Abstract
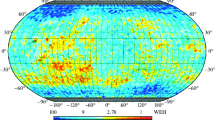
We report results of the analysis of the data on global mapping of neutron fluxes from the Martian surface, which have been obtained during the first ten months of measurements carried out by the Russian high-energy neutron detector HEND mounted aboard the AmericanMars Odysseyorbiter. This analysis allowed us to separate regions where free water (in ice form) prevailed in the surface layer (with a thickness of up to 2 m) of the Martian ground from regions where physically and chemically bound ground water was most likely to be the dominant form of water. The global mapping of regions with increased ice content in the ground-surface layer revealed a direct correlation with regions of polygonal terrains morphologically similar to terrestrial polygonal forms of permafrost origin. The potential content of bound water forms in the ground of circumpolar areas of the planet is also estimated.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Banin, A., Clark, B.C., and Wanke, H., Surface Chemistry and Mineralogy, inMars, Kieffer, H.H.,et al., Eds., Tucson: Univ. of Arizona Press, 1992, pp. 594-625.
Boynton, W.V., Feldman, W.C., Squyres, S.W.,et al., Distribution of Hydrogen in the Near-Surface of Mars: Evidence for Subsurface Ice Deposits,Science, 2002, vol. 297, pp. 81-87.
Christensen, P.R., Bandfield, J.L., Hamilton, V.E.,et al.,Mars Global SurveyorThermal Emission Spectrometer Experiment: Investigation Description and Surface Science Results,J. Geophys. Res., 2001, vol. 106, pp. 23823-23871.
Clark, B.C. and Van Hart, D.C., The Salts of Mars,Icarus, 1981, vol. 45, pp. 370-378.
Clifford, S.M. and Hillel, D., The Stability of Ground Ice in the Equatorial Regions of Mars,J. Geophys. Res., 1983, vol. 88, pp. 2456-2474.
Clifford, S.V., Bartels, C.J., and Rubenstein, E.F., The Mars Thermal Model (MARSTHERM): A FORTRAN 77 Finite-Difference Program Designed for General Distribution, Houston: LPI, 1987.
Fanale, F.P., Martian Volatiles: Their Degassing History and Geochemical Fate,Icarus, 1976, vol. 28, pp. 179-202.
Fanale, F.P., The Water and Other Volatiles of Mars,Sci. Technol. Ser Am. Astronautical Soc. Publ., 1986, vol. 71, pp. 157-174.
Farmer, C.B. and Doms, P.E., Global and Seasonal Water Vapor on Mars and Implications for Permafrost,J. Geophys. Res., 1979, vol. 84, pp. 2881-2888.
Feldman, W.C., Boynton, W.V., and Drake, D.M., Planetary Neutron Spectroscopy from Orbit, inRemote Geochemical Analysis: Elemental and Mineralogical Composition, Piters, C.M. and Englert, A.J., Eds., Cambridge, Cambridge Univ. Press, 1993, pp. 213-234.
Feldman, W.C., Boynton, W.V., Tokar, R.L.,et al., Global Distribution of Neutrons from Mars: Results fromMars Odyssey,Science, 2002, vol. 297, pp. 75-78.
Greeley, R. and Guest, J.E., Geologic Map of the Eastern Equatorial Region of Mars,US Geologic Survey, Misc. Inv. Map I-802-B, 1987.
Kuzmin, R.O., On the Structure of the Martian Cryolithosphere, inProblemy kriolitologii(Problems of Cryolithology), iss. 6, Moscow: Izd. MGU, 1977, pp. 7-23.
Kuzmin, R.O.,Kriolitosfera Marsa(Martian Cryolithosphere), Moscow: Nauka, 1983.
Kuzmin, R.O., Bobina, N.N., Zabalueva, E.V., and Shashkina, V.P., Structural Inhomogeneities of the Martian Cryolithosphere,Astron. Vestn., 1988, vol. 22,no. 3, pp. 195-212.
Kuzmin, R.O., Komarov, I.A., Isaev, V.S.,et al., The Comparative Morphometric Analysis of Polygonal Terrains on Mars and the Earth High Latitude Areas,Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXXII, 2002, Abstract # 2030.
Kuzmin, R.O., Specific Character of the Superficial Layer of the Martian Cryolithosphere,Workshop HEND, 2002 May 20–22 (www.iki.rssi.ru/eng/hendws.htm).
Kuzmin, R.O., Mitrofanov, I.G., Litvak, M.L.,et al., Mars: Detaching of the Free Water Signature (FTS) Presence Regions on the Base of HEND/OdysseyData and Their Correlation with Some Permafrost Features from MOC Data,Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXXIV, 2003, Abstract # 1369.
