Abstract
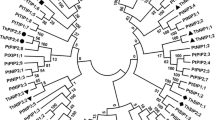
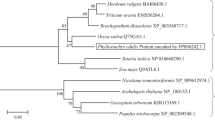
Aquaporin belongs to a highly conserved group of membrane proteins called major intrinsic proteins that facilitate water transport across biological membranes. The genome of Arabidopsis encodes 35 aquaporin genes with 13 homologs in the plasma membrane intrinsic protein (PIP) subgroup. However, the function of each individual aquaporin isoform and the integrated function of plant aquaporins under various physiological conditions remain unclear. As a step toward understanding the aquaporin function in plants under various environmental stimuli, the expressions of a gene family encoding 13 PIPs in Arabidopsis thalianaunder various abiotic stress conditions including drought, cold, and high salinity, or abscisic acid (ABA) treatment were investigated by a quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR analysis. Several PIPgenes were predominantly expressed either in the roots or in the flowers. The expressions of both the highly expressed aquaporins including PIP1;1,PIP1;2,and PIP2;7and the weakly expressed aquaporins such as PIP1;4,PIP2;1,PIP2;4, and PIP2;5were modulated by external stimuli. The analyses of our data revealed that only the PIP2;5was up-regulated by cold treatment, and most of the PIPgenes were down-regulated by cold stress. Marked up- or down-regulation in PIPexpression was observed by drought stress, whereas PIPgenes were less-severely modulated by high salinity. The responsiveness of each aquaporin to ABA were different, implying that the regulation of aquaporin expression involves both ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling pathways. Together, our comprehensive expression profile of the 13 members of the PIP gene family provides novel basis to allocate the stress-related biological function to each PIP gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon, R., Shahak, Y., Wininger, S., Bendov, R., Kapulnik, Y. and Galili, G. 2003. Overexpression of a plasma membrane aquaporin in transgenic tobacco improves plant vigor under favorable growth conditions but not under drought or salt stress. Plant Cell 15: 439-447.
An, Y.Q., McDowell, J.M., Huang, S., McKinney, E.C., Chambliss, S. and Meagher, R.B. 1996. Strong, constitutive expression of the Arabidopsis ACT2/ACT8 actin subclass in vegetative tissue. Plant J 10: 107-121.
Baiges, I., Schäffner, A.R., Affenzeller, M.J. and Mas, A. 2002. Plant aquaporins. Physiol Plant 115: 175-182.
Carvajal, M., Martinez, V. and Alcaraz, C.F. 1999. Physiological function of water channels as affected by salinity in roots of paprika pepper. Physiol Plant 105: 95-101.
Chaumont, F., Barrieu, F., Jung, R. and Chrispeels, M.J. 2000. Plasma membrane intrinsic proteins from maize cluster in two sequence subgroups with differential aquaporin activity. Plant Physiol 122: 1025-1034.
Chaumont, F., Barrieu, F., Wojcik, E., Chrispeels, M.J. and Jung, R. 2001. Aquaporins constitutes a large and highly divergent protein family in maize. Plant Physiol 125: 1206-1215.
Gao, Y.-P., Young, L., Bonham-Smith, P. and Gusta, L.V. 1999. Characterization and expression of plasma and tonoplast membrane aquaporins in primed seed of Brassica napus during germination under stress conditions. Plant Mol Biol 40: 635-644.
Hoth, S., Morgante, M., Sanchez, J.-P., Hanafey, M.K., Tingey, S.V. and Chua, N.-H. 2002 Genome-wide gene expression profiling in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals new targets of abscisic acid and largely impaired gene regulation in the abi1-1 mutant. J Cell Sci 115: 4891-4900.
Javot, H., Lauvergeat, V., Santoni, V., Martin-Laurent, F., Güçlü, J., Vinh, J., Heyes, J., Franck, K.I., Schäffner, A.R., Bouchez, D. and Maurel, C. 2003. Role of a single aquaporin isoform in root water uptake. Plant Cell 15: 509-522.
Javot, H. and Maurel, C. 2002. The role of aquaporins in root water uptake. Annals Bot 90: 301-313.
Johanson, U., Karlsson, M., Johansson, I., Gustavsson, S., Sjövall, S., Fraysse, L., Weig, A.R. and Kjellbom, P. 2001. The complete set of genes encoding major intrinsic proteins in Arabidopsis provides a framework for a new nomenclature for major intrinsic proteins in plants. Plant Physiol 126: 1358-1369.
