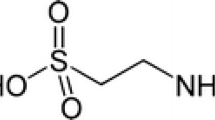
Abstract
Taurine is a semiessential amino acid, and its deficiency is involved in retinal and cardiac degenerations. In recent years, it was found that diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with taurine, and many in vivo experimental studies showed that taurine administration is able to reduce the alterations induced by DM in the retina, lens, and peripheral nerve, although its effects on diabetic kidney are dubious. Interestingly, long-term taurine supplementation reduces the mortality rate in diabetic rats. The mechanisms by which taurine exerts beneficial effects in DM are discussed below. Recently, it has been suggested that taurine deficiency may alter the endocrine pancreas “fetal programming,” increasing the risk of insulin resistance in adult life. The bulk of experimental data suggests that taurine administration could be useful in the treatment of type 1 DM and in the prevention of insulin resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Huxtable, R. J. 1992. Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol. Rev. 72:101–163.
Hayes, K., Rabin, A., and Berson, E. 1975. An ultrastructure study of nutritionally induced and reversed retinal degeneration in cats. Am. J. Path. 78:505–509.
Hayes, K. and Sturman, J. A. 1981. Taurine in metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1:401–425.
Geggel, H. S., Ament, M., Heckenlively, J. R., Martin, D. A., and Kopple, J. D. 1985. Nutritional requirement for taurine in patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition. N. Engl. J. Med. 312:142–146.
Heller-Stilb, B., van Roeyen, C., Rascher, K., Harting, H. G., Huth, A., Seeliger, M., Warskulat, U., and Haussinger, D. 2001. Disruption of the taurine transporter gene (taurinet) leads to retinal degeneration in mice. FASEB J. 10.1096/fj01-0691fje.
Reccia, R., Pignalosa, B., Grasso, A., and Campanella, G. 1980. Taurine treatment in retinitis pigmentosa. Acta. Neurol. (Napoli) 2:132–136.
Pasantes-Morales, H., Quiroz, H., and Quesada, O. 2002. Treatment with taurine, diltiazem and vitamin E retards the progressive visual field reduction in retinitis pigmentosa: A 3 years follow-up study. Metab. Brain Dis. 17:183–197.
Pion, P. D., Kittleson, M. D., Rogers, Q. R., and Morris, J. G. 1987. Myocardial failure in cats associated with low plasma taurine: A reversible cardiomyopathy. Science 237:764–768.
Pion, P. D., Sanderson, S. L., and Kittelson, M. D. 1998. The effectiveness of taurine and levocarnitine in dogs with heart disease. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 28:1495–1514.
Lake, N. 1993. Loss of cardiac myofibrils: Mechanism of contractile deficits induced by taurine deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. 264: H1323–H1326.
vom Dahl, S., Monnighoff, I., and Haussinger, D. 2000. Decrease of plasma taurine in Gaucher disease and its substained correction during enzyme replacement therapy. Amino Acids 19: 585–592.
Franconi, F., Bennardini, F., Mattana, A., Miceli, M., Ciuti, M., Mian, M., Gironi, A., Bartolomei, G., Anichini, R., and Seghieri, G. 1995. Plasma and platelet taurine are reduced in subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Effects of taurine supplementation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 61:1115–1119.
Franconi, F., Miceli, M., Fazzini, A., Seghieri, G., Caputo, S., Di Leo, M. A. S., Lepore, D., and Ghirlanda, G. 1996. Taurine and diabetes mellitus: Human and experimental models. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 403:579–582.
De Luca, G., Calpona, P. R., Caponetti, A., Romano, G., Di Benedetto, A., Cucinotta, D., and Di Giorgio, R. M. 2001.Taurine and osmoregulation: Platelet taurine content, uptake, and release in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 50:60–64.
Airaksinen, E. M., Airaksinen, M. M., Sihvola, P., and Marnela, K.-M. 1981. Decrease in the uptake and concentration of taurine in blood platelets of retinitis pigmentosa patients. Metab. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. 5:45–48.
