Abstract
Local delivery of cytokines has been shown to have a potent anti-tumor activity against a wide range of malignant brain tumors. In this study, we examined the role of systemic immunosuppression using dexamethasone on the efficacy of local IL-2 immunotherapy in treating experimental murine CNS tumors.
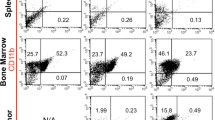
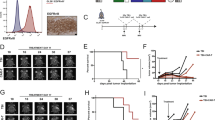
An endothelial cell line secreting hIL-2 (NTC-121) was injected intracranially in C57BL/6 mice (n= 10/group) along with B16/F10 (wild type) melanoma cells. A separate set of animals also received daily injections of either 1 mg/k or 10 mg/kg of dexamethasone. Sixty percent of mice treated with IL-2 (P < 0.001 vs. control) vs. 55%(P < 0.005) of mice treated with IL-2 and 1 mg/kg of dexamethasone were long-term survivors (LTS) of >120 days. There was no difference in survival between control animals that received only wild type cells or animals that were treated with IL-2 and 10 mg/kg of dexamethasone. Histopathological examination of brains from animals sacrificed at different times showed an accumulation of CD8 + T-cells around the site of the injected tumor only in the IL-2 group and the group that received 1 mg/kg of dexamethasone.
These results suggest that while high doses of dexamethasone can completely inhibit the immune response observed with IL-2, lower and more likely therapeutic doses of dexamethasone do not inhibit local IL-2 immunotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ewend MG, Thompson RC, Anderson R, Sills AK, Staveley-O'Carroll K, Tyler BM et al.: Intracranial paracrine interleukin-2 therapy stimulates prolonged antitumor immunity that extends outside the central nervous system. J Immunother 23(4): 438-448, 2000
Deshmukh P, Glick RP, Lichtor T, Moser R, Cohen EP: Immunogene therapy with interleukin-2-secreting fibroblasts for intracerebrally metastasizing breast cancer in mice. J Neurosurg 94(2): 287-292, 2001
Glick RP, Lichtor T, de Zoeten E, Deshmukh P, Cohen EP: Prolongation of survival of mice with glioma treated with semiallogeneic fibroblasts secreting interleukin-2. Neurosurgery 45(4): 867-874, 1999
Hanes J, Sills A, Zhao Z, Suh KW, Tyler B, DiMeco F et al.: Controlled local delivery of interleukin-2 by biodegradable polymers protects animals from experimental brain tumors and liver tumors. Pharm Res 18(7): 899-906, 2001
Lesniak M, Sampath P, DiMeco F, Viglione M, Pardoll DM, Tyler B et al.: Comparative analysis of paracrine immunotherapy in experimental brain tumors. Neurosurgical Focus 9(6)(4), 2000
Lichtor T, Glick RP, Tarlock K, Moffett S, Mouw E, Cohen EP: Application of interleukin-2-secreting syngeneic/allogeneic fibroblasts in the treatment of primary and metastatic brain tumors. Cancer Gene Ther 9(5): 464-469, 2002
Sampath P, Hanes J, DiMeco F, Tyler BM, Brat D, Pardoll DM et al.: Paracrine immunotherapy with interleukin-2 and local chemotherapy is synergistic in the treatment of experimental brain tumors. Cancer Res 59(9): 2107-2114, 1999
Thompson RC, Pardoll DM, Jaffee EM, Ewend MG, Thomas MC, Tyler BM et al.: Systemic and local paracrine cytokine therapies using transduced tumor cells are synergistic in treating intracranial tumors. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol 19(6): 405-413, 1996
Lesniak MS, Tyler BM, Pardoll DM, Brem H: Gene therapy for experimental brain tumors using a xenogenic cell line engineered to secrete hIL-2. J Neurooncol 64(1–2): 155-160, 2003
Hu X, Li WP, Meng C, Ivashkiv LB: Inhibition of IFNgamma signaling by glucocorticoids. J Immunol 170(9): 4833-4839, 2003
Pipitone N, Sinha M, Theodoridis E, Goulding N, Hall M, Lanchbury J et al.: The glucocorticoid inhibition of LFA-1 and CD2 expression by human mononuclear cells is reversed by IL-2, IL-7 and IL-15. Eur J Immunol 31(7): 2135-2142, 2001
Drano. G, Jaffee EM, Lazenby A, Golumbek P, Levitsky H, Brose K et al.: Vaccination with irradiated tumor cells engineered to secrete murine granulocyte colony macrophage stimulating factor stimulates potent, specific, and long-lasting anti-tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 3539-1543, 1993
Kaplan EL, Meier P: Nonparametric estimation from nonparametric observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53: 457-481, 1987
Brunetti M MN, Colasante A: Spontaneous and glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in human mature T lymphocytes. Blood 86: 4199-4205, 1995
Cupps TR FA: Corticosteroid-mediated immunoregulation in man. Immunol Rev 65: 133-155, 1982
Schmidt M PH, Lugering N: Glucocorticoids induce apoptosis in human monocytes: potential role of IL-1 beta. J Immunol 163: 3484-3490, 1999
Neuwelt EA KK, Hill S: Immune responses in patients with braintumors. Factors such as anti-convulsants that may contribute to impaired cell-mediated imunity. Cancer 51: 248-255, 1983
Badie B, Schartner JM, Paul J, Bartley BA, Vorpahl J, Preston JK: Dexamethasone-induced abolition of the inflammatory response in an experimental glioma model: a flow cytometry study. J Neurosurg 93(4): 634-639, 2000
Aloisi F: Immune function of microglia. Glia 36(2): 165-179, 2001
Aloisi F, Ria F, Penna G, Adorini L. Microglia are more efficient than astrocytes in antigen processing and in Th1 but not Th2 cell activation. J Immunol 160(10): 4671-4680, 1998
Owens T, Babcock A: Immune response induction in the central nervous system. Front Biosci 7: d427-438, 2002
Olson JK, Girvin AM, Miller SD: Direct activation of innate and antigen-presenting functions of microglia following infection with Theiler's virus. J Virol 75(20): 9780-9789, 2001
Drew PD, Chavis JA: Inhibition of microglial cell activation by cortisol. Brain Res Bull 52(5): 391-396, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesniak, M.S., Gabikian, P., Tyler, B.M. et al. Dexamethasone Mediated Inhibition of Local IL-2 Immunotherapy is Dose Dependent in Experimental Brain Tumors. J Neurooncol 70, 23–28 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000040821.50347.c5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000040821.50347.c5