Abstract
Purpose. To prepare the surface generated by small intestinal brush border membrane vesicles (BBMVs) for the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis, which allows the real-time measurement of binding events occurring on the intestinal membrane.
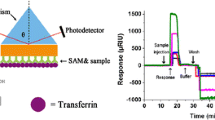
Methods. BBMVs were isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats, suspended in HEPES-buffered saline, and flowed over the surface of a SPR sensor chip composed of dextran derivatives modified with lipophilic residues. The surface coverage was determined from binding of bovine serum albumin to BBMV-immobilized sensor chip. The performance of BBMVs immobilized was evaluated by their interaction with otilonium bromide and bile salts.
Results. The stable BBMV surface was achieved when BBMV suspension was flowed over the sensor chip for 8 h at a rate of 2 μl/min. The flow of otilonium bromide resulted in an increased SPR signal because of its binding to calcium channel, which is known to be distributed over the gastrointestinal tact. When bile salts were flowed over ileal and duodenal BBMV surfaces, respectively, a slightly higher SPR signal was observed in the ileal BBMV surface, indicating the specific interaction of bile salts with bile acid transporters.
Conclusions. BBMV surfaces may be useful for the estimation of binding events on the intestinal membrane by SPR analysis, especially for the drugs that are orally administrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. Terrettaz, T. Stora, C. Duschl, and H. Vogel. Protein binding to supported lipid membranes: investigation of the cholera toxin-ganglioside interaction by simultaneous impedance spectroscopy and surface plasmon resonance. Langmuir. 9:1361-1369 (1993).
K. Glasmästar, C. Larsson, F. Höök, and B. Kasemo. Protein adsorption on supported phospholipid bilayers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 246:40-47 (2002).
D. G. Myszka and R. L. Rich. Implementing surface plasmon resonance biosensors in drug discovery. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 3:310-317 (2000).
R. J. Green, R. A. Frazier, K. M. Shakesheff, M. C. Davies, C. J. Roberts, and S. J. B. Tendler. Surface plasmon resonance analysis of dynamic biological interactions with biomaterials. Biomaterials 21:1823-1835.
E. Sckmann. Supported membranes: scientific and practical applications. Science 271:43-48 (1996).
M. A. Cooper, A. C. Try, J. Carroll, D. J. Ellar, and D. H. Williams. Surface plasmon resonance analysis at a supported lipid monolayer. Biochim. Biophy. Acta 1373:101-111 (1998).
E. Sackmann and M. Tanaka. Supported membranes on soft polymer cushions: fabrication, characterization and applications. Trends Biotechnol. 18:58-64 (2000).
P. Artursson. and J. Karlsson. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Biochem. Biophs. Res. Commun. 175:880-885 (1991).
D. M. Heuman, R. S. Bajaj, and Q. Lin. Adsorption of mixtures of bile salt taurine conjugates to lecithin-cholesterol membranes: implications for bile salt toxicity and cytoprotection. J. Lipid Res. 37:562-573 (1996).
K. Balon, B. U. Riebesehl, and B. W. Müller. Drug liposome partitioning as a tool for the prediction of human passive intestinal absorption. Pharm. Res. 16:882-888 (1999).
W. Kramer. G. Wess, G. Neckermann, G. Schubert, J. Fink, F. Girbig, U. Gutjahr, S. Kowalewski, K. H. Baringhaus, and G. Bor. Intestinal absorption of peptides by coupling to bile acids. J. Biol. Chem. 269:10621-10627 (1994).
M. J. Nowicki, B. L. Shneider, J. M. Paul, and J. E. Heubi. Glucocorticoids upregulate taurocholate transport by ileal brush-border membrane. Am. J. Physiol. 273:G197-G203 (1997).
S. A. Ibrahim and K. A. Balasubramanian. Comparative study on brush border membranes prepared from rat and monky small intestine by Ca2+ and Mg2+ precipitation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 112B:65-69 (1995).
R. Prabhu and K. A. Balasubramanian. A novel method of preparation of small intestinal brush border membrane vesicles by polyethylene glycol precipitation. Anal. Biochem. 289:157-161 (2001).
M. Kessler, O. Acuto, C. Storelli, H. Murer, M. Müller, and G. Semenza. A modified procedure for the rapid preparation of efficiently transporting vesicles from small intestinal brush border membranes: Their use in investigating some properties of D-glucouse and choline transport systems. Biochim. Biophy. Acta 506:136-154 (1978).
K. Walter, C. Schütt, and H. U. Bergmeyer. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Academic Press, New York, 1974.
M. R. Webb. A continuous spectrophotometric assay for inorganic phosphate and for measuring phosphate release kinetics in biological systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:4884-4887 (1992).
E. Erb, X. Chen, S. Allen, C. J. Roberts, S. J. B. Tendler, M. C. Davies, and S. Forséen. Characterization of the surfaces generated by liposome binding to the modified dextran matrix of a surface plasmon resonance sensor chip. Anal. Biochem. 280:29-35 (2000).
M. A. Cooper, A. Hansson, S. Löfås, and D. H. Williams. A vesicle capture sensor chip for kinetic analysis of interactions with membrane-bound receptors. Anal. Biochem. 277:196-205 (2000).
D. J. Bjorkman, C. H. Allan, S. J. Hagen, and J. S. Trier. Structural features of absorptive cell and microvillus membrane preparations from rat small intestine. Gastroenterology 91:1401-1414 (1986).
S. Okumura, T. Akao, E. Mizuki, M. Ohba, and K. Inouye. Screening of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac δ-endotoxin on the artificial phospholipid monolayer incorporated with brush border membrane vesicles of Plutella xylostella by optical biosensor technology. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 47:177-188 (2001).
M. Camilleri, and M. G. Choi Irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 11:3-15 (1997).
A. M. Accarino, F. Azpiroz, and J. Malagelada. Selective dysfunction of mechanosensitive intestinal afferents in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 108:636-643 (1995).
S. Evangelista, A. Giachetti, B. Chapelain, G. Neliat, and C. A. Maggi. Receptor binding profile of otilonium bromide. Pharmacol. Res. 38:111-117 (1998).
P. Santicioli, V. Zagorodnyuk, A. R. Renzetti, and C. A. Maggi. Antimuscarinic, calcium channel blocker and tachykinin NK2 receptor antagonist actions of otilonium bromide in the circular muscle of guinea-pig colon. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 359:420-427 (1999).
A. Enhsen, W. Kramer, and G. Wess. Bile acids in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 3:409-418 (1998).
P. W. Swaan. F. C. Zsoka, Jr., and S. Øie. Use of the intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporters for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 20:59-82 (1996).
W. Kramer, G. Wess, G. Schubert, M. Bickel, F. Gibig, U. Gutjahr, S. Kowalewski, K. H. Baringhaus, A. Enhsen, H. Glombik, S. Müllner, G. Neckermann, S. Schulz, and E. Petzinger. Liver-specific drug targeting by coupling to bile acids. J. Biol. Chem. 267:18598-18604 (1992).
J. L. Dupas and A. F. Hofmann. Passive jejunal absorption of bile acids in vivo: structure-activity relationships and rate limiting steps. Gastroenterology 86:A1067(1984).
G. J. Russell-Jones. Carrier-mediated transport, oral drug delivery. In E. Mathiowitz (eds), Encyclopedia of Controlled Drug Delivery, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1999, pp. 173-184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, S., Park, J.H., Yu, J. et al. Preparation and Characterization of Reconstructed Small Intestinal Brush Border Membranes for Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis. Pharm Res 21, 55–60 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000012152.86004.aa
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000012152.86004.aa