Hansen, S. H. 2001. The role of taurine in diabetes mellitus and development of diabetic complications. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 17:330–346.
Bustamante, J., Lobo, M. V. T., Alonso, F. J., Mukala, N. T. A., Ginè, E., Solis, J. M., Tamarit-Rodriguez, J., and Martin del Río, R. 2001. An osmotic-sensitive taurine pool is localized in rat pancreatic islet cells containing glucagon and somatostatin. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 281:E1275–E1285.
Cherif, H., Reusens, B., Dahri, S., Remacle, C., and Hoet, J. J. 1996. Stimulatory effects of taurine on the insulin secretion of fetal rat islets cultured in vitro. J. Endocrinol. 151:501–506.
Cherif, H., Reusens, B., Ahn, M. T., Hoet, J. J., and Remacle, C. 1998. Effects of taurine on the insulin secretion of rat fetal islets from dams fed a low-protein diet. J. Endocrinol. 159:341–348.
Goodman, H. O. and Shihabi, Z. K. 1990. Supplemental taurine in diabetic rats: Effect on plasma glucose and triglycerides. Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. 43:1–9.
Stevens, M. J., Lattimer, S. A., Kamijo, M., Van Huysen, C., Sima, A. A. F., and Green, D. A. 1993. Osmotically-induced nerve taurine depletion and the compatible osmolyte hypothesis in experimental diabetic neuropathy in the rat. Diabetologia 36:608–614.
Trachtman, H., Futterweitt, S., and Bienkowski, R. S. 1993. Taurine prevents glucose-induced lipid peroxidation and increased collagen production in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 191:759–565.
Trachtman, H., Futterweitt, S., Maesaka, J., Ma, C., Valderrama, E., Fuchs, A., Tarectecan, A. A., Rao, P. S., Sturman, J. A., Boles, T. H., Fu, M. X., and Baynes, J. 1995. Taurine ameliorates chronic streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rat. Am. J. Physiol. 269:F429–F438.
Kamata, K., Sugiura, M., Kojima, S., and Kasuya, Y. 1996. Restoration of endothelium-dependent relaxation in both hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus by chronic taurine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 303:47–53.
Nanami, K., Oda, H., and Yokogoshi, H. 1996. Antihypercholesterolemic action of taurine on streptozotocin-diabetic rats or on rats fed a high cholesterol diet. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 403: 561–568.
Lim, E., Park, S., and Kim, H. 1998. Effect of taurine supplementation on lipid formation and the activities of glutathione related enzymes in the liver and islet of type I and type II diabetic model mice. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 442:99–104.
You, J. S. and Chang, K. J. 1998. Effect of taurine supplementation on lipid peroxidation, blood glucose and blood lipid metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 442:163–168.
Mochizuki, H., Takido, J., Oda, H., and Yokogoshi, H. 1999. Improving effect of dietary taurine on marked hypercholesterolemia induced by a high-cholesterol diet in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63:1984–1987.
Ha, H., Yu, M. R., and Kim, K. H. 1999. Melatonin and taurine reduce early glomerulopathy in diabetic rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 26:944–950.
Obrosova, I. G. and Stevens, M. J. 1999. Effect of dietary taurine supplementation on GSH and NAD(p)-redox status, lipid peroxidation, and energy metabolism in diabetes precataractous lens. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 40:680–688.
Mitton, K. P., Linklater, H. A., Dzialoszynski, T. S., Sanford, E., Starkey, K., and Trevithick, J. R. 1999. Modelling cortical cataractogenesis 21: In diabetic rat lenses taurine supplementation vitro reduction of damage in model diabetic is due to its antioxidant activity? Exp. Eye Res. 69:279–289.