Johansson, I., Karlsson, M., Johanson, U., Larsson, C. and Kjellbom, P. 2000. The role of aquaporins in cellular and whole plant water balance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465: 324-342.
Johansson, I., Karlsson, M., Shukla, V.K., Chrispeels, M.J., Larsson, C. and Kjellbom, P. 1998. Water transport activity of the plasma membrane aquaporin PM28A is regulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell 10: 451-459.
Kaldenhoff, R., Grote, K., Zhu, J.-J. and Zimmermann, U. 1998. Significance of plasmalemma aquaporins for water transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 14: 121-128.
Kaldenhoff, R., Köllin, A. and Richter, G. 1993. A novel blue light-and abscisic acid-inducible gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encoding an intrinsic membrane protein. Plant Mol Biol 23: 1187-1198.
Kawasaki, S., Borchert, C., Deyholos, M., Wang, H., Brazille, S., Kawai, K., Galbraith, D. and Bohnert, H.J. 2001. Gene expression profiles during the initial phase of salt stress in rice. Plant Cell 13: 889-905.
Kim, J.S., Kim, Y.O., Ryu, H.J., Kwak, Y.S., Lee, J.Y. and Kang, H. 2003. Isolation of stressrelated genes of rubber particles and latex in fig tree (Ficus carica) and their expressions by abiotic stress or plant hormone treatments. Plant Cell Physiol 44: 412-419.
Kreps, J.A., Wu, Y., Chang, H.-S., Zhu, T., Wang, X. and Harper, J.F. 2002. Transcriptome changes for Arabidopsis in response to salt, osmotic, and cold stress. Plant Physiol 130: 2129-2141.
Lee, J.W., Zhang, Y.X., Weaver, C.D., Shomer, N.H., Louis, C.F. and Roberts, D.M. 1995. Phosphorylation of nodulin 26 on serine 262 affects its voltage-sensitive channel activity in planar lipid bilayers. J Biol Chem 270: 27051-27057.
Li, L., Li, S., Tao, Y. and Kitagawa, Y. 2000. Molecular cloning of a novel water channel from rice: its products expression in Xenopus oocytes and involvement in chilling tolerance. Plant Sci 154: 43-51.
Liu, Q., Umeda, M. and Uchimiya, H. 1994. Isolation and expression analysis of two rice genes encoding the major intrinsic protein. Plant Mol Biol 26: 2003-2006.
Lopez, F., Bousser, A., Sissoëff, I., Gasper, M., Lachaise, B., Hoarau, J. and Mahé A. 2003. Diurnal regulation of water transport and aquaporin gene expression in maize roots: contribution of PIP2 proteins. Plant Cell Physiol 44: 1384-1395.
Maathuis, F.J.M., Filatov, V., Herzyk, P., Krijger, G.C., Axelsen, K.B., Chen, S., Green, B.J., Li, Y., Madagan, K.L., Sánchez-Fernández, R., Forde, B.G., Palmgren, M.G., Rea, P.A., Williams, L.E., Sanders, D. and Amtmann, A. 2003. Transcriptome analysis of root transporters reveals participation of multiple gene families in the response to cation stress. Plant J. 35: 675-692.
Mariaux, J.B., Bockel, C., Salamini, F. and Bartels, D. 1998. Desiccation-and abscisic acid-responsive genes encoding major intrinsic proteins (MIPs) from the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum. Plant Mol Biol 38: 1089-1099.
Martre, P., Morillon, R., Barrieu, F., North, G.B., Nobel, P.S. and Chrispeels, M.J. 2002. Plasma membrane aquaporins play a significant role during recovery from water deficit. Plant Physiol. 130: 2101-2110.
Maurel, C., Javot, H., Lauvergeat, V., Gerbeau, P., Tournaire, C., Santoni, V. and Heyes, J. 2002. Molecular physiology of aquaporins in plants. Int Rev Cytol 215: 105-148.
Maurel, C., Kato, R.T., Guern, J. and Chrispeels, M.J. 1995. Phosphorylation regulates the 23 water channel activity of the seed-specific aquaporin α-TIP. EMBO J 14: 3028-3035.
