Abstract
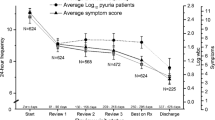
Objectives: A recent study has demonstrated that the electric activity of the overactive bladder (OAB) is `dysrhythmic'. The cause was attributed to a disordered vesical pacemaker which discharges these waves. In a subsequent study, the dysrhythmic waves have been `normalized' by vesical pacing and the optimal parameters which are required to achieve normalization have been defined. We investigated the hypothesis that vesical pacing of the OAB might improve not only the vesical electric activity but also the symptoms. Methods: Vesical pacing was used in 9 patients (age 39.2 ± 10.3; 5 women, 4 men) with OAB. Under anesthesia, the pacemaker was implanted in an inguinal subcutaneous pocket and connected to 2 pacing electrodes implanted into the vesical vault. The normalization of the waves was tested by 2 recording electrodes which were temporarily applied to the vesical wall and removed post-testing. The pacemaker was then programmed for home pacing to be activated at given times. Results: Vesical pacing effected normalization of the dysrhythmic electric waves with disappearance of the OAB symptoms in 7 patients and failed in 2. Vesical pacing was abandoned in 3/7 patients after a few months following the spontaneous disappearance of the symptoms. Conclusions: Vesical pacing has normalized the dysrhythmic electric activity and suppressed the symptoms of the OAB in 77.7% of patients. The pacemaker was removed in 5 patients: 2 failures and 3 after spontaneous waves normalization. No complications were encountered. Vesical pacing is suggested as a treatment for OAB when commonly used therapeutic modalities have failed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lenderking WR, Nakley JF, Anderson RB et al. A review of the quality of life aspects of urinary urge incontinence. Pharmacoeconomics 1996; 9: 11–23.
Kobelt G, Kirchberger I, Malone-Lee J. Quality of life aspects of the overactive bladder and the effect of treatment with tolterodine (review). Br J Urol 1999; 83: 583–598.
Mills IW, Greenland JE, McMurray G et al. Studies of the pathophysiology of idiopathic detrusor instability: the physiological properties of the detrusor smooth musce and its pattern of innervations. J Urol 2000; 163: 646–651.
Brading AF. A myogenic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology (Suppl 6A) 1997; 50: 57–67.
Brading AF, Turner WH. The unstable bladder: towards a common mechanism. Br J Urol 1994; 73: 3–8.
Shafik A. Study of the electromechanical activity of the urinary bladder. Experimental study. World J Urol 1994; 12: 316–318.
Shafik A. Electrovesicography in interstitial cystitis. Urol Int 1995; 54: 66–69.
Shafik A. Electrovesicogram in the neurogenic bladder. J Invest Surg 1996; 9: 481–486.
Shafik A. Electrovesicography in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Arch Androl 1994; 33: 201–207.
Shafik A. Electrovesicogram in stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogyn J 1996; 7: 203–207
Thuneberg L. Interstitial cells of Cajal: intestinal pacemaker cells? Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 1982; 71: pp1–130.
Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ, Liu H et al. Interstitial cells of Cajal in human colon and in Hirschsprung's disease. Gastroenterology 1996; 111: 901–910.
Ward SM, Sanders KM. Physiology and pathophysiology of the interstitial cells of Cajal: from bench to bedside. I. Functional development and plasticity of interstitial cells of Cajal networks. Am J Physiol 2001; 281: 602–611.
Wester T, Eriksson L, Olsson Y et al. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the human fetal small bowel as shown by c-kit immunohistochemistry. Gut 1999; 44: 65–71.
Liu LWC, Thuneberg L, Huizinga JD. Selective lesioning of interstitial cells of Cajal by methylene blue and light leads to loss of slow waves. Am J Physiol 1983; 266: 485–496.
Durdle NG, Kingma YJ, Bowes KL et al. Origin of slow waves in the canine colon. Gastroenterology 1983; 84: 375–382.
Daniel EE, Thomas J, Ramnarain M et al. Do gap junctions couple interstitial cells of Cajal pacing and neurotransmission to gastrointestinal smooth muscle? Neurogastroenterol Motil 2001; 13: 297–307.
Liu LWC, Huizinga JD. Electrical coupling of circular muscle to longitudinal muscle and interstitial cells of Cajal in canine colon. J Physiol (Lond) 1993; 470: 445–461.
Aube AC, Cherbut C, Barbier M et al. Altered myoelectrical activity in noninflamed ileum of rats with colitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid. Neurogastroenterol Motil 1999; 11: 55–62.
Abo M, Kono T, Lu CL et al. Effects of caffeine on gastrointestinal myoelectric activity and colonic spike activity in dogs. Scand J Gastroenterol 2000; 33: 368–374.
McClosky KD, Gurney AM. Kit positive cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol 2002; 168: 832–836.
Shafik A, El-Sibai O, Shafik AA et al. Electrovesicogram in the overactive bladder. Role in pathogenesis and diagnostic significance. Urol Res (in press).
Payne CK. Behavioral therapy for overactive bladder. Urology 2000; 55: 3–6.
Bo K, Berghmans LCM. Non-pharmacologic treatments for overactive bladder-Pelvic floor exercises. Urology 2000; 55: 7–11.
Primus G, Kramer G. Maximal external electrical stimulation for treatment of neurogenic or non-neurogenic urgency and/or urge incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 1996; 15: 187–194.
Cardozo LD. Biofeedback in overactive bladder. Urology 2000; 55: 24–28.
Yarker Y, Goa KL, Fitton A. Oxybutynin: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and its therapeutic use in detrusor instability. Drugs Aging 1995; 6: 243–262.
Madersbacher H, Jilg G. Control of detrusor hypereflexia by intravesical instillation of oxybutynin hydrochloride. Paraplegia 1991; 29: 84–90.
Torrens M, Hald T. Bladder denervation procedures. Urol Clin North Am 1979; 6: 283–293.
Shaker H, Hassouna M. Sacral nerve root neuromodulation: an effective treatment for refractory urge incontinence. J Urol 1998; 159: 1516–1519.
Shafik A, El Sibai O, Shafik AA et al. Vecical pacing: pacing parameters required for normalization of vesical electic activity in patients with overactive bladder. Front Biosci 2004; 9: 995–999.
Shafik A. A study on the continent mechanism of the external urethral sphincter with identification of the ‘voluntary urinary inhibition reflex’. J. Urol 1999; 162: 1967–1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafik, A., Shafik, I., El-Sibai, O. et al. Vesical pacing in patients with overactive bladder: Technique and results. Int Urol Nephrol 36, 29–34 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000032674.57294.16
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:UROL.0000032674.57294.16