Abstract
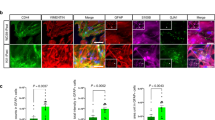
It has been demonstrated that GSK3β is involved in Alzheimer Disease (AD) pathogenesis. In order to understand the underlying mechanism, we have generated and characterized transgenic mice in which the constitutively active human GSK3β(with S9A mutation) was overexpressed in the brain under the control of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) B-chain promoter. Varying levels of human GSK3βS9A transgene protein expression was observed in six of the seven founders generated. Line 3083, 3107, 3112 and 3125 displayed higher GSK3βS9A protein expression levels. Immunostaining analysis demonstrated that transgene expression was observed mainly in cortex and hippocampus of transgenic brain. Expression of human GSK3β transgene did not significantly change the brain total GSK3β protein levels in any of the generated mouse lines, as comparing to age matched wild type mice. Although significant kinase activity was detected in human GSK3βS9A transgene protein extracted from brains of all six expressing lines, significant increase in total GSK3βS9A kinase activity was observed only in the offspring of line 3083 and 3107. By analyzing the offspring from several transgenic mouse lines, including lines other than 3083 and 3107, it was found that overexpressed constitutively active human GSK3βS9A resulted in hyperphosphorylation of tau and morphology reminiscent of pretangle-like neurons in cortex and hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed NN, Franke TF, Bellacosa A, Datta K, Gonzalez-Portal ME and Taguchi T et al. (1993) The proteins encoded by c-akt and v-akt differ in post-translational modification, subcellular localization and oncogenic potential. Oncogene 8: 1957–1963.
Ali A, Hoeflich KP and Woodgett JR (2001) Glycogen synthase kinase-3: properties, functions, and regulation. Chem Rev 101: 2527–2540.
Andra K, Abramowski D, Duke M, Probst A, Wiederhold KH and Burki K et al. (1996) Expression of APP in transgenic mice: a comparison of neuron-specific promoters. Neurobiol Aging 17: 183–190.
Baum L, Hansen L, Masliah E and Saitoh T (1996) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 alteration in Alzheimer disease is related to neurofibrillary tangle formation. Mol Chem Neuropathol 29: 253–261.
Bhat RV and Budd SL (2002) GSK3beta signalling: casting a wide net in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosignals 11: 251–261.
Brinster RL, Allen JM, Behringer RR, Gelinas RE and Palmiter RD (1988) Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 836–840.
Brownlees J, Irving NG, Brion JP, Gibb BJ, Wagner U and Woodgett J et al. (1997) Tau phosphorylation in transgenic mice expressing glycogen synthase kinase-3beta transgenes. Neuroreport 8: 3251–3255.
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M and Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378: 785–789.
Cross DA, Culbert AA, Chalmers KA, Facci L, Skaper SD and Reith AD (2001) Selective small-molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity protect primary neurones from death. J Neurochem 77: 94–102.
Ferreira A, Lu Q, Orecchio L and Kosik KS (1997) Selective phosphorylation of adult tau isoforms in mature hippocampal neurons exposed to fibrillar A beta. Mol Cell Neurosci 9: 220–234.
Frame S and Cohen P (2001) GSK3 takes centre stage more than 20 years after its discovery. Biochem J 359: 1–16.
Games D, Adams D, Alessandrini R, Barbour R, Berthelette P and Blackwell C et al. (1995) Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic mice overexpressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature 373: 523–527.
Georgopoulos S, McKee A, Kan HY and Zannis VI (2002) Generation and characterization of two transgenic mouse lines expressing human ApoE2 in neurons and glial cells. Biochemistry 41: 9293–9301.
Gotz J, Chen F, Barmettler R and Nitsch RM (2001) Tau filament formation in transgenic mice expressing P301L tau. J Biol Chem 276: 529–534.
Hetman M, Cavanaugh JE, Kimelman D and Xia Z (2000) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in neuronal apoptosis induced by trophic withdrawal. J Neurosci 20: 2567–2574.
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O and Woodgett JR (2000) Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature 406: 86–90.
Hong M, Chen DC, Klein PS and Lee VM (1997) Lithium reduces tau phosphorylation by inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Biol Chem 272: 25326–25332.
Hoshi M, Sato M, Matsumoto S, Noguchi A, Yasutake K and Yoshida N et al (2003) Spherical aggregates of beta-amyloid (amylospheroid) show high neurotoxicity and activate tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 6370–6375. Epub 2003 May 6315.
Imahori K and Uchida T (1997) Physiology and pathology of tau protein kinases in relation to Alzheimer’s disease. J Biochem (Tokyo) 121: 179–188.
Ishiguro K, Shiratsuchi A, Sato S, Omori A, Arioka M and Kobayashi S et al. (1993) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta is identical to tau protein kinase I generating several epitopes of paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett 325: 167–172.
Kaytor MD and Orr HT (2002) The GSK3 beta signaling cascade and neurodegenerative disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12: 275–278.
