Abstract
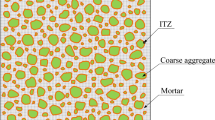
The determination of the chloride diffusion coefficient of a concrete is needed to help the prediction of the service life of concrete structure. In this paper, we propose first a critical review of models for chloride diffusion coefficients already used in literature at different scales and then we develop an analytical model, which takes into account the characteristics of the different phases of concrete. These materials are treated as a three-phase composite, consisting of a cement continuous phase, of an aggregates dispersed phase and of an interface transition zone. Chloride diffusion coefficient using an n-layered inclusion-based micromechanical modeling is predicted. The details of calculations are summarized hereafter and experimental measurements obtained on mortars are compared with predicted results.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Atkinson, A. and Nickerson, A. K.: 1984, The diffusion of ions through water-saturated cement, J. Mater. Sci. 19, 3068–3078.
Bentur, A. and Alexander, M. G.: 2000, A review of the work of the Rilem TC 159-ETC, Engineering of the interfacial transition zone in cementitious composites, Mater. Struct. 33, 82–87.
Bruggeman, D. A.: 1935, Ann. Phys. 24, 636.
Caré, S.: 2003, Influence of aggregates on chloride diffusion coefficient into mortar, Cem. Concr. Res. 33, 1021–1028.
Christensen, R. M.: 1979, Mechanics of Composite Materials, Wiley Interscience, New York.
Daian, J. F.: 2001, Evaluation des propriétés de transfert dans les matériaux cimentaires. Etude critique des modèles, Revue Française de Génie Civil, 5(2-3), 179–202.
Delagrave, A., Bigas, J. P., Ollivier, J. P., Marchand, J. and Pigeon, M.: 1997, Influence of the interfacial zone on the chloride diffusivity of mortars, Adv. Cem. Bas. Mat. 5, 86–92.
Dormieux, L. and Lemarchand, E.: 2000, Modélisation macroscopique du transport diffusif, apport des méthodes de changement d'espace, Oil Gas Sci. Technol. - Rev. IFP 55(1), 15–34.
François, R., Francy, O., Caré, S., Baroghel Bouny, V., Lovera, P. and Richet, C.: 2001, Mesure du coefficient de diffusion des ions chlorures: comparaison régime permanent-régime transitoire, Revue Française de Génie Civil 5(2-3), 309–329.
Francy, O. and François, R.: 1998, Measuring chloride diffusion coefficients from non-steady from non-steady state diffusion tests, Cem. Concr. Res. 28, 947–953.
Garboczi, E. J.: 1990, Permeability, diffusivity and microstructural parameters: a critical review, Cem. Concr. Res. 20, 591–601.
Garboczi, E. J. and Bentz, D. P.: 1996, The effect of the interfacial transition zone on concrete properties: the dilute limit, American Society of Civil Engineers, in: Proceedings of the Fourth Materials Conference, November 1996, Washington, DC.
Garboczi, E. J. and Bentz, D. P.: 1997, Analytical formulas for interfacial transition zone properties, Adv. Cem. Bas. Mat. 6, 99–108.
Garboczi, E. J. and Bentz, D. P.: 1998, Multiscale analytical/numerical theory of the diffusivity of concrete, Advn. Cem. Bas. Mat. 8, 77–88.
Hashin, Z. and Shrikman, S.: 1963, A varationnal approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multi-phases materials, J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 11, 127–140.
Hervé, E.: 2002, Thermal and thermoelastic behaviour of multiply coated inclusion-reinforced composites, Int. J. Solids Struct. 39, 1041–1058.
Hervé, E. and Zaoui, A.: 1993, N-layered inclusion-based micromechanical modelling, Int. Eng. Sci. 31(1), 1–10.
Hervé, E. and Zaoui, A.: 1995, Elastic behaviour of multiply coated fibre-reinforced composites, Int. Eng. Sci. 33(10), 1419–1433.
Hobbs, D. W.: 1999, Aggregate influence on chloride ion diffusion into concrete, Cem. Concr. Res. 29, 1995–1998.
Jaiswal, S. S., Picka, J., Igusa, T., Ankenman, B., Karr, A. and Shah, S. P.: 1998, Impact of the interfacial transition zone on the chloride permeability of concrete, in: Proceedings of the 12th ASCE Congress, San Diego, May 17-20, 1998.
McLAchlan, D. S., Blaszkiewicz, M. and Newhham, R. E.: 1990, Electrical resistivity of composites, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 2187–2203.
Van Brakel, J. and Heetjes, P. M.: 1974, Analysis of diffusion in macroporous media in terms of a porosity, a tortuosity and a constrictivity factor, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 17, 1093–1103.
Xi, Y. and Bazant, Z. P.: 1999, Modeling chloride penetration in saturated concrete, J. Mater. Civil Eng., 58–65.
Xu, K., Daian, J. F. and Quénard, D.: 1997, Multiscale structures to describe porous media. Part II. Transport properties and application to test materials, Transport in Porous Media 26, 319–338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caré, S., Hervé, E. Application of a n-Phase Model to the Diffusion Coefficient of Chloride in Mortar. Transport in Porous Media 56, 119–135 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TIPM.0000021730.34756.40
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TIPM.0000021730.34756.40