Abstract
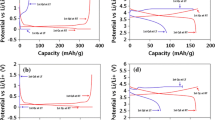
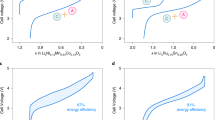
Effect of temperature on reversible and irreversible processes during lithium intercalation in graphite from 1 M LiClO4 solution in PC–DME is studied by galvanostatic cycling, cyclic voltammetry, and impedance spectroscopy. Reducing temperature diminishes both reversible and irreversible capacities. Conditions for the passive-film formation on graphite are discussed. If several first cycles are run at a negative temperature, the overall charge spent irreversibly decreases if the temperature is then elevated. The lower the initial-cycling temperature, the smaller the overall irreversible capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tarascon, J.M. and Guyomard, D., Electrochim. Acta, 1993, vol. 39, p. 1221.
Brandt, K., J. Power Sources, 1995, vol. 54, p. 151.
Megahed, S. and Ebner, W., J. Power Sources, 1995, vol. 54, p. 155.
Peled, E., Menachem, C., Bar-Tow, D., and Melman, A., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, vol. 143, p. 4.
Menachem, C., Peled, E., Burstein, L., and Rosenberg, Y., J. Power Sources, 1997, vol. 68, p. 227.
Ein-Eli, Y. and Koch, V., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, vol. 144, p. 2968.
Prem, K.T., Manuel, S.A., Thayananth, P., Subramanian, V., Gopukumar, S., Renganathan, N.G., Raghavan, M., and Muniyandi, N., J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 97-98, p. 118.
Kulova, T.L., Kanevskii, L.S., Skundin, A.M., Asryan, A.N., Bondarenko, G.N., and Sklovskii, D.E., Elektrokhimiya, 2001, vol. 37, p. 1179.
Wang, H. and Yoshio, M., J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 101, p. 35.
Buqa, H., Golob, P., Winter, M., and Besenhard, J.O., J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 97-98, p. 122.
Buqa, H., Grogger, Ch., Alvarez Santis, M.V., Besenhard, J.O., and Winter, M., J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 97-98, p. 126.
Shiao, H.-C., Chua, D., Lin, H.-P., Slane, S., and Salomon, M., J. Power Sources, 2000, vol. 87, p. 167.
Plichta, E.J. and Behl, W.K., J. Power Sources, 2000, vol. 88, p. 192.
Huang, C.-K., Sakamoto, J.S., Wolfenstine, J., and Surampudi, S., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2000, vol. 147, p. 2893.
Wang, C., Appleby, A.J., and Little, F.E., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2002, vol. 149, p. 754.
Herreyre, S., Huchet, O., Barusseau, S., Perton, F., Bodet, J.M., and Biensan, P., J. Power Sources, 2001, vol. 97-98, p. 576.
Zhang, S.S., Jow, T.R., Amine, K., and Henriksen, G.L., J. Power Sources, 2002, vol. 107, p. 18.
Katayama, N., Kawamura, T., Baba, Y., and Yamaki, J.-I., J. Power Sources, 2002, vol. 109, p. 321.
Zhang, S.S., Xu, K., Allen, J.L., and Jow, T.R., J. Power Sources, 2002, vol. 110, p. 216.
Fan, J., J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 117, p. 170.
Blomgren, G.E., J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 119-121, p. 326.
Vetter, J. and Novak, P., J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 119-121, p. 338.
Jow, T.R., Ding, M.S., Xu, K., Zhang, S.S., Allen, J.L., Amine, K., and Henriksen, G.L., J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 119-121, p. 343.
Smart, M.C., Ratnakumar, B.V., Whitcanack, L.D., Chin, K.B., Surampudi, S., Croft, H., Tice, D., and Staniewicz, R., J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 119-121, p. 349.
Levi, M.D., Wang, C., Gnanaraj, J.S., and Aurbach, D., J. Power Sources, 2003, vol. 119-121, p. 538.
Khimicheskaya entsiklopediya (Encyclopedia of Chemistry), Moscow: Bol'shaya Rossiiskaya Entsiklopediya, 1995, vol. 4.
Kedrinskii, I.A., Dmitrienko, V.E., Povarov, Yu.M., and Grudyanov, I.I., Khimicheskie istochniki toka s litievym elektrodom (Chemical Power Sources with Lithium Electrodes), Krasnoyarsk: Krasnoyarsk. Gos. Univ., 1983.
Characterization of Solutes in Nonaqueous Solvents, Mamantov, G., Ed., New York: Plenum, 1978.
Bagotzky, V.S. and Skundin, A.M., Khimicheskie istoch-niki toka (Chemical Power Sources), Moscow: Energiya, 1981.
Karapetyan, Yu.A. and Eichis, V.N., Fiziko-khimicheskie svoistva elektrolitnykh nevodnykh rastvorov (Physicochemical Properties of Nonaqueous Electrolytes), Moscow: Khimiya, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulova, T.L. Effect of Temperature on Reversible and Irreversible Processes during Lithium Intercalation in Graphite. Russian Journal of Electrochemistry 40, 1052–1059 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUEL.0000046490.73990.c3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUEL.0000046490.73990.c3