Lee KY, Clark AW, Rosales JL, Chapman K, Fung T and Johnston RN (1999) Elevated neuronal Cdc2-like kinase activity in the Alzheimer disease brain. Neurosci Res 34: 21–29.
Li B, Greenberg N, Stephens LC, Meyn R, Medina D and Rosen JM (1994) Preferential overexpression of a 172Arg-> Leu mutant p53 in the mammary gland of transgenic mice results in altered lobuloalveolar development. Cell Growth Differ 5: 711–721.
Li B, Murphy KL, Laucirica R, Kittrell F, Medina D and Rosen JM (1998) A transgenic mouse model for mammary carcinogenesis. Oncogene 16: 997–1007.
Lovestone S, Reynolds CH, Latimer D, Davis DR, Anderton BH and Gallo JM et al. (1994) Alzheimer’s disease-like phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau by glycogen synthase kinase-3 in transfected mammalian cells. Curr Biol 4: 1077–1086.
Lucas JJ, Hernandez F, Gomez-Ramos P, Moran MA, Hen R and Avila J (2001) Decreased nuclear beta-catenin, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration in GSK-3beta conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J 20: 27–39.
Moechars D, Dewachter I, Lorent K, Reverse D, Baekelandt V and Naidu A et al. (1999) Early phenotypic changes in transgenic mice that overexpress different mutants of amyloid precursor protein in brain. J Biol Chem 274: 6483–6492.
Munoz-Montano JR, Moreno FJ, Avila J and Diaz-Nido J (1997) Lithium inhibits Alzheimer’s disease-like tau protein phosphorylation in neurons. FEBS Lett 411: 183–188.
Pap M and Cooper GM (1998) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J Biol Chem 273: 19929–19932.
Pei JJ, Braak E, Braak H, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K and Winblad B et al. (1999) Distribution of active glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK-3beta) in brains staged for Alzheimer disease neurofibrillary changes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58: 1010–1019.
Rockenstein E, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Song D, Shults CW and Lang I et al. (2002) Differential neuropathological alterations in transgenic mice expressing alpha-synuclein from the platelet-derived growth factor and Thy-1 promoters. J Neurosci Res 68: 568–578.
Russ C, Lovestone S and Powell JF (2001) Identification of sequence variants and analysis of the role of the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta gene and promoter in late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 6: 320–324.
Saito Y, Vandenheede JR and Cohen P (1994) The mechanism by which epidermal growth factor inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3 in A431 cells. Biochem J 303: 27–31.
Sasahara M, Fries JW, Raines EW, Gown AM, Westrum LE and Frosch Mp et al. (1991) PDGF B-chain in neurons of the central nervous system, posterior pituitary, and in a transgenic model. Cell 64: 217–227.
Spittaels K, Van den Haute C, Van Dorpe J, Terwel D, Vandezande K and Lasrado R et al. (2002) Neonatal neuronal overexpression of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta reduces brain size in transgenic mice. Neuroscience 113: 797–808.
Sturchler-Pierrat C, Abramowski D, Duke M, Wiederhold KH, Mistl C and Rothacher S et al. (1997) Two amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse models with Alzheimer disease-like pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 13287–13292.
Sun A, Liu M, Nguyen XV and Bing G (2003) P38 MAP kinase is activated at early stages in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Exp Neurol 183: 394–405.
Sutherland C, Leighton IA and Cohen P (1993) Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by phosphorylation: new kinase connections in insulin and growth-factor signalling. Biochem J 296: 15–19.
Takashima A, Noguchi K, Michel G, Mercken M, Hoshi M and Ishiguro K et al. (1996) Exposure of rat hippocampal neurons to amyloid beta peptide (25-35) induces the inactivation of phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase and the activation of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. Neurosci Lett 203: 33–36.
Takashima A, Honda T, Yasutake K, Michel G, Murayama O and Murayama M et al. (1998) Activation of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta by amyloid beta peptide (25-35) enhances phosphorylation of tau in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Res 31: 317–323.
Van Dorpe J, Smeijers L, Dewachter I, Nuyens D, Spittaels K and Van Den Haute C et al. (2000) Prominent cerebral amyloid angiopathy in transgenic mice overexpressing the london mutant of human APP in neurons. Am J Pathol 157: 1283–1298.
Wang QM, Roach PJ and Fiol CJ (1994) Use of a synthetic peptide as a selective substrate for glycogen synthase kinase 3. Anal Biochem 220: 397–402.
Woodgett JR (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J 9: 2431–2438.
Woodgett JR (1991) cDNA cloning and properties of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Methods Enzymol 200: 564–577.
Zhu X, Sun Z, Lee HG, Siedlak SL, Perry G and Smith MA (2003) Distribution, levels, and activation of MEK1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 86: 136–142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Ryder, J., Su, Y. et al. Overexpression of GSK3βS9A Resulted in Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Morphology Reminiscent of Pretangle-Like Neurons in the Brain of PDGSK3β Transgenic Mice. Transgenic Res 13, 385–396 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRAG.0000040039.44899.6f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRAG.0000040039.44899.6f