical approach. Lancet 1995; 346: 1521–1524.
Neal DE. The national prostatectomy audit. Br J Urol 1997; 79(suppl. 2): 69–75.
Dutkiewicz S. Efficacy and tolerability of drugs for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int Urol Nephrol 2001; 32: 423–432.
Dutkiewicz S, Witeska A. Doxazosin — an alpha 1 receptor blocking agent in the long-term management of BPH (part one). Int Urol Nephrol 1995; 27(3): 311–318.
Dutkiewicz S, Witeska A, Steepień K. Doxazosin — an alpha 1 receptor blocking agent in the long-term management of BPH (part two). Int Urol Nephrol 1995; 27(4): 413–417.
Dutkiewicz S. A comparative study of long-term alpha 1-blocker Doxazosin in therapy versus surgery in the treatment of BPH. Mat Med Pol 1995; 27(4): 151–152.
Dutkiewicz S. Comparative tolerability of alpha-blockers in the treatment of BPH (including own experience). Mat Med Pol 1998; 31(3–4): 11–19.
Dutkiewicz S. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Warsaw: Polish Scientific Publishers PWN, 1994.
Cockett ATK, Khoury S, Aso Y, Chatelain C, Denis L, Griffiths K, Murphy G (ed.). Proceeding 3 — The 3rd International Consultation on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). June 26–28, 1995, Monaco: Scientific Communication International Ltd, 1996.
Lepor H, Kaplan SA, Klimberg I, Mobley DF, Fawzy A, Gaffney M, Ice K, Dias N. For the Multicenter Study Group: Doxazosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia: Longterm efficacy and safety in hypertensive and normotensive patients. J Urol 1997; 157: 525–530.
Mobley DF, Dias N, Levenstein M. Effects of doxazosin in patients with mild, intermediate and severe benign prostatic hyperplasie. Clin T-her 1998; 20: 101–109.
Mobley DF, Kaplan S, Ice K, Gaffney M., Dias N. Effects of doxazosin on the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Results from three double blind placebo — control-led studies. Int J Clin Pract 1997; 51: 282–288.
Andersen M, Dahlstrand Ch, Hoye K. Double-blind trial of the efficacy and tolerability of doxazosin in the gastrointestinal therapeutic system, doxazosin standard, and placebo in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasie. Eur Urol 2000; 38: 400–409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutkiewicz, S. Long-term treatment with doxazosin in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: 10-year follow-up. Int Urol Nephrol 36, 169–173 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000034688.65087.18
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000034688.65087.18