Kuzmin, R.O. and Zabalueva, E.V., Polygonal Terrains on Mars: Preliminary Results of Global Mapping of Their Spatial Distribution,Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXXIV, 2003, Abstract # 1912.
Leighton, R.B. and Murray, B.C., Behavior of Carbon Dioxide and Other Volatiles on Mars,Science, 1966, vol. 153, pp. 136-144.
Litvak, M.L., Mitrofanov, I.G., Kozyrev, A.S.,et al., Seasonal Variations of Subsurface Hydrogen as Seen by High Energy Neutron Detector,Mars Odyssey, 36th Brown Vernadsky Microsymposium, 2002.
McSween, H.Y., Murchie, S.L., Crisp, J.A.,et al., Chemical, Multispectral, and Textural Constraints on the Composition and Origin of Rocks at theMars PathfinderLanding Site,J. Geophys. Res., 1999, vol. 104, pp. 8679-8716.
Mellon, M.T. and Jakosky, B.M., The Distribution and Behavior of Martian Ground Ice during Past and Present Epochs,J. Geophys. Res., 1995, vol. 100, pp. 11781-11800.
Mellon, M.T., Kretke, K.A., Smith, M.D.,et al., A Global Map of Thermal Inertia fromMars Global SurveyorMapping-Mission Data,Lunar Planet Sci. Conf. XXXIII, 2002, Abstract # 1416.
Mitrofanov, I.G., Anfimov, D., Kozyrev, A.,et al., Maps of Subsurface Hydrogen from the High Energy Neutron Detector, Mars,Science,2002, vol. 297, pp. 78-81.
Pollack, J.B., Roush, T., Witteborn, F.,et al., Thermal Emission Spectra of Mars (5.4–10.5 μ),J. Geophys. Res., 1990, vol. 95, pp. 14595-14627.
Reider, R., Economov, T., Wanke, H.,et al., The Chemical Composition of Martian Soil and Rocks Returned by the Mobile X-Ray Mode,Science, 1997, vol. 278, pp. 1771-1774.
Romanovskii, N.N.,Formirovanie poligonal'no-zhil'nykh struktur(Formation of Polygonal-veined Structures), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1977.
Scott, D. and Tanaka, K., Geologic Map of the Western Equatorial Region of Mars,US Geological Survey, Misc. Inv. Map I-802-A, 1986.
Seibert, N.M. and Kargel, J.S., Small-Scale Martian Polygonal Terrain: Implications for Liquid Surface Water,Geophys. Res. Lett., 2001, vol. 28,no. 5, pp. 899-902.
Smith, D.E., Zuber, M.T., Frey, H.,et al., The Global Topography of Mars and Implication for Surface Evolution,Science, 1999, vol. 284, pp. 1495-1503.
Smith, D.E., Zuber, M.T., and Neumann, G.A., Seasonal Variations of Snow Depth on Mars,Science, 2001, vol. 294, pp. 2141-2146.
Soderblom, L., The Composition and Mineralogy of the Martian Surface from Spectroscopic Observations: 0.3 μ–50 μ, inMars, Kieffer, H.H.,et al., Eds., Tucson: Univ. of Arizona Press, 1992, pp. 557-593.
Surkov, Yu.A., Shcheglov, O.P., Ryvkin, M.L., and Vinogradova, O.A., Neutron Spectrometry, inRemote Geochemical Analysis: Elemental and Mineralogical Composition, Piters, C.M. and Englert, A.J., Eds., Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1998, pp. 427-442.
Yoshikawa, K., Contraction Cracking and Ice Wedge Polygons in Mars,Second Mars Polar Sci. Conf., 2000, Abstract # 4045.
Zolotov, M.Yu., Water-bearing Minerals in the Martian Soil (Thermodynamic Prediction of Stability),Lunar Planet, Sci. Conf. XX, 1989, pp. 1257-1258.
Zolotov, M.Yu., Zabalueva, E.V., and Kuzmin, R.O., Stability of Hydrated Salts and Goethite within the Desiccated Upper Layer of the Martian Regolith,Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXVIII, 1997, pp. 1633-1634.
Zurek, R.W., Barnes, J.B., Haberle, R.M.,et al., Dynamics of the Atmosphere of Mars, inMars, Kieffer, H.H.,et al., Eds., Tucson: Univ. of Arizona Press, 1992, pp. 835-933.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzmin, R.O., Zabalueva, E.V., Mitrofanov, I.G. et al. Regions of Potential Existence of Free Water (Ice) in the Near-Surface Martian Ground: Results from theMars OdysseyHigh-Energy Neutron Detector (HEND). Solar System Research 38, 1–11 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SOLS.0000015150.61420.5b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SOLS.0000015150.61420.5b