Abstract
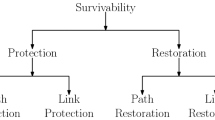
A major challenge in next generation Internet (NGI) backbone networks based on dense-wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is the provision of guaranteed quality-of-service (QoS) for a wide variety of multimedia applications. This paper proposes a new routing algorithm called multi-wavelength minimum interference path routing (MW-MIPR) to provide more reliable QoS guarantees by consideration of the potential future network's congestion status. This improves wavelength utilization by choosing a route that does not interfere too much with potential future connection requests. Moreover, we introduce a differentiated routing and wavelength assignment (RWA) mechanism combined with recovery strategy and the proposed MW-MIPR algorithm based on the differentiated service model in the NGI. Simulation results show that the proposed MW-MIPR algorithm achieves a smaller blocking probability than dynamic routing (DR) that yields the best performance among previous RWA algorithms. And we prove that a differentiated RWA combined with a recovery capability together with the proposed routing scheme provides satisfied QoS assurance for each service class in terms of signal quality and survivability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Mukherjee, Optical Communication Networks (McGraw-Hill Publishers, 1997).
R. Ramaswami, Optical NetworksA Practical Perspective (Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1998).
T. E. Stern, K. Bala, ultiwavelength Optical Networks: A Layered Approach (Addison Wesley Publishers, 1999).
I Chlamtac, A. Ganz, G. Karmi, Lightpath communications an approach to high-bandwidth optical WANs, IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 40, no. 7, (July 1992), pp. 1171–1182.
J. S. Choi, N. Goirnie, F. Lapeyrere, F. Mouveaux, D. Su, Classification of routing and wavelength assignment schemes in DWDM networks. Proceedings of OPNET 2000 (Paris, France, Jan. 2000), pp. 1109–1115.
H. Zang, J. P. Jue, B. Mukherjee, A review of routing and wavelength assignment approaches for wavelength routed optical WDM networks. Optical Networks Magazine, vol. 1, no. 1, (Jan. 2000), pp. 47–60.
S. Ramamurthy, B. Mukherjee, Fixed-alternate routing and wavelength conversion in wavelength-routed optical net-works, Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM 1998, vol. 4, (Sydney, Australia, Nov. 1998), pp. 2295–2302.
J. S. Kirn, D. C. Lee, Dynamic routing and wavelength assignment algorithms for multifiber WDM networks with many wavelengths. Proceedings of ECUMN 2002 (Coirnar, France, April 2002), pp. 180–186.
L. Li, A. K. Somani, Dynamic wavelength routing using congestion and neighborhood information, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, vol. 7, no. 5, (Oct. 1999), pp. 779–786.
S. Xu, L. Li, S. Wang, Dynamic routing and assignment of wavelength algorithms in multifiber wavelength division multiplexing networks, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 18, no. 10, (Oct. 2000), pp. 2130–2137.
S. Chen, K. Nahrstedt, An overview of quality of service routing for next-generation high-speed networks: Problems and solutions, IEEE Network, vol. 12, no. 6, (Nov./Dec. 1998), pp. 64–79.
C. B. Ahmed, N. Boudriga, M. S. Obaidat, QoS routing with wavelength conversion and call admission connection in DWDM networks. Proceedings of IEEE ICCNMC 2001 (Beijing, China, Oct. 2001), pp. 61–66.
K. Kar, M. Kodialarn, T. V. Lakshman, Minimum interference routing of bandwidth guaranteed tunnels with MPLS traffic engineering applications, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 18, no. 12, (Dec. 2000), pp. 2566–2579.
K. Kar, M. Kodialam, T. V. Lakshman, MPLS traffic engineering using enhanced minimum interference routing: An approach based on lexicographic max-flow. Proceedings of IEEE IWQOS 2000 (Karlsruhe, Germany, June, 2000), pp. 105–114.
D. Bauer, Minimum-interference routing based on flow maximization. Electronics Letters, vol. 38, no. 8, (April 2002), pp. 364–365.
S. Suri, M. Waldvogel, P. R. Warkhede, Profile-Based Routing: A New Framework for MPLS Traffic Engineering, Washington University Computer Science Technical Report WUCS-OO-21, (July 2000).
R. K. Ahuja, T. L. Magnanti, J. B. Orlin, Network Flows: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications (Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice-Hall, 1993).
M. Frey, T. Ndousse, Wavelength conversion and call connection probability in WDM networks, IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 49, no. 10, (Oct. 2001), pp. 1780–1787.
J. Fang, R. Srinivasan, A. K. Somani, Performance analysis of WDM optical networks with wavelength usage constraint, Photonic Network Communications, vol. 5, no. 2, (March 2003), pp. 137–146.
M. Ma, M. Harndi, Providing deterministic quality-of-service guarantees on WDM optical networks, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 18, no. 10, (Dec. 2000), pp. 2072–2083.
S. Blake, D. Black, M. Carlson, E. Davies, Z. Wang, W. Weiss, An Architecture for Differentiated Services, RFC 2475, IETF, (December 1998).
J. Strand, A. L. Chiu, R. Tkach, Issues for routing in the optical layer, IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 39, no. 2, (Feb. 2001), pp. 81–87.
P. S. Andre, J. 0. L. Pinto, A. L. J. Teixeira, J. F. da Rocha, T. Almeida, M. Pousa, Optical-signal-quality monitor for bit-error-ratio assessment in transparent DWDM networks based on asynchronously sampled amplitude histogram. Journal of Optical Networking, vol. 1, no. 3, (March 2002), pp. 118–127.
C. P. Larsen, P. 0. Andersson, Signal quality monitoring in optical networks. Optical Networks Magazine, vol. 1, no. 4, (Oct. 2000), pp. 17–23.
WorldCom's White Contribution COM-D.126: Proposed Optical Performance Monitoring Parameters for OTN, ITU-T SG 15 Contribution, (Oct. 2001).
Alcatel's White Contribution COM 15-33-E: Electrical (BER, Q-factor, el. SNR) and Optical (OSNR, OCR) System Performance Parameters for G.DSN, ITU-T SG 15 Contribution, (December 2000).
D. Zhou, S. Subramaniam, Survivability in optical networks, IEEE Network, vol. 14, no. 6, (Nov./Dec. 2000), pp. 16–23.
Lucent's White Contribution COM-15-39-E: L-and C-band Attenuation in Installed fiber Links, ITU-T SG 15 Contribution, (Aug. 2001).
KDDI's White Contribution D.97 (WP4/15): Recent Technical Information on C-and L-band in Optical Transmission Systems, ITU-T SG15 Contribution, (Feb. 2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, JG., Jung, JI., Park, YJ. et al. A RWA Algorithm for Differentiated Services with QoS Guarantees in the Next Generation Internet based on DWDM Networks. Photonic Network Communications 8, 319–334 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PNET.0000041241.80847.37
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PNET.0000041241.80847.37