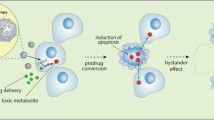
Abstract
Retrovirus (RV) has been one of the earliest recombinant vectors to be investigated in the context of cancer gene therapy. Experiments in cell culture and in animal brain tumor models have demonstrated the feasibility of RV mediated gene transduction and killing of glioma cells by toxicity generating transgenes. Phase I and II clinical studies in patients with recurrent malignant glioma have shown a favorable safety profile and some efficacy of RV mediated gene therapy. On the other hand, a prospective randomized phase III clinical study of RV gene therapy in primary malignant glioma failed to demonstrate significant extension of the progression-free or overall survival times in RV treated patients. The failure of this RV gene therapy study may be due to the low tumor cell transduction rate observed in vivo. The biological effects of the treatment may also heavily depend on the choice of transgene/prodrug system and on the vector delivery methods.
Retrovirus clinical trials in malignant glioma have nevertheless produced a substantial amount of data and have contributed toward the identification of serious shortcomings of the non-replicating virus vector gene therapy strategy. Novel types of therapeutic virus vector systems are currently being designed and new clinical protocols are being created based on the lessons learned from the RV gene therapy trials in patients with malignant brain tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moolten FL: Tumor chemosensitivity conferred by inserted herpes thymidine kinase genes: paradigm for a prospective cancer control strategy. Cancer Res 46: 5276-5281, 1986
Kramm CM, Sena-Esteves M, Barnett FH, Rainov NG, Schuback DE, Yu JS, Pechan PA, Paulus W, Chiocca EA, Breakefield XO: Gene therapy for brain tumors. Brain Pathol 5: 345-381, 1995
Rainov NG, Kramm CM: Vector delivery methods and targeting strategies for gene therapy of brain tumors. Curr Gene Ther 1: 367-383, 2001a
Lam PY, Breakefield XO: Potential of gene therapy for brain tumors. Hum Mol Genet 10: 777-787, 2001
Coffin JM: Retroviridae and their Replication in 'Virology'. In: Coffin JM (ed) Raven Press, New York, 1990, pp 1437-1500
Albritton LM, Kim JW, Tseng L, Cunningham JM: Envelope-binding domain in the cationic amino acid transporter determines the host range of ecotropic murine retroviruses. J Virol 67: 2091-2096, 1993
Chu TH, Martinez I, Sheay WC, Dornburg R: Cell targeting with retroviral vector particles containing antibodyenvelope fusion proteins. Gene Ther 1: 292-299, 1994
UckertWandWalther W: Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther 63: 323-347, 1994
Bowerman B, Brown PO, Bishop JM, Varmus HE:Anucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev 3: 469-478, 1989
Lewis PF, Emerman M: Passage through mitosis is required for oncoretroviruses but not for the human immunodefi-ciency virus. J Virol 68: 510-516, 1994
Lewis P, Hensel M, Emerman M: Human immunodeficiency virus infection of cells arrested in the cell cycle. Embo J 11: 3053-3058, 1992
Varmus HE, Swanstorm R: Replication of retroviruses. In Varmus HE, Swanstorm R (eds) RNA tumor viruses. Cold Spring Harbour, New York, 1990, pp 369-512
Chumakov I, Stuhlmann H, Harbers K, Jaenisch R: Cloning of two genetically transmitted Moloney leukemia proviral genomes: correlation between biological activity of the cloned DNA and viral genome activation in the animal. J Virol 42: 1088-1098, 1982
Danos O, Mulligan RC: Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6460-6464, 1988
Markowitz D, Goff S, Bank A: Construction and use of a safe and efficient amphotropic packaging cell line. Virology 167: 400-406, 1988
