Abstract
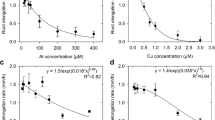
The effects of excess zinc (Zn) on solution-cultured wheat (Triticum aestivum L., cv. Yecora Rojo) and radish (Raphanus sativus L., cv. Cherry Belle) were studied, using both short-term root elongation studies and longer term split-root experiments. Alleviation of Zn rhizotoxicity by Mg and K was observed, with especially dramatic alleviation of root stunting by Mg. In the short-term studies using a simple medium (2 mM CaCl2, pH 6.0), Mg concentrations of 1–5 μM were able to significantly alleviate rhizotoxicity caused by Zn concentrations as high as 60 μM. In the split-root studies, 100 μM Mg was sufficient to abolish Zn toxicity in both wheat and radish. Paradoxically, Mg enhanced uptake and translocation of Zn while simultaneously alleviating toxicity in these longer-term experiments. In short-term experiments, additions of K (0 to 200 μM) to the basal medium alleviated Zn rhizotoxicity to a more limited extent. In split-root experiments, however, the absence or presence of K in test solutions did not affect plant growth or Zn uptake. When increased from a physiological minimum (e.g., 200 μM), Ca also alleviates Zn toxicity, but the effect is very modest in comparison to that of Mg. The results are discussed in relation to the use of short-term assays of metal tolerance in simple salt solutions, and in relation to possible roles of Mg in the physiology of Zn toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker A J M 1978 Ecophysiological aspects of zinc tolerance in Silene maritima With. New Phytol. 80, 635–642.
Berry W L and Wallace A 1989 Zinc phytotoxicity: Physiological responses and diagnostic criteria for tissues and solutions. Soil Sci. 147, 390–397.
Bloß T, Clemens S and Nies D H 2002 Characterization of the ZATlp zinc transporter from Arabidopsis thaliana in microbial model organisms and reconstituted proteoliposomes. Planta 214, 783–791.
Brune, Urbach W and Dietz K J 1994 Compartmentation and transport of zinc in barley primary leaves as basic mechanisms involved in zinc tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 17, 153–162.
Chaney R L 1993 Zinc phytotoxicity. In Zinc in Soils and Plants. Ed. A D Robson. pp. 135–150. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Clemens, S. 2001. Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis. Planta 212, 475–486.
Davies K L, Davies M S and Francis D 1995 The effects of zinc on cell viability and on mitochondrial structure in contrasting cultivars of Festuca rubra L. — a rapid test for zinc tolerance. Environ. Pollut. 88, 109–113.
Grotz N, Fox T, Connolly E, Park W, Guerinot M L, Eide D 1999 Identification of a family of zinc transporter genes from Arabidopsis that respond to zinc deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7220–7224.
Harmens H, Koevoets P L M, Verkleij J A C and Ernst W H O 1994 The role of low molecular weight organic acids in the mechanism of increased zinc tolerance in Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke. New Phytol. 126, 615–621.
Harrington C F, Roberts D J and Nickless G 1996 The effect of cadmium, zinc, and copper on the growth, tolerance index, metal uptake, and production of malic acid in two strains of the grass Festuca rubra. Can. J. Bot. 74, 1742–1752.
Hogan G D, Rauser W E 1979 Tolerance and toxicity of cobalt, copper, nickel and zinc in clones of Agrostis gigantea. New Phytol. 83, 665–670.
Kinraide T B 1998 Three mechanisms for the calcium alleviation of mineral toxicities. Plant Physiol. 118, 513–520.
Kinraide T B, Pedler J F, and Parker D R 2003 Relative effectiveness of calcium and magnesium in the alleviation of rhizotoxicity in wheat induced by copper, zinc, aluminum, sodium, and low pH. Plant Soil, 259, 201–208.
Longnecker N E and Robson A D 1993 Distribution and transport of zinc. In Zinc in Soils and Plants. Ed. A D Robson. pp. 79–91. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Parker D R, Chaney R L and Norvell W A 1995a Chemical equilibrium models: applications to plant nutrition research. In Chemical Equilibrium and Reaction Models. Eds. R H Loeppert, A P Schwab and S Goldberg. pp. 163–200. Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI.
Parker D R and Norvell W A 1999 Advances in solution culture methods for plant mineral nutrition research. Adv. Agron. 65, 151–213.
Parker D R, Norvell W A, Chaney R L 1995b GEOCHEM-PC — a chemical speciation program for IBM and compatible personal computers. In Chemical Equilibrium and Reaction Models. Eds. R H Loeppert, A P Schwab and S Goldberg. pp. 253–269. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI.
Pence N S, Larsen P B, Ebbs S D, Letham D L, Lasat M M, Garvin D F, Eide D and Kochian LV 2000 The molecular physiology of heavy metal transport in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 4956–4960.
Reuter D J and Robinson J B 1997 Plant analysis: An interpretation manual. CSIRO, Collingwood.
Ruano A, Poschenrieder C and Barcelo J 1988 Growth and biomass partitioning in zinc-toxic bush beans. J. Plant Nutr. 11, 577–588.
Shaul O, Hilgemann D W, de-Almeida-Engler J, Van Montagu M, Inz D and Galili G 1999 Cloning and characterization of a novel Mg2+/H+ exchanger. EMBO J. 18, 3973–3980.
Silva I R, Smyth T J, Israel D W and Rufty T W 2001a Altered aluminum inhibition of soybean root elongation in the presence of magnesium. Plant Soil. 230, 223–230.
Silva I R, Smyth T J, Israel D W, Raper C D and Rufty T W 2001b Magnesium is more efficient than calcium in alleviating aluminum rhizotoxicity in soybean and its ameliorative effect is not explained by the Gouy-Chapman-Stern model. Plant Cell Physiol. 42, 538–545.
Silva I R, Smyth T J, Israel D W, Raper C D and Rufty T W 2001c Magnesium ameliorates aluminum rhizotoxicity in soybean by increasing citric acid production and exudation by roots. Plant Cell Physiol. 42, 546–554.
Steel, R G D and J H Torrie 1980 Principles and procedures of statistics. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
van der Zaal B J, Neuteboom L W, Pinas J E, Chardonnens A N, Schat H, Verkleij J A C and Hooykaas P J J 1999 Overexpression of a novel Arabidopsis gene related to putative zinc-transporter genes from animals can lead to enhanced zinc resistance and accumulation. Plant Physiol. 119, 1047–1055.
Verkleij J A C, Koevoets P L M, Blake-Kalff M M A and Chardonnens A N 1998 Evidence for an important role of the tonoplast in the mechanism of naturally selected zinc tolerance in Silene vulgaris. J. Plant Physiol. 153, 188–191.
Welch R M 1995 Micronutrient nutrition of plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 14, 49–82.
Wilkins D A 1957 A technique for the measurement of lead tolerance in plants. Nature 180, 37–38.
Wong M H and Bradshaw A D 1982 A comparison of the toxicity of heavy metals using root elongation of rye grass, Lolium perenne. New Phytol. 91, 255–261.
Wu L and Antonivics J 1975 Zinc and copper uptake by Agrostis stolonifera, tolerant to both zinc and copper. New Phytol. 75, 231–237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedler, J.F., Kinraide, T.B. & Parker, D.R. Zinc rhizotoxicity in wheat and radish is alleviated by micromolar levels of magnesium and potassium in solution culture. Plant and Soil 259, 191–199 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020958.42158.f5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020958.42158.f5