Kilic, F., Bhardwaj, R., Caulfeild, J., and Trevithick, J. R. 1999. Modelling cortical cataractogenesis 22: Is in vitro reduction of damage in model diabetic is taurine due to its antioxidant activity? Exp. Eye Res. 69:291–300.
Wu, Q. D., Wang, J. H., Fennesy, F., Redmond, H. P., and Bouchier-Hayes, D. 1999. Taurine prevents high-glucose-induced human vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. 277: C1229–C1238.
Militante, J. D., Lombardini, J. B., and Schaffer, S. W. 2000. The role of taurine in the pathogenesis of the cardiomyopathy of insulin-dependent diabetes. Cardiovasc. Res. 393:393–400.
Pop-Busui, R., Sullivan, K. A., Van Huysen, C., Cao, Towns, X., and Stevens, M. J. 2001. Depletion of taurine in experimental diabetic neuropathy: Implications for nerve metabolic and functional deficits. Exp. Neurol. 168:259–272.
Obrosova, I., Minchenko, A. G., Marinescu, V., Fathallah, L., Kennedy, A., Stockert, C. M., Frank, R. N., and Stevens, M. J. 2001. Antioxidants attenuate early up regulation of retinal vascular endothelial growth factor in streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Diabetologia 44:1102–1110.
Obrosova, I., Fathallah, L., and Stevens, M. J. 2001. Taurine counteracts oxidative stress and nerve growth factor deficit in early experimental diabetic neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 172: 211–219.
Di Leo, M. A. S., Santini, S. A., Cercone, S., Marra, G., Lepore, D., Caputo, S., Antico, L., Giardina, B., Pitocco, D., Franconi, F., and Ghirlanda, G. 1999. Dose-dependent effects of taurine in the prevention of Na,K-ATPase impairment and lipid peroxidation in the retina of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 42(Suppl. 1):A315.
Di Leo, M. A. S.,Santini, S. A., Cercone, S., Marra, G., Lepore, D., Gentiloni Silveri, N., Caputo, S., Greco, A. V., Giardina, B., Franconi, F., and Ghirlanda, G. 2002. Chronic taurine supplementation ameliorates oxidative stress and Na+K+-ATPase impairment in the retina of diabetic rats. Amino Acids 23:401–406.
Di Leo, M. A. S., Ghirlanda, G., Gentiloni Silveri, N., Giardina, B., Franconi, F., and Santini, S. A. 2003. Potential therapeutic effect of antioxidants in experimental diabetic retina: A comparison between chronic taurine and vitamin E plus selenium supplementations. Free Radic. Res. 37:323–330.
Nakaya, Y., Minami, A., Haradica, N., Sakamoto, S., Niwa, Y., and Ohnaka, M. 2000. Taurine improves insulin sensitivity in the Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rat, a model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71:54–58.
Odetti, P., Pesce, C., Traverso, N. Menini, S., Pesce Manieri, E., Cosso, L., Velentini, S., Patriarca, S., Cottalasso, D., Marinari, U. M., and Pronzato, M. A. 2002. Comparative trial of N-acetyl-cysteine, taurine, and oxerutin on skin and kidney damage in long-term experimental diabetes. Diabetes 52:499–505.
Franconi, F., Di Leo, M. A. S., Santini, S. A., Gentiloni Silveri, N., Caputo, S., Giardina, B., and Ghirlanda, G. 2002. Taurine supplementation prolongs the survival and reduces glycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Taurine in the 21st century, September 20–23, Radisson Kauai Beach Resort, Hawaii.
Movassat, J. and Portha, B. 1999. Beta-cell growth in the neonatal Goto-Kakisaki rat and regeneration after treatment with streptozotocin at birth. Diabetologia 42:1098–1096.
Trachtman, H., Futterweitt, S., Prenner, J., and Hanon, S. 1994. Antioxidants reverse the antiproliferative effect of high glucose and advanced glycosylation end products in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199:346–352.