Shapiro WR, Shapiro JR: Biology and treatment of malignant glioma. Oncology (Huntingt) 12: 233-240; discussion 240, 246, 1998
Oldfield EH, Ram Z, Culver KW, Blaese RM, DeVroom HL, Anderson WF: Gene therapy for the treatment of brain tumors using intra-tumoral transduction with the thymidine kinase gene and intravenous ganciclovir. Hum Gene Ther 4: 39-69, 1993
Boviatsis EJ, Chase M, Wei MX, Tamiya T, Hurford RK Jr, Kowall NW, Tepper RI, Breakefield XO, Chiocca EA: Gene transfer into experimental brain tumors mediated by adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, and retrovirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 5: 183-191, 1994
Tamiya T, Wei MX, Chase M, Ono Y, Lee F, Breakefield XO, Chiocca EA: Transgene inheritance and retroviral infection contribute to the efficiency of gene expression in solid tumors inoculated with retroviral vector producer cells. Gene Ther 2: 531-538, 1995
Ram Z, Culver KW, Walbridge S, Blaese RM, Oldfield EH: In situ retroviral-mediated gene transfer for the treatment of brain tumors in rats. Cancer Res 53: 83-88, 1993
Ram Z, Culver KW, Walbridge S, Frank JA, Blaese RM, Oldfield EH: Toxicity studies of retroviral-mediated gene transfer for the treatment of brain tumors. J Neurosurg 79: 400-407, 1993
Long Z, Li LP, Grooms T, Lockey C, Nader K, Mychkovsky I, Mueller S, Burimski I, Ryan P, Kikuchi G, Ennist D, Marcus S, Otto E and McGarrity G: Biosafety monitoring of patients receiving intracerebral injections of murine retroviral vector producer cells. Hum Gene Ther 9: 1165-1172, 1998
Shand N, Weber F, Mariani L, Bernstein M, Gianella-Borradori A, Long Z, Sorensen AG, Barbier N: A phase 1-2 clinical trial of gene therapy for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme by tumor transduction with the herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene followed by ganciclovir. GLI328 European-Canadian Study Group. Hum Gene Ther 10: 2325-2335, 1999
Boris-Lawrie K, Temin HM: The retroviral vector. Replication cycle and safety considerations for retrovirus-mediated gene therapy. Ann NY Acad Sci 716: 59-70; discussion 71, 1994
Mann R, Mulligan RC, Baltimore D: Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell 33: 153-159, 1983
Lyons RM, Forry-Schaudies S, Otto E, Wey C, Patil-Koota V, Kaloss M, McGarrity GJ and Chiang YL: An improved retroviral vector encoding the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene increases antitumor efficacy in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 2: 273-280, 1995
Short MP, Choi BC, Lee JK, Malick A, Breakefield XO, Martuza RL: Gene delivery to glioma cells in rat brain by grafting of a retrovirus packaging cell line. J Neurosci Res 27: 427-439, 1990
Rainov NG, Kramm CM, Aboody-Guterman K, Chase M, Ueki K, Louis DN, Harsh GRt, Chiocca A, Breakefield XO: Retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of experimental brain neoplasms using the herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase/ganciclovir paradigm. Cancer Gene Ther 3: 99-106, 1996
Kaloss M, Linscott M, Wey C, Lu P, Long Z, McGarrity GJ, Otto E, Lyons RM: Distribution of retroviral vectors and vector producer cells using two routes of administration in rats. Gene Ther 6: 1389-1396, 1999
Long Z, Lu P, Grooms T, Mychkovsky I, Westley T, Fitzgerald T, Sharma-Chibber S, Shand N, McGarrity G, Otto E: Molecular evaluation of biopsy and autopsy specimens from patients receiving in vivo retroviral gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther 10: 733-740, 1999