Moshelion, M., Becker, D., Biela, A., Uehlein, N., Hedrich, R., Otto, B., Hadas, L., Moran, N. and Kaldenho., R. 2002. Plasma membrane aquaporins in the motor cells of Samanea samam: diurnal and circadian regulation. Plant Cell 14: 727-739.
Murashige, T. and Skoog, F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15: 473-497.
Murata, K., Mitsuoka, K., Hirai, T., Walz, T., Agre, P., Heymann, J.B., Engel, A. And Fujiyoshi, Y. 2000. Structural determinants of water permeation through aquaporin-1. Nature 407: 599-605.
Quigley, F., Rosenberg, J.M., Shachar-Hill, Y. and Bohnert, H.J. 2001. From genome to function: the Arabidopsis aquaporins. Genome Biol 3: 1-17.
Schäffner, A.R. 1998. Aquaporin function, structure, and expression: are there more surprise to surface in water relation? Planta 204: 131-139.
Seki, M., Narusaka, M., Ishida, J., Nanjo, T., Fujita, M., Oono, Y., Kamiya, A., Nakajima, M., Enju, A., Sakurai, T., Satou, M., Akiyama, K., Taji, T., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., Carninci, P., Kawai, J., Hayashizaki, Y. and Shinozaki, K. 2002. Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31: 279-292.
Siefritz, F., Otto, B., Bienert G.P., van der Krol, A. and Kaldenhoff, R. 2004. The plasma 24 membrane aquaporin NtAQP1 is a key component of the leaf unfolding mechanism in tobacco. Plant J 37: 147-155.
Siefritz, F., Tyree, M.T., Lovisolo, C., Schubert, A. and Kaldenhoff, R. 2002. PIP1 plasma membrane aquaporins in tobacco: from cellular effects to function in plants. Plant Cell 14: 869-876.
Smart, L.B., Moskal, W.A., Cameron, K.D. and Bennett, A.B. 2001. MIP genes are down-regulated under drought stress in Nicotiana glauca. Plant Cell Physiol 42: 686-693.
Steudle, E. 1994. Water transport across roots. Plant Soil 167: 79-90.
Steudle, E., Murrmann, M. and Peterson, C.A. 1993. Transport of water and solutes across maize roots modified by puncturing the endodermis. Further evidence for the composite transport model of the root. Plant Physiol 103: 335-349.
Steudle, E. and Peterson, C.A. 1998. How does water get through roots? J Exp Bot 49: 775-788.
Suga, S., Komatsu, S. and Maeshima, M. 2002. Aquaporin isoforms responsive to salt and water stresses and phytohormones in radish seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 43: 1229-1237.
Tyerman, S.D., Bohnert, H.J., Maurel, C., Steudle, E. and Smith, J.A.C. 1999. Plant aquaporins: their molecular biology, biophysics and significance for plant water relations. J Exp Bot 50: 1055-1071.
Tyerman, S.D. and Niemietz, C.M. 2002. Plant aquaporins: multifunctional water and solute channels with expanding roles. Plant Cell Environ 25: 173-194.
Uno, Y., Urao, T., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., Kanechi, M., Inagaki, N., Maekawa, S. and Shinozaki, K. 1998. Early saltstress effects on expression of genes for aquaporin homologues in the halophyte sea aster (Aster tripolium L.). J Plant Res 111: 411-419.
Weig, A., Deswarte, C. and Chrispeels, M.J. 1997. The major intrinsic protein family of Arabidopsis has 23 members that form three distinct groups with functional aquaporins in each group. Plant Physiol 114: 1347-1357.
Yamada, S., Katsuhara, M., Kelly, W.M., Michalowski, C.B. and Bohnert, H.J. 1995. A family of transcripts encoding water channel proteins: tissue-specific expression in the common ice plant. Plant Cell 7: 1129-1142.
Yamada, S., Komory, T., Myers, P.M., Kuwata, S. and Imaseki, H. 1997. Expression of plasma membrane water channel genes under water stress in Nicotiana excelsior. Plant Cell Physiol 38: 1226-1231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, J.Y., Kim, D.G., Kim, Y.O. et al. An Expression Analysis of a Gene Family Encoding Plasma Membrane Aquaporins in Response to Abiotic Stresses in Arabidopsis Thaliana . Plant Mol Biol 54, 713–725 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000040900.61345.a6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLAN.0000040900.61345.a6