Kirpichnikov, D. and Sowers, J. R. 2001. Diabetes mellitus and diabetes associated vascular disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab.12:225–429.
Baynes, J. W. and Thorpe, S. R. 1999. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: A new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 48:1–9.
Wright, C. E., Tallan, H. H., and Lin, Y. Y. 1986. Taurine: Biological update Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55:427–453.
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Cruz, C. 1984. Protective effect of taurine and zinc on peroxidation induced damage in photoreceptor outer segments. J. Neurosci. Res. 11:303–311.
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Cruz, C. 1985. Taurine and hypotaurine inhibit light induced lipid peroxidation and protect rod outer segment structures. Brain Res. 330:154–157.
Alvarez, J. G. and Storey, B. T. 1983. Taurine, hypotaurine, epinephrine and albumin inhibit lipid peroxidation in rabbit spermatozoa from O2 toxicity due to lipid peroxidation. Biol. Reprod. 28:1129–1136.
Dawson, R., Tang, E., Shib, D., Hern, H., Hu, M., Baker, D., and Eppler, B. 1998. Taurine inhibition of iron-stimulated catecholamine oxidation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 442:155–162.
Schuller-Levis, G. B., Gordon, R. E., Park, E., Pendino, K. J., and Laskin, D. L. 1995. Taurine protects rat bronchioles from acute ozone-induced lung inflammation and hyperplasia. Exp. Lung Res. 21:877–888.
Milei, J. R., Ferreira, R., Llesuy, S., Focarda, J., Covarrubias, J., and Boveris, A. R. 1992. Reduction of reperfusion injury with preoperative rapid intravenous infusion of taurine during myocardial revascularization. Am. Heart J. 123:339–345.
Tadolini, B., Pintus, G., Pinna, G., Bennardini, F., and Franconi, F. 1995. Effect of taurine and hypotaurine on lipid peroxidation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 213:820–826.
Weiss, S. J., Klein, R., Slivka, A., and Wei, M. 1982. Chlorination of taurine by human neutrophils: Evidence for hypochlorous acid generation. J. Clin. Invest. 70:598–607.
Zglinczynski, J. M., Stelmaszynka, T., Domasnski, J., and Ostrowski, W. 1971. Chloramines as intermediate of oxidation reaction of amino acids by myeloperoxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 233:419–424.
Cantin, A. 1994. Taurine modulation of hypochlorous acid-induced lung epithelial cell injury in vitro. J. Clin. Invest. 93:606–614.
Kearns, S. and Dawson, R. 2000. Cytoprotective effect of taurine against hypochlorous acid toxicity to PC12 cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 483:563–570.
Raschke, P., Massoudy, P., and Becker, B. F. 1995. Taurine protects the heart from neutrophil-induced reperfusion injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 19:461–471.
Omi, H., Okayama, N., Shimizu, M., Okouchi, M., Ito, S., Fukutomi, T., and Itoh, M. 2002. Participation of high glucose concentrations in neutrophil adhesion and surface expression of adhesion molecules on cultured human endothelial cells: Effect of antidiabetic medicines. Diab. Compl. 16:201–218.
Zhang, R., Brennan, M. L., Fu, X., Aviles, R. J., Pearce, G. L., Penn, M. S., Topol, E. J., Sprecher, D. L., and Hazen, S. L. 2001. Association between myeloperoxidase levels and risk of coronary artery disease. J. Am. Med. Ass. 286:2136–2142.
Brennan, M, Anderson, M. M., Shih, D. M., Qu, X., Wang, X., Mehta, A. C., Lim, L. L., Shi, W., Hazen, S. L., Jacob, J. J., Crowley, J. R., Heinecke, J. W., and Lusis, A. J. 2001. Increased atherosclerosis in myeloperoxidase-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 107:419–430.
Ogasawara, M., Nakamura, T., Koyama, I., Remoto, M., and Yoshida, T. 1994. Reactivity of taurine with aldehydes and its physiological role. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 359:71–78.