Rainov NG:Aphase III clinical evaluation of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and ganciclovir gene therapy as an adjuvant to surgical resection and radiation in adults with previously untreated glioblastoma multiforme. Hum Gene Ther 11: 2389-2401, 2000b
Barba D, Hardin J, Sadelain M, Gage FH: Development of anti-tumor immunity following thymidine kinase-mediated 235 killing of experimental brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 4348-4352, 1994
Ram Z, Culver KW, Oshiro EM, Viola JJ, DeVroom HL, Otto E, Long Z, Chiang Y, McGarrity GJ, Muul LM, Katz D, Blaese RM, Oldfield EH: Therapy of malignant brain tumors by intratumoral implantation of retroviral vector-producing cells. Nat Med 3: 1354-1361, 1997
Puumalainen AM, Vapalahti M, Agrawal RS, Kossila M, Laukkanen J, Lehtolainen P, Viita H, Paljarvi L, Vanninen R, Yla-Herttuala S: Beta-galactosidase gene transfer to human malignant glioma in vivo using replication-deficient retroviruses and adenoviruses. Hum Gene Ther 9: 1769-1774, 1998
Rainov NG, Kramm CM, Banning U, Riemann D, Holzhausen HJ, Heidecke V, Burger KJ, Burkert W, Korholz D: Immune response induced by retrovirusmediated HSV-tk/GCV pharmacogene therapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Gene Ther 7: 1853-1858, 2000a
Sena-Esteves M, Hampl JA, Camp SM, Breakefield XO: Generation of stable retrovirus packaging cell lines after transduction with herpes simplex virus hybrid amplicon vectorsdouble dagger. J Gene Med 4: 229-239, 2002
Ezzeddine ZD, Martuza RL, Platika D, Short MP, Malick A, Choi B, Breakefield XO: Selective killing of glioma cells in culture and in vivo by retrovirus transfer of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. New Biol 3: 608-614, 1991
Takamiya Y, Short MP, Ezzeddine ZD, Moolten FL, Breakefield XOand Martuza RL: Gene therapy of malignant brain tumors: a rat glioma line bearing the herpes simplex virus type 1-thymidine kinase gene and wild type retrovirus kills other tumor cells. J Neurosci Res 33: 493-503, 1992
Bi WL, Parysek LM, Warnick R, Stambrook PJ: In vitro evidence that metabolic cooperation is responsible for the bystander effect observed with HSV tk retroviral gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther 4: 725-731, 1993
Freeman SM, Abboud CN, Whartenby KA, Packman CH, Koeplin DS, Moolten FL, Abraham GN: The 'bystander effect': tumor regression when a fraction of the tumor mass is genetically modified. Cancer Res 53: 5274-5283, 1993
Ishii-Morita H, Agbaria R, Mullen CA, Hirano H, Koeplin DA, Ram Z, Oldfield EH, Johns DG, Blaese RM: Mechanism of 'bystander effect' killing in the herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene therapy model of cancer treatment. Gene Ther 4: 244-251, 1997
Burrows FJ, Gore M, Smiley WR, Kanemitsu MY, Jolly DJ, Read SB, Nicholas T, Kruse CA: Purified herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase retroviral particles: III. Characterization of bystander killing mechanisms in transfected tumor cells. Cancer Gene Ther 9: 87-95, 2002
Tapscott SJ, Miller AD, Olson JM, Berger MS, Groudine M, Spence AM: Gene therapy of rat 9L gliosarcoma tumors by transduction with selectable genes does not require drug selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 8185-8189, 1994
Vile RG, Castleden S, Marshall J, Camplejohn R, Upton C, Chong H: Generation of an anti-tumour immune response in a non-immunogenic tumour: HSVtk killing in vivo stimulates a mononuclear cell infiltrate and a Th1-like profile of intratumoural cytokine expression. Int J Cancer 71: 267-274, 1997
