Abstract
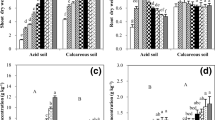
A glasshouse study was conducted to investigate the effect of supplying phytate and FePO4 and interspecific root interactions on the uptake of Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn and Zn by plants in a mixed culture of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). The pots were separated into two compartments by (i) a solid root barrier to eliminate root contact and solute movement, or (ii) a nylon mesh (30 μm) to prevent root contact but permit solute exchange, or (iii) were not separated into compartments. Wheat plants were grown in one compartment and chickpea in the other. Two P sources, sodium phytate and FePO4, were tested at 60 μg P g−1 soil. Compared to supplying phytate, supplying FePO4 increased concentrations and contents of Ca, Mg, Mn and Zn in wheat and chickpea, and of Fe in chickpea only. When supplied with phytate, intermingling of root systems of the two species increased the content of Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn and Zn in wheat, but reduced the content of Ca, Mg, Fe and Zn in chickpea. When supplied with FePO4, root intermingling enhanced the content of Ca, Fe and Zn in wheat, but did not affect the content of Ca, Fe and Zn in chickpea. It is concluded that interspecific root interactions and the form of P supply affect the content of Ca, Fe and Zn in both species. Possible mechanisms involved are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ae N, Arihara J, Okada K, Yoshihara T and Johansen C 1990 Phosphorus uptake by pigeon pea and its role in cropping systems of the Indian subcontinent. Science 248, 477–480.
Alloush G A Z, Zeto S K and Clark R B 2000 Phosphorus source, organic matter, and arbuscular mycorrhiza effects on growth and mineral acquisition of chickpea grown in acidic soil. J. Plant Nutr. 23, 1351–1369.
Dalal R C 1977 Soil organic phosphorus. Adv. Agron. 29, 83–117.
Gardner W K and Boundy K A 1983 The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albusL. IV. The effect of interplanting wheat and white lupin on the growth and mineral composition of the two species. Plant Soil 70, 391–402.
Grierson P F and Adams M A 2000 Plant species affect acid phosphatase, ergosterol and microbial P in a Jarrah (Eucalyptus marginataDonn ex Sm.) forest in South-western Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 1817–1827.
Handreck K A 1991 Interactions between iron and phosphorus in the nutrition of Banksia ericifoliaL.f. var. ericifolia(Proteaceae) in soil-less potting media. Aust. J. Bot. 39, 373–384.
Hauggaard-Nielsen H, Ambus P and Jensen E S 2001Interspecific competition, N use and interference with weeds in pea-barley intercropping. Field Crops Res. 70, 101–109.
Hopkins B G, Jolley V D and Brown J C 1992 Plant utilization of iron solubilized by oat phytosiderophore. J Plant Nutr. 15, 1612–1620.
Horst W J and Waschkies C 1987 Phosphorus nutrition of spring wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) in mixed culture with white lupin (Lupinus albusL.). Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 150, 1–8.
Jensen E S 1996 Barley uptake of deposited in the rhizosphere of associated field pea. Soil Biol. Biochem. 28, 159–162.
Johnson C M and Ulrich A 1959 Analytical methods for use in plant analysis. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stat. Bull. No. 766.
Kamal K, Hagagg L and Awad F 2000 Improved Fe and Zn acquisition by guava seedlings grown in calcareous soils intercropped with graminaceous species. J. Plant Nutr. 23, 2071–2080.
Karpenstein-Machan M and Stuelpnagel R 2000 Biomass yield and nitrogen fixation of legumes monocropped and intercropped with rye and rotation effects on a subsequent maize crop. Plant Soil 218, 215–232.
Lambers H, Juniper D, Cawthray G R, Veneklaass E J and Martinez-Ferri 2002 The pattern of carboxylate exudation in Banksia grandis(Proteaceae) is affected by the form of phosphate added to the soil. Plant Soil 238, 111–122.
Li L, Sun J H, Zhang F S, Li X L, Yang S C and Rengel Z 2001 Wheat/maize or wheat/soybean strip intercropping. I. Yield advantage and interspecific interactions on nutrients. Field Crops Res 71, 123–137.
Li L, Tang C, Rengel Z and Zhang F S 2003a Chickpea facilitates phosphorus uptake by wheat from an organic phosphorus. Plant Soil 248, 297–303.
Li L, Zhang F S., Li X L, Christie P, Yang S C and Tang C 2003b Interspecific facilitation of nutrient uptakes by intercropped maize and faba bean. Nutri. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 65, 61–71.
Li M G, Osaki M, Rao I M and Tadano T 1997 Secretion of phytase from the roots of several plant species under phosphorusdeficient conditions. Plant Soil 195, 161–169.
Lopez H W, Fanny L, Charles C, Christian R 2002 Minerals and phytic acid interactions: Is it a real problem for human nutrition? Inter. J Food Sci. Tech. 37, 727–739.
Marschner H 1995 Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 2nd edn. Academic Press, London.
Osborne L D and Rengel Z 2002 Growth and P uptake by wheat genotypes supplied with phytate as the only P source. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 53, 845–850.
Rao I M, Borrero V, Ricaurte J and Garcia R 1999 Adaptive attributes of tropical forage species to acid soils. V. Differences in phosphorus acquisition from less available inorganic and organic sources of phosphate. J. Plant Nutr. 22, 1175–1196.
Richardson A E, Hadobas P A and Hayes J E 2000 Acid phosphomonoesterase and phytase activities of wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) roots and utilization of organic phosphorus substrates by seedlings grown in sterile culture. Plant Cell Environ. 23, 397–405.
Richardson A E, Hadobas P A, Hayes J E, O'Hara C P and Simpson R J 2001 Utilization of phosphorus by pasture plants supplied with myo-inositol hexaphosphate is enhanced by the presence of soil micro-organisms. Plant Soil 229, 47–56.
Römheld V and Marschner H 1986 Mobilization of iron in the rhizosphere of different plant species. Adv. Plant Nutr. 2, 155–204.
SAS Institute 1985 SAS User's Guide: Statistics. Version 5. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina, USA.
Stern W R 1993 Nitrogen fixation and transfer in intercrop systems. Field Crops Res. 34, 335–356.
Tang C, Unkovich M J and Bowden J W 1999 Factors affecting soil acidification under legumes III. Effects of nitrate supply. New Phytol. 143, 513–521.
Vandermeer J 1989 The Ecology of Intercropping. Cambridge University Press, New York.
Veneklaas E J, Stevens J, Cawthray G R, Turner S, Grigg A M and Lambers H 2003 Chickpea and white lupin rhizosphere carboxylates vary with soil properties and enhance phosphorus uptake. Plant Soil 248, 187–197.
Zhu Y G, Smith F A and Smith S E 2002 Phosphorus efficiencies and their effects on Zn, Cu, and Mn nutrition of different barley (Hordeum vulgare) cultivars grown in sand culture. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 53, 211–216.
Zhu Y G, Smith S E and Smith F A 2001 Zinc (Zn)-phosphorus (P) interactions in two cultivars of spring wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) differing in P uptake efficiency. Ann. Bot. 88, 941–945.
Zuo Y M, Zhang F S, Li X L and Cao Y P 2000 Studies on the improvement in iron nutrition of peanut by intercropping with maize on a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 220, 13–25.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Tang, C., Rengel, Z. et al. Calcium, magnesium and microelement uptake as affected by phosphorus sources and interspecific root interactions between wheat and chickpea. Plant and Soil 261, 29–37 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000035579.39823.16
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000035579.39823.16