Abstract
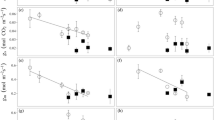
Stress-induced restrictions to carbon balance, growth, and reproduction are the causes of tree-line formation at a global scale. We studied gas exchange and water relations of Polylepis tarapacana in the field, considering the possible effects of water stress limitations imposed on net photosynthetic rate (P N). Daily courses of microclimatic variables, gas exchange, and leaf water potential were measured in both dry-cold and wet-warm seasons at an altitude of 4 300 m. Marked differences in environmental conditions between seasons resulted in differences for the dry-cold and wet-warm seasons in mean leaf water potentials (−1.67 and −1.02 MPa, respectively) and mean leaf conductances (33.5 and 58.9 mmol m−2 s−1, respectively), while differences in mean P N (2.5 and 2.8 μmol m−2 s−1, respectively) were not as evident. This may be related to limitations imposed by water deficit and lower photon flux densities during dry and wet seasons, respectively. Hence P. tarapacana has coupled its gas exchange characteristics to the extreme daily and seasonal variations in temperature and water availability of high elevations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun, G.: [Digital methods for monitoring forest patterns in an Andean environment: The Polylepis example.]-In: Liberman-Cruz, M., Baied, C. (ed.): Desarrollo Sostenible de Ecosistemas de Montaña: Manejo de Areas Frágiles en los Andes. Pp. 285-294. United Nations University Press, La Paz 1997. [In Span.]
Cavieres, L.A., Rada, F., Azócar, A., García-NÚñez, C., Cabrera, H.M.: Gas exchange and low temperature resistance in two tropical high mountain tree species from the Venezuelan Andes.-Acta oecol. 21: 203-211, 2000.
Goldstein, G., Meinzer, F.C., Rada, F.: Environmental biology of a tropical treeline species, Polylepis sericea.-In: Rundel, P.W., Smith, A.P., Meinzer, F.C. (ed.): Tropical Alpine Envi-ronments: Plant Form and Function. Pp. 129-149. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1994.
Goldstein, G., Rada, F., Canales, M.J., Zabala, O.: Leaf gas ex-change of two giant caulescent rosette species.-Acta oecol. 10: 359-370, 1989.
Kessler, M.: The genus Polylepis (Rosaceae) in Bolivia.-Candollea 50: 131-171, 1995.
Körner, C.: A re-assessment of high elevation treeline positions and their explanation.-Oecologia 115: 445-459, 1998.
Körner, C.: Alpine Plant Life: Functional Plant Ecology of High Mountain Ecosystems.-Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York 1999.
Levitt, J.: Responses of Plants to Environmental Stresses. Vol. 1. Chilling, Freezing and High Temperature Stresses.-Aca-demic Press, New York 1980.
Liberman-Cruz, M.: [Microclimate and distribution of Polylepis tarapacana in Sajama National Park, Bolivia.]-Documents phytosociologiques N.S. 10: 235-272, 1986. [In Span.]
Liberman-Cruz, M., Gaffta, D., Pedrotti, F.: [Population structure of Polylepis tarapacana in the Sajama Mount, Bolivia.]-In: Liberman-Cruz, M., Baied, C. (ed.): Desarrollo Sostenible de Ecosistemas de Montaña: Manejo de Areas Frágiles en los Andes. Pp. 59-70. United Nations University Press, La Paz 1997. [In Span.]
Meinzer, F., Goldstein, G., Jaimes, M.: The effect of atmo-spheric humidity on stomatal control of gas exchange in two tropical coniferous species.-Can. J. Bot. 62: 591-595, 1984.
Monasterio, M.: [Plant formations in the Venezuelan Paramos.]-In: Monasterio, M (ed.): Estudios Ecológicos de los Páramos Andinos. Pp. 93-158. Ediciones de la Universidad de Los Andes, Mérida 1980. [In Span.]
Rada, F., Azócar, A., Briceño, B., González, J., García-NÚñez, C.: Carbon and water balance in Polylepis sericea, a tropical treeline species.-Trees 10: 218-222, 1996.
Rada, F., Azócar, A., González, J., Briceño, B.: Leaf gas ex-change in Espeletia schultzii Wedd, a giant caulescent rosette species, along an altitudinal gradient in the Venezuelan Andes.-Acta oecol. 19: 73-79, 1998.
Rada, F., García-NÚñez, C., Boero, C., Gallardo, M., Hilal, M., González, J., Prado, F., Liberman-Cruz, M., Azócar, A.: Low-temperature resistance in Polylepis tarapacana, a tree growing at the highest altitudes in the world.-Plant Cell Environ. 24: 377-381, 2001.
Rada, F., Goldstein, G., Azócar, A., Meinzer, F.: Daily and sea-sonal osmotical changes in a tropical treeline species.-J. exp. Bot. 36: 989-1000, 1985.
Rundel, P.W.: Tropical Alpine Climates.-In: Rundel, P.W., Smith, A.P., Meinzer, F.C. (ed.): Tropical Alpine Environ-ments: Plant Form and Function. Pp. 21-44. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1994.
Sakai, A., Larcher, W.: Frost survival of plants. Responses and Adaptations to Freezing Stress.-Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York-London-Paris-Tokyo 1987.
Schulze, E.-D., Beck, E., Scheibe, R., Ziegler, P.: Carbon di-oxide assimilation and stomatal response of afroalpine giant rosette plants.-Oecologia 65: 207-213, 1985.
Schulze, E.-D., Hall, A.E.: Stomatal responses, water loss and CO2 assimilation rates of plants in contrasting environments.-In: Lange, O.L., Nobel, P.S., Osmond, C.B., Ziegler, H. (ed.): Physiological Plant Ecology II. Pp. 181-230. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York 1982.
Stevens, G.C., Fox, J.F.: The causes of treeline.-Annu. Rev. Ecol. System. 22: 177-191, 1991.
Tranquillini, W.: Physiological Ecology of the Alpine Timber-line.-Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York 1979.
Tyree, M.T., Hammel, H.T.: The measurement of the turgor pressure and the water relations of plants by the pressure-bomb technique.-J. exp. Bot. 23: 267-282, 1972.
Wang, R.Z.: C4 plants in the vegetation of Tibet, China: Their natural occurrence and altitude distribution pattern.-Photo-synthetica 41: 21-26, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Núñez, C., Rada, F., Boero, C. et al. Leaf Gas Exchange and Water Relations in Polylepis tarapacana at Extreme Altitudes in the Bolivian Andes. Photosynthetica 42, 133–138 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHOT.0000040581.94641.ed
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHOT.0000040581.94641.ed