Li, H., Li, J. C., Jiang, S. S., Du, H., and Gu, X. P. 1996. Inhibiting effect of taurine on nonenzymatic glycosylation on aortic collagen in diabetic rats. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 12:445–447.
Devanmanoharan, C., Ali, P. S., and Varna, A. H. 1997. Prevention of lens protein glycation by taurine. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 177:245–250.
Eppler, B. and Dawson, R. 2001. Dietary manipulations in aged male Fishers 344 rat tissue: Taurine concentration, taurine biosynthesis, and oxidative markers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 62:29–39.
Nonaka, H., Tsujino, T., Watari, Y., Emoto, N., and Yokoyama, M. 2001. Taurine prevents the decrease in expression and secretion of extracellular superoxide dismutase induced by homocysteine: Amelioration of homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress by taurine. Circulation 104:1165–1170.
Keys, S. A. and Zimmerman, W. F. 1999. Antioxidant activity of retinol, glutathione, and taurine in bovine photoreceptor cell membranes. Exp. Eye Res. 68:693–702.
Franconi, F., Stendardi, I., Failli, P., Matucci, R., Baccaro, C., Montorsi, L., Bandinelli, R., and Giotti, A. 1985. The protective effects of taurine on hypoxia (performed in the absence of glucose) and on reoxygenation (in the presence of glucose) in guineapig heart. Biochem. Pharmacol. 34:2611–2620.
Malcangio, M., Bartolini, A., Ghelardini, C., Bennardini, F., Malberg-Aiello, P., Franconi, F., and Giotti, A. 1989. Effect of I.C.V. taurine on the impairment of learning, convulsion and death caused by hypoxia. Psycopharmacology 98:316–320.
Schaffer, S. W., Lombardini, J. B., and Azuma, J. 2000. Interaction between the actions of taurine and angiotensin II. Amino Acids 18:305–318.
Mozaffari, M. S. and Abebe, W. 2000. Cardiovascular responses of the taurine-depleted rat to vasoactive agents. Amino Acids 19: 625–634.
Seshiah, P. N., Weber, D. S., Rocic, P., Valppu, L., Taniyama, Y., and Griendling, K. K. 2002. Angiotensin II stimulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity: Upstream mediators. Circ. Res. 91: 406–413.
Hsieh, T. J., Zhang, S. L., Filep, J. G., Tang, S. S., Infelfinger, J. R., and Chan, S. D. 2002. High glucose stimulate angiotensinogen gene expression via reactive oxygen species generation in rat kidney proximal tubular cells. Endocrinology 143:2975–2985.
Cunningham, C., Tipton, K. F., and Dixon, H. B. F. 1998. Conversion of taurine into N-chloramine (taurine chloramine) and sulphoacetaldehyde in response to oxidative stress. J. Biochem. 330:939–945.
Marcinkiewicz, J., Grabowska, A., Bereta, J., and Stelmaszynska, T. 1995. Taurine chloramines, a product of activated neutrophils, inhibits the generation of nitric oxide and other macrophage inflammatory mediators. J. Leukoc. Biol. 58:667–674.
Liu, Y., Tonna-DeMaise, M., Park, E., Schuller-Levis, G., and Quinn, M. R. 1998. Taurine chloramine inhibits production of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 in activated C6 glioma cells by suppressing inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Mol. Brain Res. 59:189–195.
Park, E., Jia, J., Quinn, M. R., and Schuller-Levis, G. 2002. Taurine chloramine inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and decreases cytokine production in activated human leukocytes. Clin. Immunol. 102:179–184.
Ogino, T., Kobuchi, H., Sen, C. K., Roy, S., Packer, L., and Maguire, J. J. 1997. Monochloramine inhibits phorbol ester-inducible neutrophil respiratory burst activation and T cell interleukin-2 receptor expression by inhibiting inducible protein kinase C activity. J. Biol. Chem. 272:26247–26252.
