Abstract
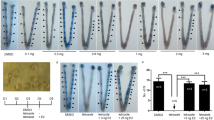
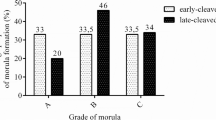
Nitric oxide is an important intraovarian regulatory factor. The periimplantation period is a critical phase in mouse development. Although it was shown that nitric oxide plays an essential role during gestation, its role in the preimplantation period is not yet fully clear. We studied the involvement of nitric oxide in developmental competence (embryonic defects and morphology of pre- and postimplantation embryos) using nitric oxide synthase inhibitors, which suppress all forms of nitric oxide synthase, and female mice, to which the inhibitors had been administered before their mating with intact males. The level of mortality of pre- and postimplantation embryos in females mated to intact males increased soon after the administration of inhibitors. Studies of the morphology of embryos have shown that there was a delay in embryogenesis at the stages of cleavage and gastrulation. The results obtained suggest that nitric oxide is a potent regulator of embryonic differentiation, specifically in pre- and postimplantation mouse embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Albertini, D., Cytoplasmic Reorganization during the Resumption of Meiosis in Cultured Preovulatory Rat Oocytes, Devel. Biol., 1987, vol. 120, pp. 121–131.
Albertini, D., Cytoplasmic Microtubular Dynamics and Chromatin Organization during Mammalian Oogenesis and Oocyte Maturation, Mutat. Res., 1992, vol. 296, pp. 57–68.
Araki, K., Naito, K., Haraguchi, S., et al., Meiotic Abnor-malities of c-mos Knockout Mouse Oocytes: Activation after First Meiosis or Entrance into Third Meiotic Metaphase, Biol. Reprod., 1996, vol. 55, pp. 1315–1324.
Blashkiv, V.T., Korniichuk, A.N., Voznesenskaya, T.Yu., and Portnichenko, A.G., Role of Nitric Oxide in Oocyte Ovula-tion and Meiotic Maturation and Implantation in Mice, Byull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 2001, vol. 132, no. 11, pp. 494–496.
Chen, H., Jiang, W., and Tzeng, C., Nitric Oxide as a Regu-lator in Preimplantation Embryo Development and Apopto-sis, Fertil. Steril., 2001, vol. 75, no. 6, pp. 1163–1171.
Gouge, R., Marshburn, P., Gordon, B., et al., Nitric Oxide as a Regulator of Embryonic Development, Biol. Reprod., 1998, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 875–879.
Lebedev, S.G., Estimation of Viability of Horse Embryos during Transplantations, Nauch. Tr. VNIIK "Biologicheskie Osnovy Tekhnologii Konevodstva" (Proceedings of Research Institute of Horse Breeding "Biological Foundations of Technology of Horse Breeding"), 1990, pp. 307–321.
Longo, F. and Chen, D., Development of Cortical Polarity in Mouse Egg: Involvement of the Meiotic Apparatus, Devel. Biol., 1985, vol. 107, pp. 382–394.
Mank, A., Biologiya razvitiya mlekopitayushchikh. Metody (Biology of Mammalian Development. Methods), Moscow: Mir, 1990.
Nakamura, Y., Kashida, Sh., Nakata, M., et al., Changes in Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity in the Ovary of Gonadotropin Treated Rats: The Role of Nitric Oxide during Ovulation, Endocrin. J., 1999, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 529–538.
Nishikimi, A., Matsukawa, T., Hoshino, K., et al., Localiza-tion of Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity in Unfertilized Oocytes and Fertilized Embryos during Preimplantation Development in Mice, Reproduction, 2001, vol. 122, no. 6, pp. 957–963.
Purcell, T., Given, R., Chwalisz, K., and Garfield, R., Nitric Oxide Synthase Distribution during Implantation in the Mouse, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 1999, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 467–475.
Sanotskii, I.V., Metody eksperimental'nogo issledovaniya po ustanovleniyu porogov deistviya promyshlennykh yadov na generativnuyu funktsiyu s tsel'yu gigienicheskogo normiro-vaniya (Experimental Methods for Determination of Thresh-old of the Effect of Industrial Poisons on Generative Func-tion with the Aim of Hygienic Standardization), Moscow: NII gigieny truda i profzabolevanii AMN SSSR, 1978.
Saxena, D., Purohit, S., Kumer, G., and Laloraya, M., Increased Appearance of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Uterus and Embryo at Implantation, Nitric Oxide, 2000, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 384–391.
Van Voorhis, B., Moore, K., Strijbos, P., et al., Expression and Localization of Inducible and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Rat Ovary, J. Clin. Invest., 1995, vol. 96, pp.2719–2726.
Zackrisson, U., Mikuni, M., Wallin, A., et al., Cell-Specific Localization of Nitric Oxide Synthases (NOS) in the Rat Ovary during Follicular Development, Ovulation and Luteal Formation, Hum. Reprod., 1996, vol. 11, pp. 2667–2673.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blashkiv, T.V., Voznesenskaya, T.Y. Influence of Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors on Embryo Destruction and Morphological Features in Pre- and Postimplantation Mouse Embryos. Russian Journal of Developmental Biology 35, 279–282 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUDO.0000043820.20030.f3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUDO.0000043820.20030.f3