Abstract
Purpose. Membrane-bound efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp), may limit the brain entry and distribution of HIV-1 protease inhibitors and be in part responsible for HIV-1-associated dementia treatment failure. The purpose of this study was to characterize the transport properties of saquinavir and indinavir in a brain microvessel endothelial cell line and in microglia, the immune cells of the brain and primary HIV-1 cellular target.
Methods. Biochemical and transport studies were performed in an immortalized rat brain endothelial cell line (RBE4), a rat microglia cell line (MLS-9), and a P-gp overexpressing Chinese hamster ovary cell line (CHRC5).
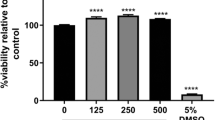
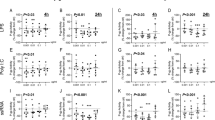
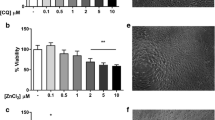
Results. Western blot analysis using the P-gp monoclonal antibody C219 detected a single band at approximately 170 to 180 kDa (a size previously reported for P-gp) in all cell lines. Cellular accumulation of [14C]saquinavir and [3H]indinavir by RBE4, MLS-9, and CHRC5 monolayers was significantly enhanced in the presence of P-gp inhibitors, HIV-1 protease inhibitors, the ATPase inhibitor sodium azide, and the ATP depleting agent 2',4'-dinitrophenol respectively. [14C]Saquinavir and [3H]indinavir efflux from both cell systems was rapid and significantly reduced in the presence of PSC833.
Conclusions. These results provide evidence for P-gp mediated transport of saquinavir and indinavir in RBE4 and MLS-9 and suggest that this transporter can restrict, at least in part, the permeation of HIV-1 protease inhibitors at both the brain barrier site and in brain parenchyma.
Similar content being viewed by others
references
J. C. McArthur, N. Haughey, S. Gartner, K. Conant, C. Pardo, A. Nath, and N. Sacktor. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia: an evolving disease. J. Neurovirol. 9:205–221 (2003).
M. Kaul, G. A. Garden, and S. A. Lipton. Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature 410:988–994 (2001).
A. E. Kim, J. M. Dintaman, D. S. Waddell, and J. A. Silverman. Saquinavir, an HIV protease inhibitor, is transported by P-glycoprotein. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 286:1439–1445 (1998).
N. Sacktor, R. H. Lyles, R. Skolasky, C. Kleeberger, O. A. Selnes, E. N. Miller, J. T. Becker, B. Cohen, and J. C. McArthur. and Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. HIV-associated neurologic disease incidence changes: Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study, 1990–1998. Neurology 56:257–260 (2001).
S. Kravcik, G. Victor, J. B. Angel, A. D. Badley, G. E. Garber, and D. W. Cameron. Activity of the combination of nelfinavir and saquinavir against human immunodeficiency virus after failure of prior protease inhibitor therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 29:702–703 (1999).
A. H. Schinkel, U. Mayer, E. Wagenaar, C. A. Mol, L. van Deemter, J. J. Smit, M. A. van der Valk, A. C. Voordouw, H. Spits, O. van Tellingen, J. M. Zijlmans, W. E. Fibbe, and P. Borst. Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:4028–4033 (1997).
R. B. Kim, M. F. Fromm, C. Wandel, B. Leake, A. J. Wood, D. M. Roden, and G. R. Wilkinson. The drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 101:289–294 (1998).
E. F. Choo, B. Leake, C. Wandel, H. Imamura, A. J. Wood, G. R. Wilkinson, and R. B. Kim. Pharmacological inhibition of P-glycoprotein transport enhances the distribution of HIV-1 protease inhibitors into brain and testes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 28:655–660 (2000).
R. L. Juliano and V. Ling. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:152–162 (1976).
M. M. Gottesman, C. A. Hrycyna, P. V. Schoenlein, U. A. Germann, and I. Pastan. Genetic analysis of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Genet. 29:607–649 (1995).
J. J. Smit, A. H. Schinkel, R. P. Oude Elferink, A. K. Groen, E. Wagenaar, L. van Deemter, C. A. Mol, R. Ottenhoff, N. M. van der Lugt, and M. A. van Roon. et al. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell 75:451–462 (1993).
C. B. Washington, H. R. Wiltshire, M. Man, T. Moy, S. R. Harris, E. Worth, P. Weigl, Z. Liang, D. Hall, L. Marriott, and T. F. Blaschke. The disposition of saquinavir in normal and P-glycoprotein deficient mice, rats, and in cultured cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 28:1058–1062 (2000).
V. V. Rao, J. L. Dahlheimer, M. E. Bardgett, A. Z. Snyder, R. A. Finch, A. C. Sartorelli, and D. Piwnica-Worms. Choroid plexus epithelial expression of MDR1 P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein contribute to the blood-cerebro-spinal-fluid drug-permeability barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:3900–3905 (1999).
E. Beaulieu, M. Demeule, L. Ghitescu, and R. Beliveau. P-glycoprotein is strongly expressed in the luminal membranes of the endothelium of blood vessels in the brain. Biochem. J. 326:539–544 (1997).
P. L. Golden and W. M. Pardridge. P-Glycoprotein on astrocyte foot processes of unfixed isolated human brain capillaries. Brain Res. 819:143–146 (1999).
G. Lee, L. Schlichter, M. Bendayan, and R. Bendayan. Functional expression of P-glycoprotein in rat brain microglia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299:204–212 (2001).
R. Bendayan, G. Lee, and M. Bendayan. Functional expression and localization of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier. Microsc. Res. Tec. 57:365–380 (2002).