Park, E., Quinn, M. R., Wright, C. E., and Schuller-Levis, G. 1993. Taurine chloramine inhibits the synthesis of nitric oxide and release of tumor necrosis factor in activated RAW-264.7. J. Leukoc. Biol. 54:119–124.
Kontny, E., Grabowska, A., Kowalczewski, J., Kurowska, M., Janicka, I., Marcinkiewicz, J., and Maslinski, W. 1999. Taurine chloramine inhibition of cell proliferation and cytokine production by rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 42:2552–2560.
Gordon, R. E., Shaked, A. A., and Solano, D. F. 1986. Taurine protects hamster bronchioles from acute NO2 induced alteration: A histological, ultrastructural, and freeze fracture studies. Am. J. Path. 125:10404–10413.
Wang, Q. J., Giri, S. N., Hyde, D. M., and Nakaashima, J. M. 1989. Effects of taurine on bleomycin-induced fibrosis in hamsters. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 190:330–338.
Davies, J. M., Horwitz, D. A., and Davies, K. J. A. 1993. Potential roles of hypochlorous acid and N-chloramines in collagen breakdown by phagocytic cells in synovitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 15:637–643.
Murakami, S., Yamagishi, I., Asami, Y., Ohta, Y., Toda, Y., Nara, Y., and Yamori, Y. 1996. Hypolipidemic effect of taurine in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacology 52:303–313.
Murakami, S., Kondo-Ohta, Y., and Tomisawa, K. 1999. Improvement in cholesterol metabolism in mice given chronic treatment of taurine and fed a high-fat diet. Life Sci. 64:83–91.
Balkan, J., Kanbagli, O., Hatipoglu, A., Kucuk, M., Cevikbas, U., Aykac-Toker, G., and Uysal, M. 2002. Improving effect of dietary taurine supplementation on the oxidative stress and lipid levels in the plasma, liver and aorta of rabbits fed on a high-cholesterol diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66:1755–1758.
Yokogoshi, H. and Oda, H. 2002. Dietary taurine enhances cholesterol degradation and reduces serum and liver cholesterol concentrations in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Amino Acids 23:433–439
Petty, M. A., Kintz, J., and DiFrancesco, G. F. 1990. The effects of taurine on atherosclerosis development in cholesterol fed rabbits. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 180:119–127.
Murakami, S., Kondo, Y., Toda, Y., Kitajima, H., Kameo, K., Sakono, M., and Fukuda, N. 2002. Effect of taurine on cholesterol metabolism in hamsters: Up-regulation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor by taurine. Life Sci. 70:2355–2366.
Kondo, Y., Toda, Y., Kitajima, H., Oda, H., Nagate, T., Kameo, K., and Muratami, S. 2001. Taurine inhibits development of atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Clin. Exp.Pharmacol. Physiol. 28:809–815.
Murakami, S., Kondo, Y., Sakurai, T., Kitajima, H., and Nagate, T. 2002. Taurine suppresses development of atherosclerosis in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic (WHHL) rabbits. Atherosclerosis 163:79–87.
Steinberg, D. and Witztum, J. L. 2002. Is the oxidative modification hypothesis relevant to human atherosclerosis. Circulation 105:2107–2111.
Yamori, Y., Liù, L., Ikeda, K., Miura, A., Mizuhushi, S., Miki, T., and Nara, Y. 2001. Distribution of twenty-four hour urinary taurine excretion and association with ischemic disease mortality in 24 population 16 countries: Results from WHO-cardiac study. Hypertens. Res. 24:453–461.
Hayes, K., Pronezn, K. A., Adessa, A. E., and Stephan, Z. F. 1989. Taurine modulates platelet aggregation in cats and in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 49:1211–1215.
