Abstract
Purpose. The validity of using drug amount-depth profiles in stratum corneum to predict uptake of clobetasol propionate into stratum corneum and its transport into deeper skin layers was investigated.
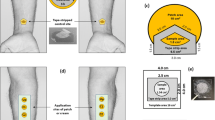
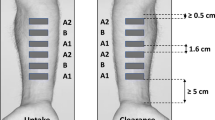
Methods. In vitro diffusion experiments through human epidermis were carried out using Franz-type glass diffusion cells. A saturated solution of clobetasol propionate in 20% (V/V) aqueous propylene glycol was topically applied for 48 h. Steady state flux was calculated from the cumulative amount of drug permeated vs. time profile. Epidermal partitioning was conducted by applying a saturated drug solution to both sides of the epidermis and allowing time to equilibrate. The tape stripping technique was used to define drug concentration-depth profiles in stratum corneum for both the diffusion and equilibrium experiments.
Results. The concentration-depth profile of clobetasol propionate in stratum corneum for the diffusion experiment is biphasic. A logarithmic decline of the drug concentration over the first four to five tape strips flattens to a relatively constant low concentration level in deeper layers. The drug concentration-depth profile for the equilibrium studies displays a similar shape.
Conclusions. The shape of the concentration-depth profile of clobetasol propionate is mainly because of the variable partitioning coefficient in different stratum corneum layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. S. Leopold and H. I. Maibach. Effect of lipophilic vehicles on in vivo skin penetration of methyl nicotinate in different races. Int. J. Pharm. 139:161-167 (1996).
M. Bach and B. C. Lippold. Percutaneous penetration enhancement and its quantification. Eu. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 46:1-13 (1998).
Code of Federal Regulations. US Government Printing Office, Washington DC, 1999.
Guidance. Topical Dermatologic Corticosteroids: in Vivo Bioequivalence, US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Rockville, MD, USA, 1995.
F. Pirot, Y. N. Kalia, A. L. Stinchcomb, G. Keating, A. Bunge, and R. H. Guy. Characterization of the permeability barrier of human skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:1562-1567 (1997).
G. J. Singh, W. P. Adams, L. J. Lesko, V. P. Shah, J. A. Molzon, R. L. Williams, and L. K. Pershing. Development of in vivo bioequivalence methodology for dermatologic corticosteroids based on pharmacodynamic modeling. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 66:346-357 (1999).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall. Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265-275 (1951).
F. Dreher, A. Arens, J. J. Hostynek, S. Mudumba, J. Ademola, and H. I. Maibach. Colorimetric method for quantifying human Stratum corneum removed by adhesive-tape stripping. Acta Derm. Venereol. 78:186-189 (1998).
H. E. Bodde, M. A. M. Kruithof, J. Brussee, and H. K. Koerten. Visualization of normal and enhanced mercuric chloride transport through human skin in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 53:13-24 (1989).
A. Weerheim and M. Ponec. Determination of stratum corneum lipid profile by tape stripping in combination with high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 293:191-199 (2001).
M. Simon, D. Bernard, A. M. Minondo, C. Camus, F. Fiat, P. Corcuff, R. Schmidt, and G. Serre. Persistence of both peripheral and non-peripheral corneodesmosomes in the upper stratum corneum of winter xerosis skin versus only peripheral in normal skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 116:23-30 (2001).
B. Querleux, S. Richard, J. Bittoun, O. Jolivet, P. I. Idy, R. Bazin, and J. L. Leveque. In vivo hydration profile in skin layers by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Skin Pharmacol. 7:210-216 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mueller, B., Anissimov, Y.G. & Roberts, M.S. Unexpected Clobetasol Propionate Profile in Human Stratum Corneum After Topical Application in Vitro . Pharm Res 20, 1835–1837 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000003382.20030.54
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHAM.0000003382.20030.54