Abstract
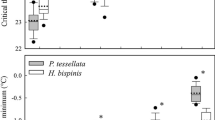
Salinity tolerance in some marine teleost fishes was studied. Based on a comparison of sexually mature specimens in the summer season, the investigated species can be arranged in the order of decreasing capability for hyperosmoregulation into the following series: the Far Eastern dace Trybolodon brandti, the haarder Mugil soiuy > the frog sculpin Myoxocephalus stelleri > the snowy sculpin M. brandti > the plain sculpin M. jaok > the masked greenling Hexagrammos octogrammus > the pipefish Syngnathus acusimilis. The adult Far Eastern dace and the haarder showed high salinity tolerance and fully adapted to fresh water. Sculpins and the masked greenling usually occur only in seas or brackish water, but they were capable of enduring fresh water for a long time. Unlike them, the pipefish, which is also a euryhaline fish and occurs in river estuaries and brackish bays, perished in fresh water within 1 h. Representatives of the genus Myoxocephalus show between-species differences in salinity tolerance, which allows them to colonize extensive near-shore areas of the sea and to occupy specific ecological niches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boikov, P.Ya., Maksimovich, A.A., Natochin, Yu.V., et al. Osmolality and Electrolytes of Blood Serum of Spawning Pink Salmon Oncorhynchus gorbuscha during Transition from the Sea to the River and Reverse Transfer to the Sea, Vopr. Ikhtiol. 1988, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 367-472.
Zaprudnova, P.A. and Martemyanov, V.I., Seasonal Variations in Cation Concentration in the Blood Plasma of Freshwater Fishes, Vopr. Ikhtiol. 1988, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 671-676.
Martemyanov, V.I., Stress as a Source of Errors in Ecologo-Physiological and Biochemical Studies of Fishes, Otsenka pogreshnostei metodov gidrobiologicheskikh i ikhtiologicheskikh issledovanii (Estimation of Errors of Hydrobiolgical and Ichthyological Research Methods), Rybinsk, 1982, pp. 124-134.
Martemyanov, V.I., Regulation Ranges of Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium Concentration in Plasma, Erythrocytes and Muscle Tissue of Rutilus rutilus in Nature, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol. 2001, vol. 37, no. 2, pp.107- 111.
Novikov, N.P., Sokolovsky, A.S., Sokolovskaya, T.G., and Yakovlev, Yu.M., Ryby Primorya (Fishes of Primorye), Vladivostok: Dalpress, 2002.
Serkov, V.M., Determination of the Physiological Status of Smoltifying Salmon, Biol. Morya 1996, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 311-314.
Serkov, V.M. and Kornienko, M.S., Dynamics of Sodium and Calcium Ion Concentration in Blood of Hexagrammos octogrammus Pallas (Scorpaeniformes, Hexagrammidae) at Changing Ambient Salinity, Vopr. Ikhtiol. 2003, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 134-136.
Brusle, J., Sexuality and Biology of Reproduction in Grey Mullets, Aquaculture of Grey Mullet Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1981, pp. 99-154.
De Silva, S.S., Biology of Juvenile Grey Mullet: A Short Review, Aquaculture, 1980, vol. 19, pp. 21-36.
Iwata, M., Hirano, T., and Hasegawa, S., Behavior and Plasma Sodium Regulation of Chum Salmon Fry during Transition into Seawater, Aquaculture, 1982, vol. 28, pp. 133-142.
Jonassen, T.M., Pittman, K., and Imsland, A.K., Seawater Acclimation of Tilapia, Oreochromis spilurus spilurus Gunter, Fry and Fingerlings, Aquaculture, 1997, vol. 28, pp. 205-214.
Kutty, M.N., Energy Metabolism of Mullets, Aquaculture of Grey Mullet, Cambridge, U. K.: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1981, pp. 219-264.
Swanson, C., Reid, T., Young, P.S., and Cech, J.J.Jr., Comparative Environmental Tolerances of Threatened Delta Smelt (Hypomesus transpacificus) and Introduced Wakasagi (H. nipponensis) in an Altered California Estuary, Oecologia, 2000, vol. 123, pp. 384-390.
Thomson, J.M., The Grey Mullets, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev., 1966, vol. 4, pp. 301-335.
Whitfield, A.K., A Review of Factors Influencing Fish Utilization of South African Estuaries, Trans. Roy. Soc. S. Afr., 1996, vol. 51, pp. 115-138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serkov, V.M. Salinity Tolerance of Some Teleost Fishes of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Russian Journal of Marine Biology 29, 368–371 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUMB.0000011704.84991.fc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUMB.0000011704.84991.fc