Mullen CA, Anderson L, Woods K, Nishino M, Petropoulos D: Ganciclovir chemoablation of herpes thymidine kinase suicide gene-modified tumors produces tumor necrosis and induces systemic immune responses. Hum Gene Ther 9: 2019-2030, 1998
Culver KW, Ram Z, Wallbridge S, Ishii H, Oldfield EH, Blaese RM: In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vectorproducer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors. Science 256: 1550-1552, 1992
Barba D, Hardin J, Ray J, Gage FH: Thymidine kinasemediated killing of rat brain tumors. J Neurosurg 79: 729-735, 1993
Lee H, Song JJ, Kim E, Yun CO, Choi J, Lee B, Kim J, Chang JW, Kim JH: Efficient gene transfer of VSV-G pseudotyped retroviral vector to human brain tumor. Gene Ther 8: 268-273, 2001
Tamura K, Tamura M, Ikenaka K, Yoshimatsu T, Miyao Y, Nanmoku K, Shimizu K: Eradication of murine brain tumors by direct inoculation of concentrated high titer-recombinant retrovirus harboring the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Gene Ther 8: 215-222, 2001
Sandmair AM, Loimas S, Poptani H, Vainio P, Vanninen R, Turunen M, Tyynela K, Vapalahti M, Yla-Herttuala S: Low efficacy of gene therapy for rat BT4C malignant glioma using intra-tumoural transduction with thymidine kinase retrovirus packaging cell injections and ganciclovir treatment. Acta Neurochir 141: 867-872, 1999
Sandmair AM, Turunen M, Tyynela K, Loimas S, Vainio P, Vanninen R, Vapalahti M, Bjerkvig R, Janne J, Yla-Herttuala S: Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene therapy in experimental rat BT4C glioma model: effect of the percentage of thymidine kinase-positive glioma cells on treatment effect, survival time, and tissue reactions. Cancer Gene Ther 7: 413-421, 2000
Klatzmann D, Valery CA, Bensimon G, Marro B, Boyer O, Mokhtari K, Diquet B, Salzmann JL, Philippon J: A phase I/II study of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase 'suicide' gene therapy for recurrent glioblastoma. Study Group on Gene Therapy for Glioblastoma. Hum Gene Ther 9: 2595-2604, 1998
Izquierdo M, Martin V, de Felipe P, Izquierdo JM, Perez-Higueras A, Cortes ML, Paz JF, Isla A, Blazquez MG: Human malignant brain tumor response to herpes simplex thymidine kinase (HSVtk)/ganciclovir gene therapy. Gene Ther 3: 491-495, 1996
Izquierdo M, Cortes ML, Martin V, de Felipe P, Izquierdo JM, Perrez-Higueras A, Paz JF, Isla A, Blazquez MG: Gene therapy in brain tumors: implications of the size of glioblastoma on its curability. Acta Neurochir Supple (Wien) 68: 111-117, 1997
Packer RJ, Raffel C, Villablanca JG, Tonn JC, Burdach SE, Burger K, LaFond D, McComb JG, Cogen PH, Vezina G, Kapcala LP: Treatment of progressive or recurrent pediatric malignant supratentorial brain tumors with herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene vector-producer cells followed by intravenous ganciclovir administration. J Neurosurg 92: 249-254, 2000
Kramm CM, Korholz D, Rainov NG, Niehues T, Fischer U, Steffens S, Frank S, Banning U, Horneff G, Schroten H, Burdach S: Systemic activation of the immune system during ganciclovir treatment following intratumoral herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene transfer in an adolescent ependymoma patient. Neuropediatrics 33: 6-9, 2002
Palu G, Cavaggioni A, Calvi P, Franchin E, Pizzato M, Boschetto R, Parolin C, Chilosi M, Ferrini S, Zanusso A, Colombo F: Gene therapy of glioblastoma multiforme via combined expression of suicide and cytokine genes: a pilot study in humans. Gene Ther 6: 330-337, 1999
Boothman DA, Davis TW, Sahijdak WM: Enhanced expression of thymidine kinase in human cells following ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 30: 391-398, 1994
