Abstract
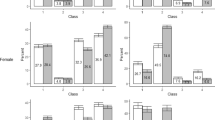
Background: Erectile dysfunction is a common sexual function disorder in men. The aim of the present study was to determine the rates of erectile dysfunction and requests for treatment in male patients refered to our outpatient urology clinics and those accompanying them who were older than 20 years. Methods: The study comprised 2 groups: group 1 included male patients older than 20 years whom attend to the outpatient urology clinics, and group 2 included their companies whom were older than 20 years. Subjects were asked whether they had erectile dysfunction or not, if so whether they had been treated or not, if not then why, and whether they desired treatment or not at present. Results: Erectile dysfunction was determined in 224 subjects (13.9%) in group 1, and 57 (8.5%) in group 2. It was found that approximately one half (49.1%) of patients with erectile dysfunction did not complaint about this. The main reasons for this were failure to perceive sexual dysfunction as a problem, and shame. Of 281 men who determined to have erectile dysfunction, 71 indicated that they desired treatment. In those who did not desire treatment, the main reasons were failure to perceive it as a problem, and shame. Conclusions: These findings show that the doctor has a great responsibility in determining erectile dysfunction. Therefore discussions of sexual health should be made a routine part of doctor-patient discussions, and patients, especially those over 50, should be asked whether they have a complaint of erectile dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH consensus development panel on impotence. JAMA 1993; 270: 83–90.
Kinsley AC, Pomeroy WB, Martin CE. Age and sexual outlet. In: Kinsley AC, Pomeroy WB, Martin CE, eds. Sexual Behavior in the Human Male. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1948: 218–262.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG et al. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 15: 54–61.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G et al. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997; 49: 822–830.
Hattat H, Ergen A, Anafarta K et al. Erektil Disfonksiyon Egitmen Kitapçıgı. İstanbul: Pfizer yayİnlarİ. 1998: 4–5 (Turkish).
Akkuş E, Kadıoğlu A, Esen A et al. Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction in Turkey: a population-based study. Eur Urol 2002; 41: 298–304.
Dunn KM, Croft PR, Hackett GI. Sexual problems: a study of the prevalence and need for health care in the general population. Fam Pract 1998; 15: 519–524.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuru, A.F., Şahin, H., Akay, A.F. et al. Erectile dysfunction rates and requests for treatment in patients attending outpatient urology clinics and those accompanying them. Int Urol Nephrol 36, 223–226 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000034671.66707.fa
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000034671.66707.fa