D. J. Begley, D. Lechardeur, Z. D. Chen, C. Rollinson, M. Bardoul, F. Roux, D. Scherman, and N. J. Abbott. Functional expression of P-glycoprotein in an immortalised cell line of rat brain endothelial cells, RBE4. J. Neurochem. 67:988–995 (1996).
F. Roux, O. Durieu-Trautmann, N. Chaverot, M. Claire, P. Mailly, J. M. Bourre, A. D. Strosberg, and P. O. Couraud. Regulation of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and alkaline phosphatase activities in immortalized rat brain microvessel endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 159:101–113 (1994).
A. Regina, A. Koman, M. Piciotti, and B. El Hafny. M.S. Center, R. Bergmann, P.O. Couraud and F. Roux. Mrp1 multidrug resistance-associated protein and P-glycoprotein expression in rat brain microvessel endothelial cells. J. Neurochem. 71:705–715 (1998).
W. Zhou, F. S. Cayabyab, P. S. Pennefather, L. C. Schlichter, and T. E. DeCoursey. HERG-like K+ channels in microglia. J. Gen. Physiol. 111:781–794 (1998).
S. Dallas, X. Zhu, S. Baruchel, L. Schlichter, and R. Bendayan. Functional expression of the multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) in microglia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 307:282–290 (2003).
E. Georges, G. Bradley, J. Gariepy, and V. Ling. Detection of P-glycoprotein isoforms by gene-specific monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:152–156 (1990).
C. G. L. Lee, M. M. Gottesman, C. O. Cardarelli, M. Ramachandra, K. T. Jeang, S. V. Ambudkar, I. Pastan, and S. Dey. HIV-1 protease inhibitors are substrates for the MDR1 multidrug transporter. Biochemistry 37:3594–3601 (1998).
H. Gutmann, G. Fricker, J. Drewe, M. Toeroek, and D. S. Miller. Interactions of HIV protease inhibitors with ATP-dependent drug export proteins. Mol. Pharmacol. 56:383–389 (1999).
G. J. Dore, P. K. Correll, Y. Li, J. M. Kaldor, D. A. Cooper, and B. J. Brew. Changes to AIDS dementia complex in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 13:1249–1253 (1999).
L. C. Schlichter, G. Sakellaropoulos, B. Ballyk, P. S. Pennefather, and D. J. Phipps. Properties of K+ and Cl- channels and their involvement in proliferation of rat microglia cells. Glia 17:225–236 (1996).
J. Drewe, H. Gutmann, G. Fricker, M. Torok, C. Beglinger, and J. Huwyler. HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir: a more potent inhibitor of P-glycoprotein than the cyclosporine analog SDZ PSC 833. Biochem. Pharmacol. 57:1147–1152 (1999).
S. P. Cole and R. G. Deeley. Multidrug resistance mediated by the ATP-binding cassette ransporter protein MRP. Bioessays 20:931–940 (1998).
P. Borst, R. Evers, M. Kool, and J. Wijnholds. A family of drug transporters: the multidrug resistance-associated proteins. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 92:1295–1302 (2000).
Y. Zhang, H. Han, W. F. Elmquist, and D. W. Miller. Expression of various multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) homologues in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Brain Res. 876:148–153 (2000).
J. Hirrlinger, J. Konig, and R. Dringen. Expression of mRNAs of multidrug resistance proteins (Mrps) in cultured rat astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglial cells and neurones. J. Neurochem. 82:716–719 (2002).
K. Jones, P. G. Bray, S. H. Khoo, R. A. Davey, E. R. Meaden, S. A. Ward, and D. J. Back. P-Glycoprotein and transporter MRP1 reduce HIV protease inhibitor uptake in CD4 cells: potential for accelerated viral drug resistance? AIDS 15:1353–1358 (2001).
G. C. Williams, A. Liu, G. Knipp, and P. J. Sinko. Direct evidence that saquinavir is transported by multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP1) and canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter (MRP2). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46:3456–3462 (2002).
W. Zhang, J. Mojsilovic-Petrovic, M. F. Andrade, H. Zhang, M. Ball, and D. B. Stanimirovic. Expression and functional characterization of ABCG2 in brain endothelial cells and vessels. FASEB J. 17:2085–2087 (2003).
T. Eisenblätter, S. Hüwel, and H. Galla. Characterization of the brain multidrug resistance protein (BMDP/ABCG2/BCRP) expressed at the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res. 971:221–231 (2003).
L. A. Doyle, W. Yang, L. V. Abruzzo, T. Krogmann, Y. Gao, A. K. Rishi, and D. D. Ross. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:15665–15670 (1998).
T. Litman, T. E. Druley, W. D. Stein, and S. E. Bates. From MDR to MXR: new understanding of multidrug resistance systems, their properties and clinical significance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58:931–959 (2001).
L. A. Doyle and D. D. Ross. Multidrug resistance mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2). Oncogene 22:7340–7358 (2003).
A. Gupta, Y. Zhang, J. D. Unadkat, and Q. Mao. HIV protease inhibitors are inhibitors but not substrates of the human breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. In Press (2004).
P. T. Ronaldson, M. Bendayan, D. Gingras, M. Piquette-Miller, and R. Bendayan. Cellular localization and functional expression of P-glycoprotein in rat astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. In Press (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronaldson, P.T., Lee, G., Dallas, S. et al. Involvement of P-Glycoprotein in the Transport of Saquinavir and Indinavir in Rat Brain Microvessel Endothelial and Microglia Cell Lines. Pharm Res 21, 811–818 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000026433.27773.47
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000026433.27773.47