Franconi, F., Martini, F., Stendardi, I., Matucci, R., Zilletti, L., and Giotti, A. 1982. Effect of taurine on calcium levels and contractility in guinea-pig ventricular strips. Biochem. Pharmacol. 31:3181–3187.
Satoh, H. 1994. Cardioprotective actions of taurine against intracellular and extracellular calcium-induced effect. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 359:181–196.
Militante, J. D. and Lombardini, J. B. 2000. Stabilization of calcium uptake in rat rod outer segments by taurine and ATP. Amino Acids 19:561–570.
Chen, Y. X. 1995. Protective action of taurine on ischemia-reperfusion liver injury in rats and its metabolism. Chin. Med. J. 73:977–986.
Qi, B., Yamagami, T., Naruse, Y., Sokejima, S., and Kagamimori, S. 1995. Effect of taurine on depletion of erythrocyte membrane NaKATPase activity due to ozone exposure or cholesterol enrichment. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 41:627–634.
Vilchis, C. and Salceda, R. 1996. Effect of diabetes mellitus on levels and uptake of putative amino acid neurotrasmtitters in rat retina and retinal pigment epithelium. Neurochem. Res. 21: 1167–1171.
Stevens, M. J., Hosaka, Y., Masterson, J. A., Jones, S. M., Thomas, T. P., and Larkin, D. D. 1999. Downregulation of the human taurine transporter by glucose in cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 277:E760–E771.
Malone, J. L., Lowitt, S., and Cook, W. R. 1990. Non osmotic diabetic cataracts. Pediat. Res. 27:293–296.
Franconi, F., Martini, F., Manghi, N., Galli, A., Bennardini, F., and Giotti, A. 1981. Uptake of 3H-taurine into myocardial membranes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 30:77–85.
Hales, C. N. and Baker, D. J. P. 1992. Type-2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus: The thrifty phenotypes hypothesis. Diabetologia 35:595–601.
Sturman, J. A. 1993. Taurine in development. Physiol. Rev. 73:119–147
Norberg, S., Powel, T. L., and Jansson, T. 1998. Intrauterine growth restriction is associated with reduced activity of placental transporters. Pediat. Res. 44:233–238.
Dahri, S., Snock, A., Reusens, B., Remacle, C., and Hoet, J. J. 1991. Islet function in offspring of mothers on low protein diet during gestation. Diabetes 40(suppl 2) 115–120.
Oliver, M. H., Hawkins, P., Breier, B. H., Van Zijl, P. L., Sargison, S. A., and Harding, J. E. 2001. Maternal undernutrition during the periconceptual period increases plasma taurine levels and insulin response to glucose but not arginine in the late gestation fetal sheep. Endocrinology 142:4576–4579.
Merezak, S., Hardikar, A. A., Yajnik, C. S., Remacle, C., and Reusens, B. 2001. Intrauterine low protein diet increases fetal beta-cell sensitivity to NO and IL-1 beta: The protective role of taurine. J. Endocrinol. 171:299–308.
Boujender, S., Reusens, B., Merezak, S., Ahn, M. T., Arany, E., Hill, D., and Remacle, C. 2002. Taurine supplementation to a low protein diet during foetal and early postnatal life restores a normal proliferation and apoptosis of rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 45:856–866.
Aerts, L. and Van Assche, F. A. 2001. Low taurine, gamma-aminobutyric acid and carnosine levels in plasma of diabetic rats: Consequences for the offspring. J. Perinat. Med. 29: 81–84.
Fennessy, F. M., Moneley, D. S, Wang, J. H., Kelly, C. J., and Bouchier-Hayes, D. J. 2003. Taurine and vitamin C modify monocyte and endothelial dysfunction in young smokers. Circulation 107:410–415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franconi, F., Di Leo, M.A.S., Bennardini, F. et al. Is Taurine Beneficial in Reducing Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus?. Neurochem Res 29, 143–150 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000010443.05899.2f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000010443.05899.2f