Kim JH, Kim SH, Brown SL, Freytag SO: Selective enhancement by an antiviral agent of the radiation-induced cell killing of human glioma cells transduced with HSV-tk gene. Cancer Res 54: 6053-6056, 1994
Harsh GR, Deisboeck TS, Louis DN, Hilton J, Colvin M, Silver JS, Qureshi NH, Kracher J, Finkelstein D, Chiocca EA, Hochberg FH: Thymidine kinase activation of ganciclovir in recurrent malignant gliomas: a gene-marking and neuropathological study. J Neurosurg 92: 804-811, 2000
Kramer ED, Packer RJ, Ginsberg J, Goldman S, Thompson S, Bayer LA, Shen V, Harris R, Khan S, Finlay JL: Acute neurologic dysfunction associated with high-dose chemotherapy and autologous bone marrow rescue for primary malignant brain tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 27: 230-237, 1997
Prados MD, Russo C: Chemotherapy of brain tumors. Semin Surg Oncol 14: 88-95, 1998
Sandmair AM, Loimas S, Puranen P, Immonen A, Kossila M, Puranen M, Hurskainen H, Tyynela K, Turunen M, Vanninen R, Lehtolainen P, Paljarvi L, Johansson R, Vapalahti M, Yla-Herttuala S: Thymidine kinase gene therapy for human malignant glioma, using replication-deficient retroviruses or adenoviruses. Hum Gene Ther 11: 2197-2205, 2000
Russell DW, Berger MS, Miller AD: The effects of human serum and cerebrospinal fluid on retroviral vectors and packaging cell lines. Hum Gene Ther 6: 635-641, 1995
Blasberg RG, Tjuvajev JG: Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase as a marker/reporter gene for PET imaging of gene therapy. Q J Nucl Med 43: 163-169, 1999
Gambhir SS, Herschman HR, Cherry SR, Barrio JR, Satyamurthy N, Toyokuni T, Phelps ME, Larson SM, Balatoni J, Finn R, Sadelain M, Tjuvajev J, Blasberg R: Imaging transgene expression with radionuclide imaging technologies. Neoplasia 2: 118-138, 2000
Rainov NG, Fels C, Droege JW, Schafer C, Kramm CM, Chou TC: Temozolomide enhances herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir therapy of malignant glioma. Cancer Gene Ther 8: 662-668, 2001b
Inamura T, Nomura T, Bartus RT, Black KL: Intracarotid infusion of RMP-7, a bradykinin analog: a method for selective drug delivery to brain tumors. J Neurosurg 81: 752-758, 1994
LeMay DR, Kittaka M, Gordon EM, Gray B, Stins MF, McComb JG, Jovanovic S, Tabrizi P, Weiss MH, Bartus R, Anderson WF, Zlokovic BV: Intravenous RMP-7 increases delivery of ganciclovir into rat brain tumors and enhances the effects of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther 9: 989-995, 1998
Herrlinger U, Woiciechowski C, Sena-Esteves M, Aboody KS, Jacobs AH, Rainov NG, Snyder EY, Breakefield XO: Neural precursor cells for delivery of replication-conditional HSV-1 vectors to intracerebral gliomas. Mol Ther 1: 347-357, 2000
Lieberman DM, Laske DW, Morrison PF, Bankiewicz KS, Oldfield EH: Convection-enhanced distribution of large molecules in gray matter during interstitial drug infusion. J Neurosurg 82: 1021- 1029, 1995
Parsa AT, Chi JH, Hurley PT, Jeyapalan SA, Bruce JN: Immunomodulation of glioma cells after gene therapy: induction of major histocompatibility complex class I but not class II antigen in vitro. Neurosurgery 49: 681-688; discussion 688-689, 2001
DiMeco F, Rhines LD, Hanes J, Tyler BM, Brat D, Torchiana E, Guarnieri M, Colombo MP, Pardoll DM, Finocchiaro G, Brem H, Olivi A: Paracrine delivery of IL-12 against intracranial 9L gliosarcoma in rats. J Neurosurg 92: 419-427, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rainov, N.G., Ren, H. Clinical Trials with Retrovirus Mediated Gene Therapy – what Have we Learned?. J Neurooncol 65, 227–236 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000003652.71665.f2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000003652.71665.f2